Unitarism emphasizes a unified and harmonious organizational culture where management and employees share common goals, minimizing conflict and promoting collaboration. This approach treats the organization as an integrated and cohesive system, fostering loyalty and commitment from Your workforce. Explore the rest of the article to understand how unitarism impacts workplace dynamics and employee relations.
Table of Comparison
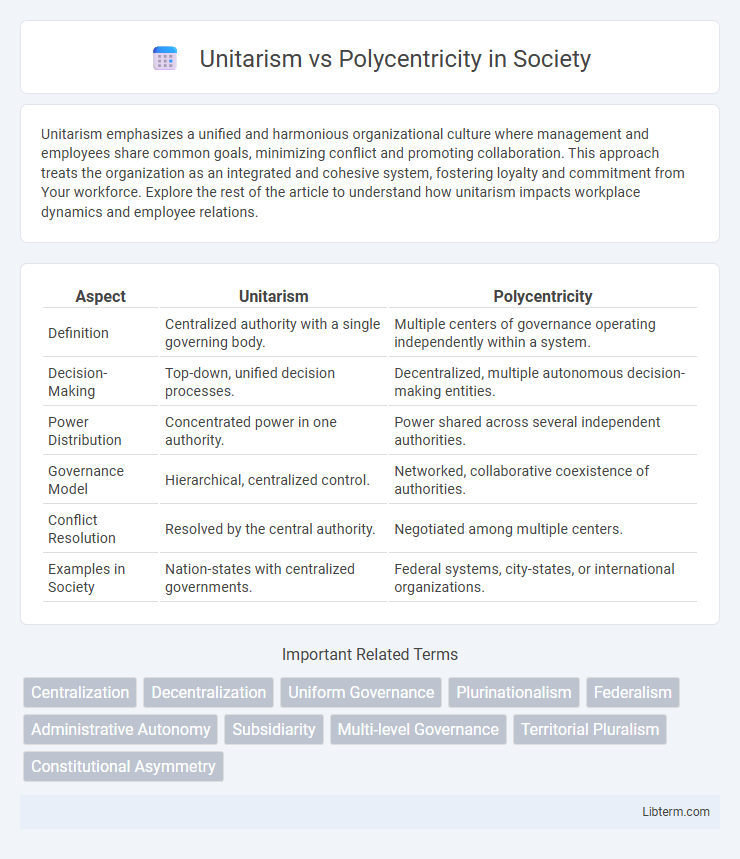
| Aspect | Unitarism | Polycentricity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Centralized authority with a single governing body. | Multiple centers of governance operating independently within a system. |
| Decision-Making | Top-down, unified decision processes. | Decentralized, multiple autonomous decision-making entities. |
| Power Distribution | Concentrated power in one authority. | Power shared across several independent authorities. |
| Governance Model | Hierarchical, centralized control. | Networked, collaborative coexistence of authorities. |
| Conflict Resolution | Resolved by the central authority. | Negotiated among multiple centers. |
| Examples in Society | Nation-states with centralized governments. | Federal systems, city-states, or international organizations. |
Understanding Unitarism and Polycentricity
Unitarism emphasizes a single, centralized authority structure where decision-making power is concentrated to maintain organizational unity and coherence. Polycentricity, by contrast, advocates for multiple autonomous centers of decision-making within an organization or system, allowing for diverse, context-sensitive management and governance. Understanding these concepts highlights the tension between centralized control and decentralized autonomy in organizational theory and governance models.
Historical Background of Unitarist and Polycentric Models
The Unitarist model originates from early 20th-century industrial relations theories emphasizing a single, cohesive organizational interest dominated by a unified leadership perspective. Polycentricity emerged in the mid-20th century as a response to multinational corporations' need to manage diverse and autonomous subsidiaries across different national contexts. This historical evolution highlights Unitarism's focus on centralized control versus Polycentricity's adaptation to decentralized, localized management strategies.
Core Principles of Unitarism
Unitarism emphasizes a single, cohesive authority within an organization, where management and employees share common goals and values, minimizing conflicts. It prioritizes organizational unity, loyalty, and a harmonized workplace culture under centralized leadership. The core principle revolves around the belief that divergent interests between management and staff are unnecessary and detrimental to organizational success.
Defining Features of Polycentricity
Polycentricity features multiple autonomous centers of decision-making operating within a single organizational framework, emphasizing decentralized governance and local responsiveness. It contrasts with unitarism by promoting diverse leadership units that adapt policies to specific community needs, enhancing flexibility and innovation. This structure fosters competition and collaboration among various units, driving efficiency and tailored problem-solving across different regions or sectors.
Governance Structures: Centralization vs. Decentralization
Unitarism emphasizes centralized governance structures where decision-making authority is concentrated at the top levels of management, promoting uniform policies and a cohesive organizational culture. In contrast, polycentricity supports decentralized governance, allowing autonomous decision-making within different units or subsidiaries, fostering flexibility and local responsiveness. This decentralization in polycentric models enhances adaptability but may challenge consistency and control across the organization.
Cultural Implications in Unitarism and Polycentricity
Unitarism emphasizes a singular organizational culture that aligns with the home country's values, promoting uniformity and control in multinational corporations. Polycentricity recognizes and adapts to the cultural diversity of host countries, allowing subsidiaries to operate with a localized management style that respects local customs and norms. The cultural implications of Unitarism often lead to cultural homogenization, whereas Polycentricity fosters cultural pluralism and sensitivity within global operations.
Economic Impacts of Unitarist and Polycentric Approaches
Unitarism emphasizes centralized control, potentially leading to streamlined economic policies but may stifle innovation and local responsiveness in diverse markets. Polycentric approaches promote multiple centers of decision-making, enhancing economic adaptability and fostering innovation by allowing tailored policies that address regional differences. Empirical studies indicate polycentric systems often yield greater economic resilience and sustainable growth due to decentralized resource management and competitive regional development.
Case Studies: Countries Practicing Unitarism and Polycentricity
Countries practicing unitarism, such as France and Japan, centralize decision-making within a strong national government, promoting uniform policies across all regions. In contrast, polycentricity is evident in countries like the United States and Switzerland, where multiple overlapping jurisdictions and autonomous local governments manage public services independently. Case studies highlight how unitarism facilitates streamlined administration, while polycentric systems enhance local responsiveness and adaptability.
Advantages and Challenges of Unitarism vs. Polycentricity
Unitarism offers advantages such as streamlined decision-making and consistent policy implementation across an organization, fostering unity and reducing internal conflicts. However, it faces challenges like potential centralization leading to rigidity and neglect of local contexts, which can hinder adaptability. Conversely, polycentricity promotes flexibility by empowering multiple centers of authority, enhancing responsiveness to diverse environments, but can result in coordination difficulties and inconsistent practices across units.
Future Trends and Debates in Governance Models
Future trends in Unitarism versus Polycentricity highlight an increasing shift towards decentralized governance frameworks that prioritize local autonomy and collaborative decision-making. Emerging debates focus on balancing the efficiency of Unitarism with the flexibility and resilience offered by Polycentric models, especially in addressing complex global challenges like climate change and urbanization. Technological advancements, such as blockchain and AI, are expected to further influence governance structures by enhancing transparency and participatory mechanisms in polycentric systems.
Unitarism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com