Individual-centric approaches prioritize personal preferences and unique needs, ensuring tailored solutions that enhance satisfaction and effectiveness. By focusing on the individual, strategies become more adaptive and relevant to specific contexts, promoting better engagement and outcomes. Discover how embracing an individual-centric mindset can transform your experience and impact by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
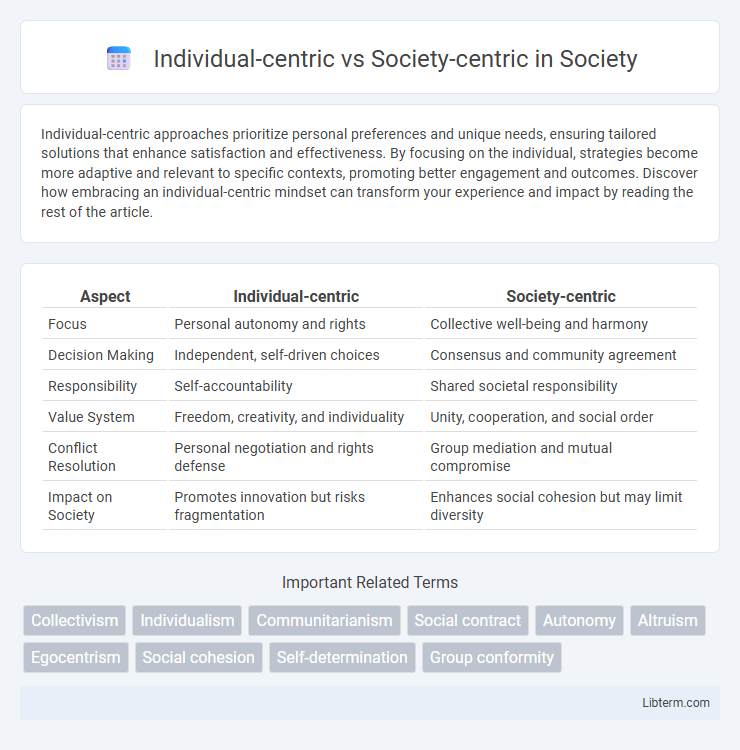
| Aspect | Individual-centric | Society-centric |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Personal autonomy and rights | Collective well-being and harmony |
| Decision Making | Independent, self-driven choices | Consensus and community agreement |
| Responsibility | Self-accountability | Shared societal responsibility |
| Value System | Freedom, creativity, and individuality | Unity, cooperation, and social order |
| Conflict Resolution | Personal negotiation and rights defense | Group mediation and mutual compromise |
| Impact on Society | Promotes innovation but risks fragmentation | Enhances social cohesion but may limit diversity |
Defining Individual-Centric and Society-Centric Approaches
Individual-centric approaches prioritize personal autonomy, rights, and self-expression, emphasizing the importance of individual choice and responsibility in decision-making. Society-centric approaches focus on collective well-being, social harmony, and shared responsibilities, prioritizing community values and the common good over individual preferences. These contrasting frameworks shape policies, ethics, and cultural norms by balancing personal freedoms with societal obligations.
Historical Context: Evolution of Individualism and Collectivism
The historical context of individualism versus collectivism reveals how Western societies, especially post-Enlightenment Europe and America, increasingly emphasized individual rights, personal freedom, and self-expression, shaping the modern concept of individualism. Conversely, many Eastern cultures, such as Confucian-influenced China and India, have roots in collectivist traditions prioritizing community, social harmony, and familial duty, reflecting centuries of societal interdependence. This evolution is evident in political philosophies, economic systems, and social norms, with the tension between individual autonomy and societal obligations continuing to influence global cultural and ideological landscapes.
Core Values: Personal Freedom vs. Collective Responsibility
Personal freedom emphasizes individual rights, autonomy, and self-expression as core values shaping ethical decisions and social interactions. Collective responsibility prioritizes the well-being of the community, advocating for shared duties and mutual support to achieve social harmony and justice. Balancing these values influences policies, cultural norms, and priorities in governance and societal development.
Impact on Social Policies and Governance
Individual-centric approaches emphasize personal freedoms and responsibilities, influencing social policies that prioritize individual rights, privacy, and self-determination. Society-centric perspectives focus on collective well-being, shaping governance through policies that promote social equity, public health, and community welfare. Balancing these paradigms affects legislation on healthcare, education, and welfare programs, determining resource allocation and regulatory frameworks.
Education Systems: Fostering Independence or Community
Individual-centric education systems prioritize personal growth, critical thinking, and self-directed learning to nurture independence and innovation among students. Society-centric models emphasize collaboration, social responsibility, and communal values to strengthen cultural cohesion and collective problem-solving skills. Balancing these approaches enhances educational outcomes by preparing learners to contribute both autonomously and harmoniously within their communities.
Economic Models: Innovation vs. Social Welfare
Individual-centric economic models emphasize innovation, entrepreneurship, and market competition as drivers of growth, prioritizing personal incentives and property rights to stimulate creativity and efficiency. Society-centric models focus on social welfare by redistributing resources, regulating markets, and providing public goods to reduce inequality and ensure collective well-being. Balancing these approaches involves integrating private sector innovation with government interventions to foster inclusive economic development.
Cultural Differences: East vs. West Perspectives
Eastern cultures typically emphasize society-centric values, prioritizing community harmony, collective responsibilities, and interdependence, whereas Western cultures lean towards individual-centric values, promoting personal autonomy, self-expression, and individual rights. These cultural differences influence social behaviors, decision-making processes, and conflict resolution strategies, reflecting deep-rooted philosophical traditions such as Confucianism in the East and liberal individualism in the West. Understanding these perspectives is crucial for cross-cultural communication, global business, and international relations.
Ethical Dilemmas: Balancing Rights and Duties
Ethical dilemmas often arise from the tension between individual-centric approaches, which prioritize personal rights and autonomy, and society-centric perspectives, which emphasize collective duties and social responsibilities. Balancing these competing interests requires nuanced frameworks that respect individual freedoms while ensuring societal welfare and justice. Effective solutions integrate legal principles, cultural values, and ethical theories to mediate conflicts between personal entitlements and communal obligations.
Challenges and Criticisms of Each Approach
Individual-centric approaches emphasize personal freedom and autonomy but face challenges such as neglecting social responsibilities and exacerbating inequality. Society-centric models prioritize communal welfare and social cohesion, yet they often encounter criticisms for limiting individual rights and suppressing diversity. Balancing these paradigms requires addressing the tension between personal liberties and collective obligations while promoting inclusive policies.
Finding Harmony: Integrating Individual and Societal Needs
Balancing individual rights and societal responsibilities requires recognizing the importance of both personal freedoms and collective well-being. Effective policies prioritize shared goals such as social equity, public health, and economic opportunity while respecting individual autonomy. Integrating these needs fosters social cohesion, innovation, and sustainable development within diverse communities.
Individual-centric Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com