Civic engagement empowers communities by encouraging individuals to actively participate in democratic processes, local governance, and social initiatives. Understanding your role in shaping policies and contributing to societal well-being can lead to meaningful change and stronger communities. Explore the rest of this article to discover practical ways you can enhance your civic participation.
Table of Comparison
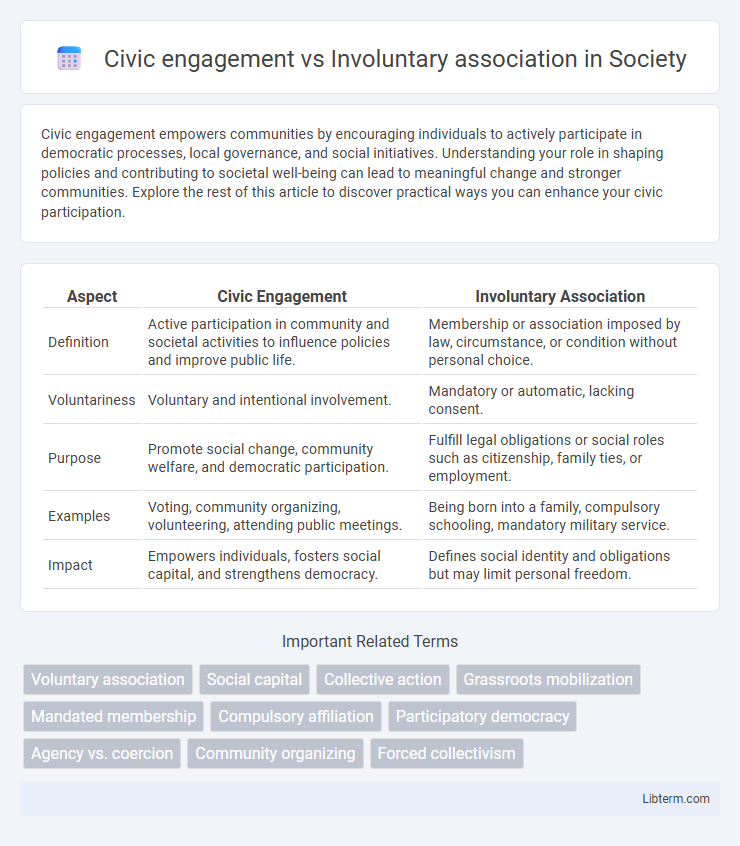
| Aspect | Civic Engagement | Involuntary Association |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Active participation in community and societal activities to influence policies and improve public life. | Membership or association imposed by law, circumstance, or condition without personal choice. |
| Voluntariness | Voluntary and intentional involvement. | Mandatory or automatic, lacking consent. |
| Purpose | Promote social change, community welfare, and democratic participation. | Fulfill legal obligations or social roles such as citizenship, family ties, or employment. |
| Examples | Voting, community organizing, volunteering, attending public meetings. | Being born into a family, compulsory schooling, mandatory military service. |
| Impact | Empowers individuals, fosters social capital, and strengthens democracy. | Defines social identity and obligations but may limit personal freedom. |
Defining Civic Engagement
Civic engagement refers to active participation in activities aimed at improving community well-being and influencing public policy through volunteering, voting, or advocacy. Unlike involuntary associations, which are groups individuals join based on circumstances beyond their control, civic engagement requires deliberate, voluntary involvement for societal benefit. This distinction highlights the role of intentional actions in fostering democratic governance and social responsibility.
Understanding Involuntary Association
Involuntary association involves individuals being grouped or identified based on characteristics beyond their control, such as race, ethnicity, or socioeconomic status, affecting their social participation and access to resources. Understanding involuntary association is crucial for analyzing social dynamics where membership is assigned rather than chosen, influencing opportunities and systemic inequalities. This contrasts with civic engagement, where individuals voluntarily participate in community or political activities to influence decision-making and social change.
Key Differences Between Civic Engagement and Involuntary Association
Civic engagement involves voluntary participation in community activities aimed at improving society, driven by personal commitment and collective goals. Involuntary association occurs when individuals are part of groups or organizations due to external requirements or social constraints, without active consent or participation. The key difference lies in agency and intention: civic engagement reflects proactive involvement, while involuntary association denotes passive membership.
Historical Evolution of Civic Participation
Civic engagement historically evolved from voluntary collective actions aimed at community betterment, rooted in the rise of democratic ideals and civil society movements. In contrast, involuntary association emerged predominantly under authoritarian regimes or colonial frameworks, where participation was mandated rather than chosen, often limiting genuine deliberation. This evolution highlights a shift from coerced compliance to active, voluntary involvement as a cornerstone of modern democratic participation.
The Role of Choice in Civic Life
Civic engagement thrives on the principle of voluntary participation, reflecting individuals' conscious choice to contribute to community well-being and democratic processes. In contrast, involuntary association compromises autonomy by mandating involvement without explicit consent, potentially diminishing genuine commitment and effectiveness in civic outcomes. The role of choice in civic life underscores the importance of personal agency for fostering meaningful engagement and sustaining vibrant civic institutions.
Social Impacts of Involuntary Associations
Involuntary associations, such as mandatory memberships in professional organizations or government-imposed groupings, often lead to passive participation, limiting genuine civic engagement and reducing social trust. These forced affiliations can create social fragmentation by fostering resentment and weakening the sense of community belonging that voluntary civic engagement typically promotes. The social impacts include decreased social capital, lower collective efficacy, and increased alienation among members, undermining the overall democratic fabric of society.
Civic Engagement and Community Building
Civic engagement involves active participation in community decision-making, fostering social cohesion and empowering individuals to influence local policies and development. It strengthens community building by encouraging collaboration among diverse groups, enhancing trust, and creating shared goals that address collective needs. Unlike involuntary association, where membership is imposed, civic engagement is driven by voluntary commitment and intentional involvement to improve societal well-being.
Challenges in Distinguishing Voluntary vs Involuntary Participation
Distinguishing between civic engagement and involuntary association is challenged by ambiguous participation motives and overlapping social pressures. Individuals often engage in community activities due to social expectations or implicit obligations, blurring the line between voluntary civic participation and coerced involvement. Accurately identifying true voluntary engagement requires analyzing participation contexts, individual autonomy, and the presence of external incentives or constraints.
Legal and Ethical Dimensions of Association
Civic engagement involves voluntary participation in community activities, reflecting individuals' legal rights and ethical responsibility to contribute to societal well-being. In contrast, involuntary association, such as mandatory memberships or legally imposed affiliations, raises complex ethical concerns regarding personal freedom and consent under the law. Legal frameworks carefully balance the protection of individual autonomy with the collective interests that involuntary associations may serve in public policy and social order.
Fostering Authentic Civic Engagement
Fostering authentic civic engagement requires encouraging voluntary participation driven by genuine interest and shared values, contrasting with involuntary association where membership is imposed or coerced. True civic engagement cultivates empowered communities that actively deliberate and contribute to public decision-making processes, enhancing social trust and democratic legitimacy. Emphasizing autonomy and meaningful involvement ensures sustained commitment and authentic collective action.
Civic engagement Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com