Disidentification refers to the psychological process of detaching from certain identities or roles that no longer serve your personal growth or well-being. This concept is key in overcoming limiting beliefs and fostering a more authentic sense of self. Explore the article further to understand how disidentification can transform your mindset and life.
Table of Comparison
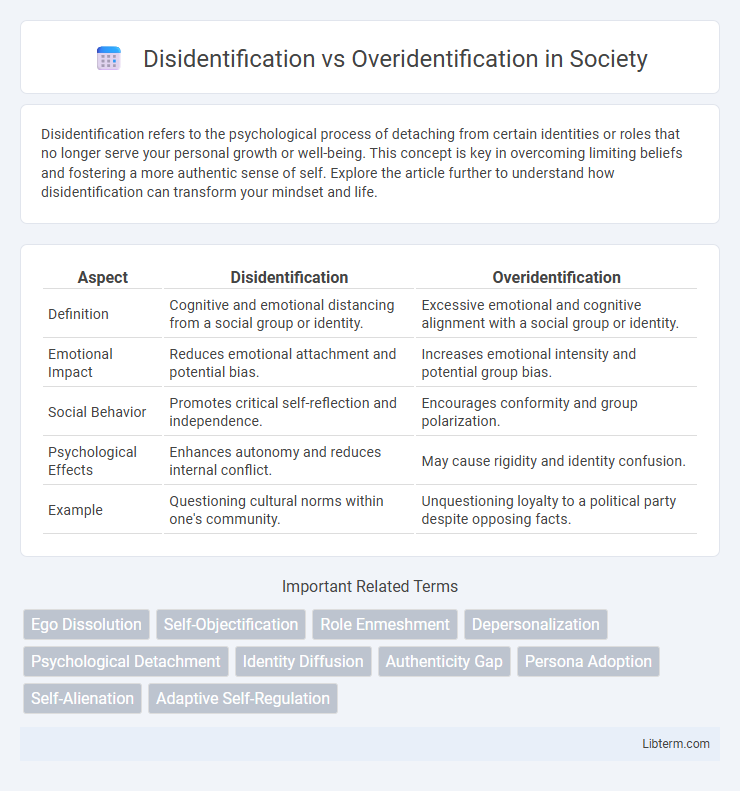
| Aspect | Disidentification | Overidentification |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cognitive and emotional distancing from a social group or identity. | Excessive emotional and cognitive alignment with a social group or identity. |
| Emotional Impact | Reduces emotional attachment and potential bias. | Increases emotional intensity and potential group bias. |
| Social Behavior | Promotes critical self-reflection and independence. | Encourages conformity and group polarization. |
| Psychological Effects | Enhances autonomy and reduces internal conflict. | May cause rigidity and identity confusion. |
| Example | Questioning cultural norms within one's community. | Unquestioning loyalty to a political party despite opposing facts. |
Understanding Disidentification and Overidentification
Disidentification involves a nuanced psychological process where individuals distance themselves from certain identities or societal labels without completely rejecting them, allowing for a flexible self-concept. Overidentification occurs when a person excessively associates with an identity or role, leading to rigid self-perception and potential emotional distress. Understanding the distinction between disidentification and overidentification is crucial for mental health professionals aiming to support identity exploration and emotional resilience.
Key Differences Between Disidentification and Overidentification
Disidentification involves maintaining a critical distance from a particular identity or belief system, allowing individuals to question and reshape their self-concept, whereas overidentification occurs when a person excessively associates with an identity, often leading to rigid behavior and emotional distress. Key differences include the level of emotional attachment and flexibility; disidentification promotes adaptive reinterpretation of identity, while overidentification results in inflexibility and potential self-limitation. Psychological research highlights that disidentification can enhance resilience and personal growth, contrasting with the negative outcomes linked to overidentification, such as identity foreclosure and reduced self-awareness.
Psychological Roots of Disidentification
Disidentification originates in psychological defense mechanisms where individuals unconsciously distance themselves from identities or traits that elicit internal conflict or trauma. This process allows for the preservation of self-coherence by rejecting aspects threatening the ego or core self-concept. Contrarily, overidentification occurs when an individual excessively aligns with a particular identity, often resulting in rigidity and vulnerability to psychological distress.
Causes and Consequences of Overidentification
Overidentification occurs when individuals excessively align their identity with a particular group, belief, or role, often driven by insecurity, a need for belonging, or fear of rejection. This psychological overattachment can lead to rigid thinking, loss of personal autonomy, and increased susceptibility to groupthink, ultimately stifling critical self-reflection and personal growth. Consequences of overidentification include social polarization, reduced emotional resilience, and impaired decision-making abilities due to an inability to objectively evaluate conflicting perspectives.
Disidentification in Personal Identity Formation
Disidentification plays a critical role in personal identity formation by allowing individuals to distance themselves from dominant cultural norms and expectations, thereby creating space for authentic self-expression. This process involves selectively rejecting or reshaping imposed identities without fully assimilating into oppositional frameworks, which contrasts with overidentification where one rigidly adopts external identities. Emphasizing disidentification fosters resilience and a nuanced understanding of self, enabling individuals to craft a multifaceted and dynamic personal identity.
Overidentification and Self-Concept Distortion
Overidentification involves an excessive attachment to particular beliefs or identities, which distorts the self-concept by limiting flexibility and fostering rigid self-perceptions. This psychological state contributes to emotional distress and impairs adaptive functioning by reinforcing narrow self-definitions tied to specific attributes or experiences. Understanding overidentification is crucial for addressing self-concept distortion and promoting psychological well-being through increased self-awareness and cognitive restructuring.
Societal Factors Influencing Identity Processes
Societal factors such as cultural norms, systemic discrimination, and social stigmatization significantly influence the processes of disidentification and overidentification within marginalized groups. Disidentification emerges as a strategy to negotiate identity when dominant societal narratives invalidate or oppress certain identities, allowing individuals to resist assimilation while maintaining a sense of self. Conversely, overidentification may result from internalized societal pressures and stereotypes, leading individuals to conform rigidly to group characteristics as a means of securing social acceptance or political solidarity.
Benefits of Balanced Self-Identification
Balanced self-identification fosters psychological resilience by integrating disidentification and overidentification, allowing individuals to maintain a flexible sense of self. This equilibrium promotes emotional regulation, reducing the risk of anxiety and depression while enhancing mindfulness and self-awareness. Embracing a balanced self-identification supports mental well-being and adaptive coping strategies in diverse life situations.
Addressing Disidentification in Therapy and Counseling
Addressing disidentification in therapy involves helping clients explore and detach from rigid self-concepts that limit emotional growth and resilience. Therapists utilize techniques such as mindfulness, cognitive restructuring, and narrative therapy to encourage clients to recognize and separate from unhelpful identifications, fostering greater psychological flexibility. This process contrasts with managing overidentification, where reinforcing boundaries between self and problematic emotions prevents entanglement with distressing thoughts or behaviors.
Strategies to Prevent Overidentification
Strategies to prevent overidentification involve fostering critical self-awareness and maintaining psychological flexibility to avoid rigid attachment to specific identities. Encouraging reflection on one's beliefs and behaviors helps to recognize biased self-perceptions, reducing the risk of conflating personal worth with external labels or roles. Practicing mindfulness and engaging in diverse social experiences further support the ability to remain open to change and resist overidentifying with a single identity construct.
Disidentification Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com