The political elite play a critical role in shaping policies and governance structures that impact society at large. Their decisions often influence economic development, social justice, and international relations, making their power both significant and controversial. Explore the rest of the article to understand how your interests intersect with the actions of the political elite.
Table of Comparison
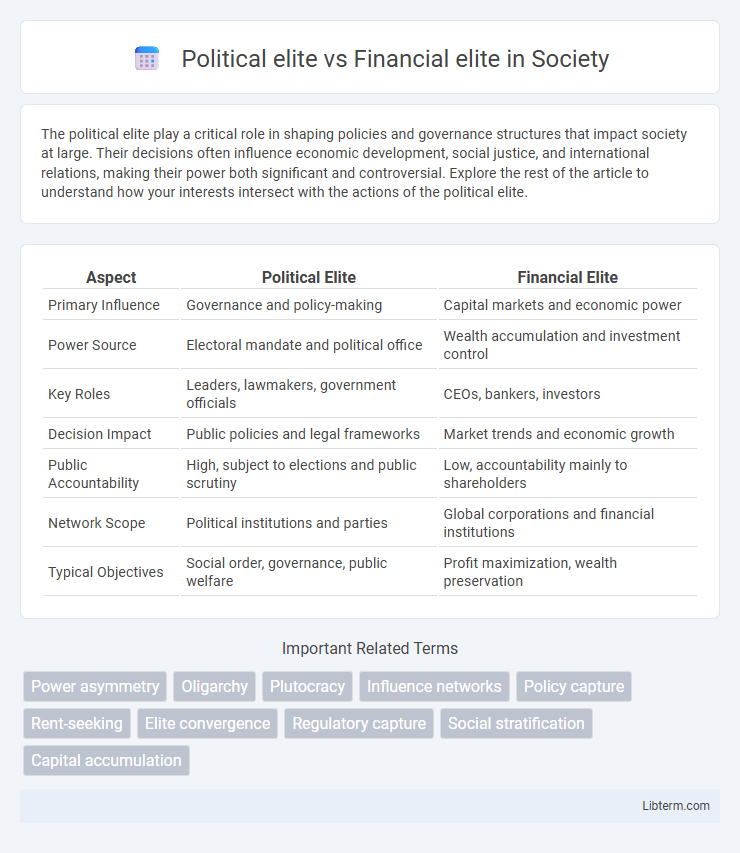
| Aspect | Political Elite | Financial Elite |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Influence | Governance and policy-making | Capital markets and economic power |
| Power Source | Electoral mandate and political office | Wealth accumulation and investment control |
| Key Roles | Leaders, lawmakers, government officials | CEOs, bankers, investors |
| Decision Impact | Public policies and legal frameworks | Market trends and economic growth |
| Public Accountability | High, subject to elections and public scrutiny | Low, accountability mainly to shareholders |
| Network Scope | Political institutions and parties | Global corporations and financial institutions |
| Typical Objectives | Social order, governance, public welfare | Profit maximization, wealth preservation |
Defining the Political Elite: Power and Influence
The political elite consists of individuals who hold authoritative positions within government institutions, shaping policy and public decision-making through formal power structures. Their influence stems from elected or appointed roles, enabling direct control over legislation, governance, and national security. Unlike the financial elite, whose power is rooted in economic capital and market control, the political elite wields power through political legitimacy and institutional authority.
The Financial Elite: Wealth as Authority
The financial elite wield significant power through immense wealth, enabling control over markets, industries, and political influence by funding campaigns and shaping policies. Their economic resources grant them authority that often surpasses traditional political power, dictating trends and decisions in global finance and corporate governance. Wealth functions as a tool of dominance, allowing the financial elite to maintain and expand their influence across both domestic and international spheres.
Historical Intersections between Political and Financial Elites
Political and financial elites have historically intersected through the control of economic policies and resource allocation, often shaping national and global power structures. Key moments such as the Gilded Age in the United States and the rise of corporate monopolies in the late 19th century highlight how financial elites leveraged political connections to influence legislation and protect their interests. This intertwining of political authority and financial capital continues to impact regulatory frameworks, campaign financing, and economic inequality worldwide.
Sources of Power: Government vs. Capital
Political elite derive their power primarily from governmental authority, legislative control, and policy-making capabilities, enabling them to shape laws and regulate societal frameworks. Financial elite accumulate power through ownership of capital, control of financial institutions, and influence over markets, granting them economic leverage and the ability to impact investment flows. The dynamic between these elites highlights a division where political power is rooted in institutional governance, while financial power emanates from economic capital and wealth accumulation.
Mechanisms of Influence: Legislation vs. Market Control
Political elites exert influence primarily through legislation, shaping laws, regulations, and public policies that govern societal behavior and economic activities. Financial elites control markets by directing capital flows, manipulating investment trends, and leveraging ownership of key industries to impact economic outcomes. These mechanisms of influence highlight the distinction between governance-driven power and wealth-driven control in shaping social and economic structures.
The Role of Lobbying and Campaign Financing
Lobbying and campaign financing are pivotal tools wielded by both political and financial elites to influence policy-making and regulatory environments. Political elites often rely on financial elites to secure campaign contributions, enabling sustained electoral success and policy support that align with financial interests. Financial elites invest heavily in lobbying to shape legislation favoring market deregulation, tax advantages, and industry-friendly laws, thereby consolidating their economic power and political influence.
Socioeconomic Impact: Elite Decisions on Society
Political elite shape public policies that regulate social welfare, education, and healthcare, directly influencing income distribution and social mobility. Financial elite control capital flows and investment decisions, impacting economic growth, job creation, and wealth concentration. The interplay between these elites determines socioeconomic inequality and access to opportunities within society.
Elite Networks: Collaboration and Conflicts
Political elite and financial elite form interconnected networks that influence key decision-making processes, where political leaders rely on financial elites for campaign funding and policy support while financial elites depend on political connections for regulatory advantages and market access. These elite networks facilitate collaboration on legislative agendas and economic strategies, yet conflicts arise due to divergent goals, power struggles, and competing interests in resource allocation. Understanding the dynamics of these elite interactions reveals how governance and financial systems are shaped by both cooperation and contention within elite circles.
Globalization: Shifting Dynamics of Elite Power
Political elites traditionally wield power through governance and policy-making, while financial elites exert influence via capital control and global markets. Globalization intensifies the interconnectedness of these groups, enabling financial elites to shape international economic policies and political elites to rely on transnational financial networks for economic growth. The shifting dynamics of elite power reveal a complex interplay where political authority increasingly intersects with financial interests in shaping global governance.
Future Trends: Convergence or Divergence of Elites
Emerging future trends indicate a complex interplay between political elite and financial elite, where technological advancements and global economic shifts increasingly blur their boundaries through shared influence in regulatory frameworks and capital allocation. Data from recent studies reveals a growing convergence driven by digital currencies, lobbying networks, and multinational corporate governance, yet rising populist movements and regulatory reforms may also enforce divergence by challenging elite consensus and promoting transparency. Monitoring the evolution of elite power structures requires analyzing cross-sector collaborations alongside socio-political resistance patterns to anticipate shifts in global influence distribution.
Political elite Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com