Discrimination undermines fairness by treating individuals unjustly based on race, gender, age, or other characteristics, affecting personal and professional opportunities. Understanding the various forms and consequences of discrimination helps promote equality and social justice in your community. Explore the full article to learn how you can identify and combat discrimination effectively.
Table of Comparison
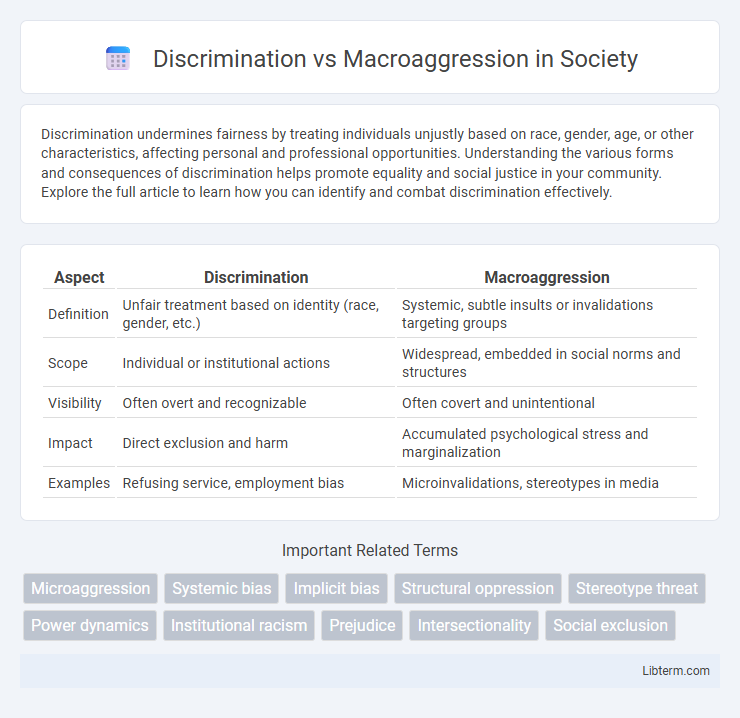
| Aspect | Discrimination | Macroaggression |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unfair treatment based on identity (race, gender, etc.) | Systemic, subtle insults or invalidations targeting groups |
| Scope | Individual or institutional actions | Widespread, embedded in social norms and structures |
| Visibility | Often overt and recognizable | Often covert and unintentional |
| Impact | Direct exclusion and harm | Accumulated psychological stress and marginalization |
| Examples | Refusing service, employment bias | Microinvalidations, stereotypes in media |
Understanding Discrimination: Definition and Forms
Discrimination involves unjust or prejudicial treatment of individuals based on characteristics such as race, gender, age, or religion, manifesting in various forms including overt actions, systemic bias, and institutional policies. Macroaggressions are large-scale, overt discriminatory actions that reinforce harmful stereotypes and social inequities, often embedded in societal structures and norms. Understanding discrimination requires recognizing both explicit acts of bias and the subtle, systemic mechanisms that sustain inequality across different social contexts.
What Are Macroaggressions? Key Characteristics
Macroaggressions are subtle, often unintentional, behaviors or comments that convey prejudice or discrimination toward marginalized groups. They differ from overt discrimination by their indirect nature, manifesting as microinsults, microinvalidations, or microassaults that accumulate and impact mental health. Key characteristics include their repetitive occurrence, implicit bias, and the ability to perpetuate systemic inequality without explicit intent.
Discrimination vs Macroaggression: Core Differences
Discrimination involves overt actions or policies that unfairly target individuals or groups based on characteristics such as race, gender, or age, creating direct barriers to equality and opportunity. Macroaggressions consist of widespread, systemic behaviors or cultural norms that subtly perpetuate inequality and reinforce negative stereotypes without explicit intent. The core difference lies in discrimination's explicit exclusion or harm versus macroaggressions' implicit, structural influence on social dynamics and power imbalances.
Historical Context of Discrimination
Discrimination, rooted in systemic injustices, reflects deep-seated historical power imbalances dating back to slavery, colonization, and segregation policies that institutionalized inequality. Macroaggressions represent contemporary manifestations of these entrenched biases, often expressed through explicit discriminatory acts that reinforce social hierarchies. Understanding the historical context of discrimination reveals its pervasive influence on laws, socioeconomic disparities, and cultural norms shaping present-day societal dynamics.
Macroaggressions in Everyday Life
Macroaggressions in everyday life manifest as overt, intentional acts of discrimination that reinforce systemic inequalities and social hierarchies. These actions include public slurs, exclusionary policies, and blatant disrespect towards marginalized groups, significantly impacting mental health and social inclusion. Understanding the distinction between macroaggressions and more covert microaggressions helps in addressing their broader societal implications and promoting equity.
Psychological Impact: Comparing Both Phenomena
Discrimination often leads to chronic stress, anxiety, and depression by imposing systemic barriers and social exclusion on targeted individuals, whereas microaggressions cause cumulative psychological harm through subtle, repeated invalidations that erode self-esteem and sense of belonging. Both phenomena disrupt mental health, but discrimination typically results in overt emotional trauma, while microaggressions generate persistent, low-level distress that undermines resilience over time. Understanding these psychological impacts is crucial for developing effective mental health interventions tailored to the unique challenges posed by each form of bias.
Recognizing Subtle and Overt Behaviors
Discrimination involves overt actions or policies that unfairly target individuals or groups based on characteristics such as race, gender, or age, often clearly identifiable and legally addressed. Macroaggressions are subtle, often unintentional behaviors or remarks that reinforce stereotypes and perpetuate systemic inequalities, making them harder to detect and confront. Recognizing these behaviors requires awareness of both explicit acts of discrimination and the nuanced, everyday micro-level interactions that accumulate into larger social harms.
Legal and Social Responses
Discrimination involves overt actions or policies that unfairly treat individuals based on protected characteristics, typically addressed through legal frameworks such as anti-discrimination laws and civil rights legislation. Macroaggressions represent broader, systemic patterns of subtle biases and institutional behaviors, often requiring social responses like diversity training, advocacy campaigns, and policy reforms to foster inclusivity. Legal remedies primarily target explicit discriminatory acts, while social initiatives aim to dismantle pervasive cultural norms that sustain macroaggressions.
Strategies for Prevention and Intervention
Effective strategies for preventing discrimination and macroaggressions involve implementing comprehensive diversity training programs that increase awareness of implicit biases and promote inclusive behaviors. Organizations should establish clear policies and reporting mechanisms to address incidents promptly and support affected individuals through counseling and mediation services. Engaging in continuous education and fostering open dialogue cultivates empathy and accountability, reducing the occurrence of subtle and overt discriminatory actions.
Toward Equity: Promoting Inclusive Environments
Discrimination involves overt actions or policies that disadvantage individuals based on identity, whereas macroaggressions are subtle, systemic behaviors that reinforce inequality. Toward equity, promoting inclusive environments requires recognizing both explicit discrimination and the pervasive impact of macroaggressions on marginalized groups. Implementing comprehensive diversity training and fostering open dialogue are essential strategies to dismantle these barriers and create equitable spaces.
Discrimination Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com