Identification is the process of recognizing and verifying an individual's identity through various methods such as biometric data, identification cards, or digital credentials. This critical step ensures security and access control in both physical and digital environments, protecting sensitive information and preventing unauthorized entry. Discover how effective identification techniques can safeguard your personal information and streamline security measures by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
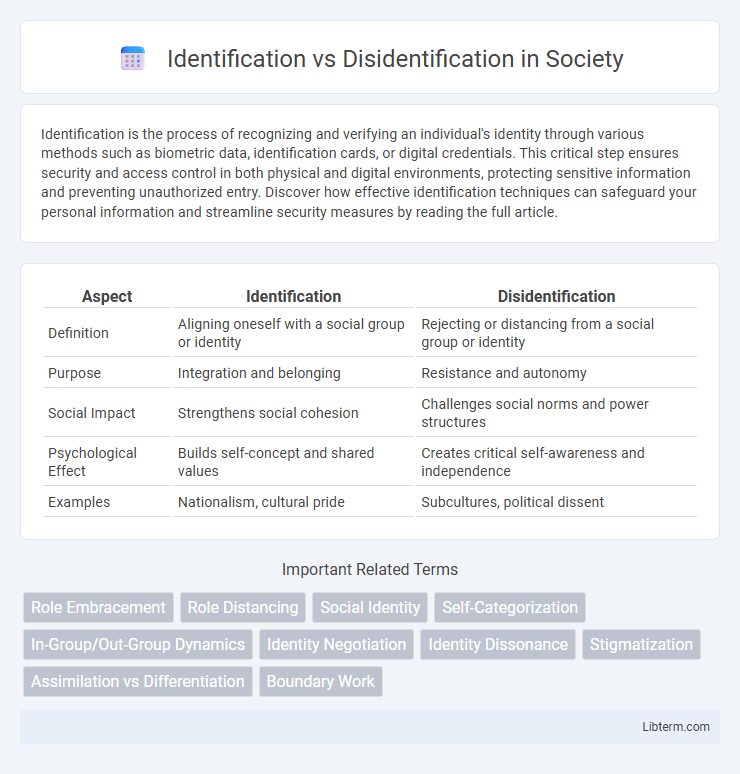
| Aspect | Identification | Disidentification |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Aligning oneself with a social group or identity | Rejecting or distancing from a social group or identity |
| Purpose | Integration and belonging | Resistance and autonomy |
| Social Impact | Strengthens social cohesion | Challenges social norms and power structures |
| Psychological Effect | Builds self-concept and shared values | Creates critical self-awareness and independence |
| Examples | Nationalism, cultural pride | Subcultures, political dissent |
Understanding Identification: A Conceptual Overview
Identification involves the psychological process where an individual aligns their beliefs, values, or behaviors with those of a group or role, leading to a sense of belonging and self-definition. It plays a crucial role in shaping identity by internalizing external characteristics as part of the self-concept. Disidentification, by contrast, refers to the distancing from or rejection of certain group attributes, serving as a mechanism to maintain or reconstruct personal identity boundaries.
The Psychology Behind Identification
Identification in psychology refers to the unconscious process where an individual assimilates aspects, properties, or attributes of another person, often to boost self-esteem or create a sense of belonging. Disidentification involves distancing oneself from certain traits, roles, or groups to maintain a unique identity or protect against negative associations. Understanding these mechanisms reveals how people navigate social dynamics, manage self-concept, and influence behavior in group settings.
What is Disidentification? Definition and Key Points
Disidentification is a psychological process where individuals distance themselves from specific social identities or groups to resist imposed stereotypes or expectations. It serves as a strategy for marginalized individuals to assert autonomy and reshape self-concept outside dominant cultural norms. Key points include its role in identity resistance, its impact on self-expression, and its function as a response to exclusion or discrimination.
The Role of Identity in Human Experience
Identification involves aligning one's sense of self with specific beliefs, groups, or roles, shaping personal and social identity through shared values and experiences. Disidentification occurs when individuals reject or distance themselves from these affiliations, often to preserve autonomy or resist imposed categories. Identity plays a pivotal role in human experience by influencing behavior, emotional well-being, and social belonging.
Mechanisms of Identification: How We Attach
Mechanisms of identification involve psychological processes where individuals internalize attributes, beliefs, or values of others to form a sense of self. This attachment occurs through empathy, mirroring behaviors, and social learning, enabling individuals to incorporate groups or role models into their identity. The strength of identification shapes motivations and social bonds, influencing personal and collective behaviors.
The Process and Benefits of Disidentification
Disidentification is a psychological process where individuals detach from a self-concept or group identity that no longer serves their well-being, facilitating personal growth and resilience. This process involves critically examining and selectively disengaging from limiting beliefs or social roles, resulting in increased autonomy and self-awareness. The benefits of disidentification include enhanced emotional regulation, reduced internal conflict, and greater flexibility in adopting new, empowering identities.
Identification vs Disidentification: Core Differences
Identification involves aligning oneself with particular groups, roles, or beliefs, leading to a cohesive sense of identity and belonging. Disidentification, by contrast, entails a critical distancing from these affiliations, often as a strategy to resist or redefine imposed identities. Core differences include identification fostering conformity and integration, while disidentification promotes individuality and subversion within social contexts.
Societal Impacts of Identification and Disidentification
Identification fosters social cohesion by creating shared values and a sense of belonging within communities, which can strengthen collective identity and promote cooperative behaviors. Disidentification, conversely, can lead to social fragmentation and marginalization when individuals reject dominant group norms, potentially inciting conflict or fostering alternative social movements. Societal impacts of these processes influence cultural integration, political engagement, and group dynamics, shaping both inclusion and exclusion in diverse societies.
Cultivating Healthy Disidentification Practices
Cultivating healthy disidentification practices involves consciously separating one's self-worth from external labels and societal expectations, promoting psychological resilience and authentic self-expression. Techniques such as mindfulness, self-reflection, and critical thinking enable individuals to recognize and disengage from limiting identities imposed by culture or peer pressure. Consistent practice fosters emotional well-being by reducing internal conflicts and enhancing personal autonomy in identity formation.
Transformation Through Disidentification
Transformation through disidentification involves breaking away from dominant cultural identities to create new forms of self-understanding and agency. This process challenges established norms by refusing to fully assimilate or reject imposed identities, enabling individuals to navigate and reshape social structures. Disidentification serves as a critical strategy in marginalized communities to resist oppression and cultivate transformative experiences of empowerment.
Identification Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com