Corporate social responsibility (CSR) encompasses a company's commitment to ethical practices, environmental sustainability, and positive social impact. Businesses integrating CSR into their operations enhance their reputation, build customer trust, and contribute to long-term community welfare. Explore the rest of this article to discover how your organization can effectively implement CSR strategies.
Table of Comparison
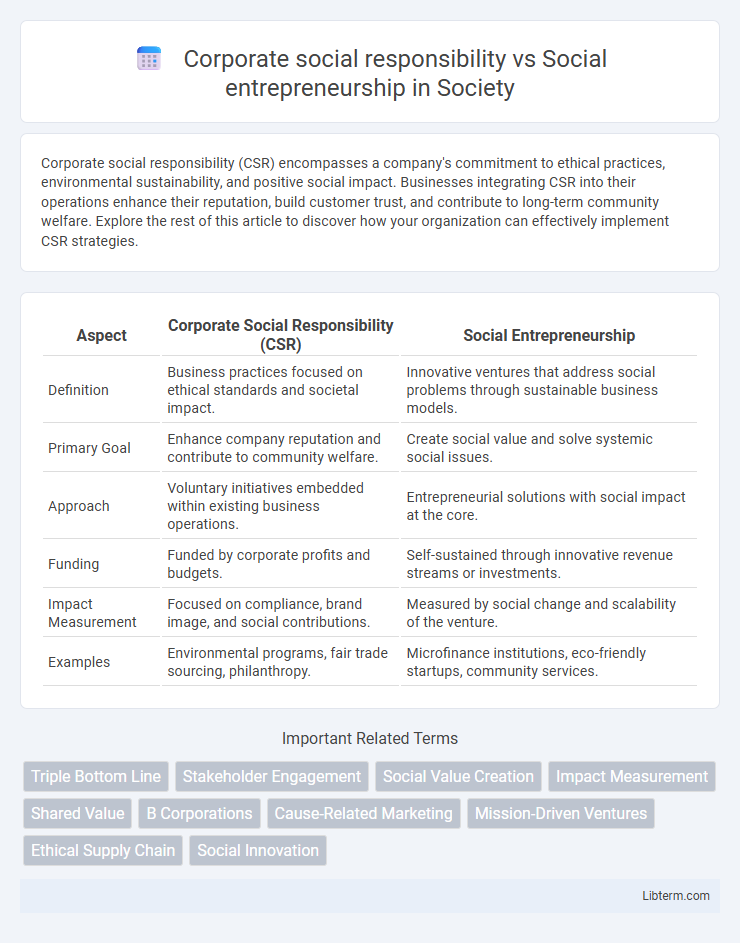
| Aspect | Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) | Social Entrepreneurship |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Business practices focused on ethical standards and societal impact. | Innovative ventures that address social problems through sustainable business models. |
| Primary Goal | Enhance company reputation and contribute to community welfare. | Create social value and solve systemic social issues. |
| Approach | Voluntary initiatives embedded within existing business operations. | Entrepreneurial solutions with social impact at the core. |
| Funding | Funded by corporate profits and budgets. | Self-sustained through innovative revenue streams or investments. |
| Impact Measurement | Focused on compliance, brand image, and social contributions. | Measured by social change and scalability of the venture. |
| Examples | Environmental programs, fair trade sourcing, philanthropy. | Microfinance institutions, eco-friendly startups, community services. |
Introduction to Corporate Social Responsibility and Social Entrepreneurship
Corporate social responsibility (CSR) refers to a company's commitment to ethical practices, environmental sustainability, and positive social impact within its operational framework. Social entrepreneurship emphasizes innovative approaches to solving social problems through business models that prioritize social value creation alongside financial viability. Both concepts integrate social objectives but differ in scope, with CSR embedded in existing corporations and social entrepreneurship driving mission-driven startups or ventures.
Defining Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) refers to a corporation's commitment to operate ethically, contribute to economic development, and improve the quality of life for employees, local communities, and society at large. Unlike social entrepreneurship, which centers on innovative business models to solve social problems, CSR typically involves integrating social and environmental concerns into business operations and stakeholder interactions. CSR initiatives often include sustainability efforts, philanthropy, ethical labor practices, and transparent governance to enhance long-term corporate accountability.
Understanding Social Entrepreneurship
Social entrepreneurship focuses on creating innovative solutions to address social problems through sustainable business models, distinguishing it from traditional corporate social responsibility (CSR), which often emphasizes compliance and philanthropy within established companies. Unlike CSR, social entrepreneurship prioritizes direct impact and scalability of social value by integrating mission-driven goals into the core business strategy. Key examples include enterprises that tackle issues such as poverty, education, and environmental sustainability by leveraging market-based approaches for long-term community benefit.
Key Differences Between CSR and Social Entrepreneurship
Corporate social responsibility (CSR) primarily involves established corporations integrating social and environmental concerns into their business operations and stakeholder interactions, focusing on compliance, risk management, and reputation enhancement. Social entrepreneurship centers on innovative business models that prioritize social impact and solving societal problems with sustainable financial returns, often through startups or mission-driven enterprises. Key differences lie in CSR's role as a corporate-driven obligation versus social entrepreneurship's proactive, market-based approach to systemic change.
Goals and Motivations: Profit vs Purpose
Corporate social responsibility (CSR) primarily focuses on aligning business practices with ethical standards to enhance brand reputation and ensure sustainable profits by addressing social and environmental concerns. Social entrepreneurship centers on creating innovative solutions to social problems with the primary motivation of achieving positive social impact rather than maximizing financial gain. While CSR integrates purpose-driven initiatives into profit-oriented strategies, social entrepreneurship prioritizes mission-driven goals over profitability.
Impact Measurement in CSR and Social Enterprises
Impact measurement in Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) focuses on assessing the effectiveness of a company's initiatives in improving social and environmental outcomes, often using metrics aligned with sustainability goals and stakeholder expectations. Social entrepreneurship emphasizes innovative solutions to social problems with impact measurement centered on social return on investment (SROI), community empowerment, and long-term scalable benefits. Both fields rely on quantitative and qualitative data but differ in scope, with CSR typically measuring impact within corporate frameworks and social enterprises prioritizing mission-driven outcomes and systemic change.
Examples of Successful CSR Initiatives
Nike's Community Impact Fund supports education and youth programs, exemplifying a successful Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) initiative that enhances community development. Similarly, Starbucks' commitment to ethical sourcing and environmental sustainability demonstrates effective CSR practices that benefit both society and the company's supply chain. These initiatives highlight how corporate actions can create positive social change while aligning with business goals.
Case Studies in Social Entrepreneurship
Case studies in social entrepreneurship highlight innovative approaches addressing social challenges through sustainable business models, contrasting with traditional corporate social responsibility (CSR) practices that often focus on philanthropy within established corporations. Unlike CSR, which integrates social goals as a component of broader corporate strategy, social entrepreneurship merges social impact directly with entrepreneurial ventures, exemplified by organizations like TOMS Shoes and Grameen Bank, which innovate to solve societal issues while achieving financial viability. These case studies underscore the transformative potential of social entrepreneurship in creating scalable and systemic change, shifting from the often limited scope of CSR initiatives.
Challenges Facing CSR and Social Entrepreneurs
Corporate social responsibility (CSR) faces challenges including stakeholder skepticism, limited measurable impact, and balancing profit with ethical commitments, whereas social entrepreneurs struggle with securing sustainable funding, scaling innovative solutions, and navigating regulatory barriers. CSR initiatives often encounter resistance when aligning diverse corporate goals with social values, while social entrepreneurs must continuously adapt to changing social needs and market conditions to maintain relevance and effectiveness. Both sectors require strategic collaboration, transparency, and robust impact assessment tools to overcome these hurdles and achieve long-term social change.
Future Trends: Integrating CSR and Social Entrepreneurship
Future trends indicate a growing convergence between corporate social responsibility (CSR) and social entrepreneurship, where businesses increasingly embed social innovation into their core strategies. Companies leverage social entrepreneurship models to enhance CSR impact, driving sustainable development goals through scalable, market-driven solutions. This integration fosters collaborative ecosystems, blending profit motives with social value creation for long-term stakeholder benefit.
Corporate social responsibility Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com