Organizations play a crucial role in structuring resources, coordinating efforts, and achieving collective goals efficiently. Effective organizational strategies enhance productivity, foster innovation, and improve overall performance across industries. Discover how optimizing your organization's framework can unlock new opportunities and drive success in the following article.
Table of Comparison
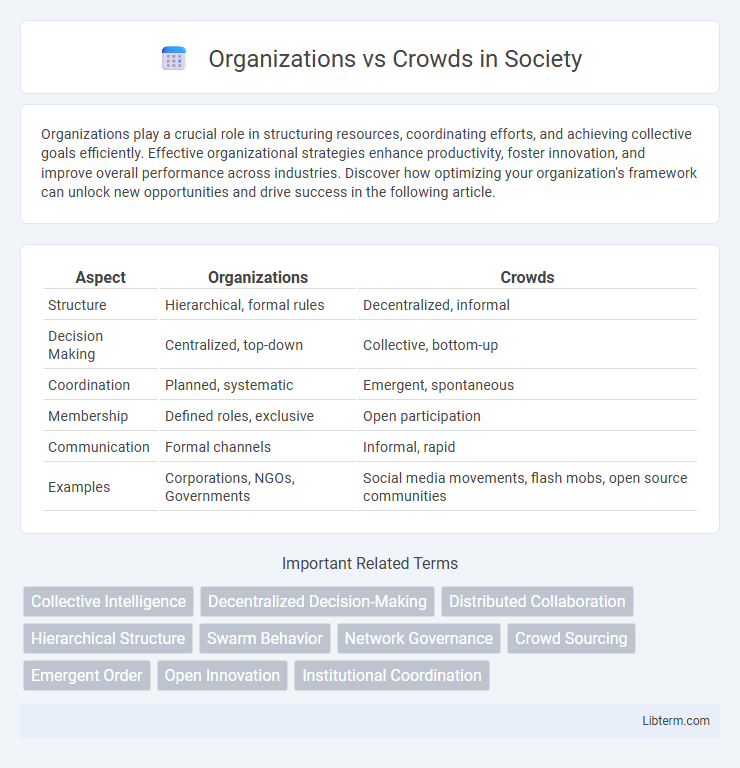
| Aspect | Organizations | Crowds |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Hierarchical, formal rules | Decentralized, informal |
| Decision Making | Centralized, top-down | Collective, bottom-up |
| Coordination | Planned, systematic | Emergent, spontaneous |
| Membership | Defined roles, exclusive | Open participation |
| Communication | Formal channels | Informal, rapid |
| Examples | Corporations, NGOs, Governments | Social media movements, flash mobs, open source communities |
Understanding Organizations and Crowds
Organizations consist of structured groups with defined roles, rules, and hierarchical decision-making processes that facilitate coordination and accountability. Crowds are decentralized assemblies of individuals whose collective behavior emerges spontaneously without formal structure, relying on shared interests or goals. Understanding the differences in communication patterns, coordination mechanisms, and decision-making processes is crucial for leveraging the strengths of both entities in problem-solving and innovation.
Key Differences Between Organizations and Crowds
Organizations are structured groups with defined roles, formal rules, and coordinated decision-making processes, whereas crowds consist of loosely connected individuals acting spontaneously without centralized control. Organizations emphasize hierarchy, accountability, and long-term objectives, while crowds are driven by immediate collective behavior and shared interests. The key difference lies in organization's systematic coordination versus crowd's emergent, often unpredictable dynamics.
Structure and Hierarchy: Organization vs Crowd
Organizations feature defined structures with clear hierarchies, assigned roles, and formal decision-making processes, ensuring efficiency and accountability. Crowds operate through decentralized, often fluid interactions without fixed leadership or rigid roles, enabling adaptability and collective intelligence. The contrast lies in organizations' top-down coordination versus crowds' emergent, bottom-up dynamics.
Decision-Making Processes: Collective vs Centralized
Organizations utilize centralized decision-making processes where leadership directs and controls critical choices, ensuring consistency and accountability within hierarchical structures. Crowds rely on collective decision-making, harnessing diverse perspectives and decentralized input to achieve more innovative and democratic outcomes. The contrast lies in organizations prioritizing efficiency and control, while crowds emphasize collaboration and adaptability in problem-solving.
Communication Patterns in Organizations and Crowds
Communication patterns in organizations typically follow structured hierarchies, with formal channels guiding information flow between designated roles and departments, enhancing clarity and accountability. In contrast, crowds exhibit decentralized and dynamic communication, where interactions are spontaneous, peer-to-peer, and often facilitated by social media platforms, leading to rapid information dissemination but potential inconsistencies. Understanding these distinct communication frameworks is critical for optimizing collaboration and decision-making in both organizational and crowd-based contexts.
Accountability and Responsibility
Organizations establish clear lines of accountability and defined responsibilities through hierarchical structures and formal roles, ensuring decisions and outcomes can be traced to specific individuals or departments. Crowds operate via decentralized participation, which diffuses responsibility and often makes accountability ambiguous, as collective input lacks explicit ownership. This fundamental difference affects how trust, oversight, and performance are managed in organizational versus crowd-based initiatives.
Flexibility and Adaptability
Organizations typically operate with structured hierarchies and predefined roles, which can limit their flexibility in rapidly changing environments. Crowds leverage diverse, decentralized contributions that enable faster adaptation to new information or challenges. This collective intelligence allows crowds to innovate and respond dynamically, often outperforming rigid organizational frameworks in volatile contexts.
Innovation and Problem Solving Approaches
Organizations leverage structured hierarchies and specialized teams to drive innovation through controlled processes and strategic resource allocation. Crowds harness the collective intelligence of diverse, decentralized participants, enabling rapid ideation and problem-solving via open collaboration and real-time feedback. Combining organizational discipline with crowdsourced creativity maximizes innovation potential and accelerates complex problem resolution.
Impact on Collaboration and Productivity
Organizations provide structured environments with defined roles and processes that enhance collaboration by streamlining communication and aligning goals, resulting in consistent productivity. Crowds leverage diverse expertise and decentralized contributions, fostering innovation through collective intelligence but potentially facing challenges in coordination and accountability. The impact on productivity varies as organizations excel in predictable output, while crowds drive dynamic problem-solving and adaptability in complex tasks.
Choosing the Right Model: Organization or Crowd
Choosing between an organization and a crowd depends on the specific goals, resources, and complexity of the task. Organizations provide structured roles, clear responsibilities, and predictable outcomes, ideal for projects requiring control and consistency. Crowds offer diverse perspectives, rapid scalability, and innovation potential, making them suitable for tasks benefiting from collective intelligence and open participation.
Organizations Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com