Integrated space maximizes functionality by seamlessly combining multiple uses within a single environment, enhancing both efficiency and comfort. Thoughtful design elements optimize spatial relationships, ensuring every square foot serves a purpose while maintaining aesthetic appeal. Discover how integrated space solutions can transform Your living or working environment in this comprehensive guide.
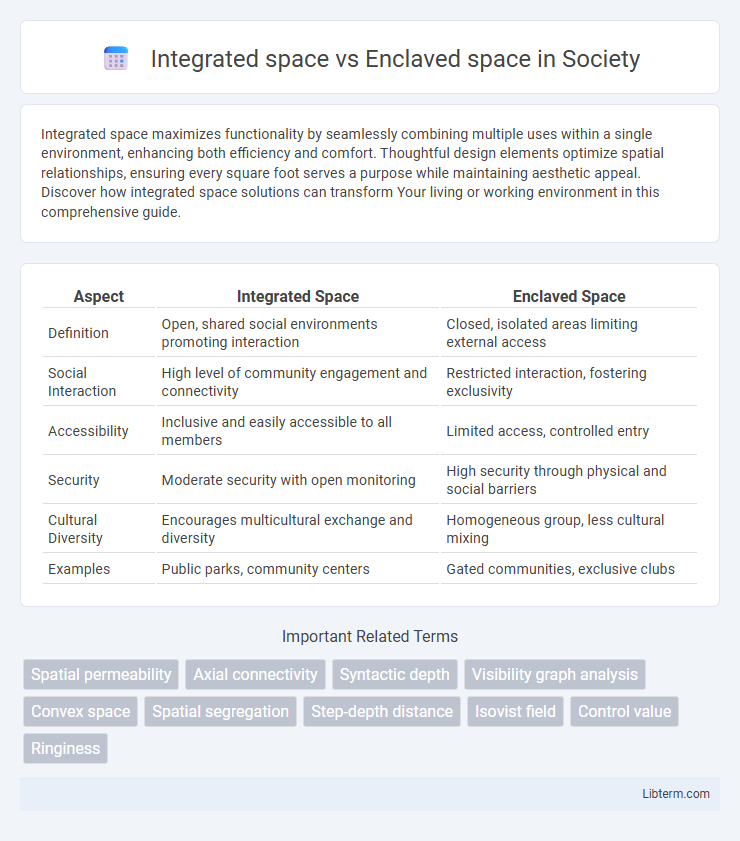
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Integrated Space | Enclaved Space |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Open, shared social environments promoting interaction | Closed, isolated areas limiting external access |
| Social Interaction | High level of community engagement and connectivity | Restricted interaction, fostering exclusivity |
| Accessibility | Inclusive and easily accessible to all members | Limited access, controlled entry |
| Security | Moderate security with open monitoring | High security through physical and social barriers |
| Cultural Diversity | Encourages multicultural exchange and diversity | Homogeneous group, less cultural mixing |
| Examples | Public parks, community centers | Gated communities, exclusive clubs |
Understanding Integrated Space: Definition and Characteristics
Integrated space refers to environments designed for seamless interaction and connectivity among various functional areas, promoting collaboration and fluid movement. It features open layouts, shared resources, and minimal physical barriers, enhancing communication and flexibility within work or living spaces. Key characteristics include multifunctionality, accessibility, and adaptability, which support diverse activities and dynamic user needs effectively.
What is Enclaved Space? Key Features Explained
Enclaved space refers to a distinct, enclosed area within a larger environment designed to provide privacy, security, and autonomy, often separated by physical or symbolic boundaries. Key features include limited accessibility, controlled entry points, and a strong sense of territoriality that fosters exclusivity and protection from outside influences. This concept is commonly applied in urban design, architecture, and social spaces to create safe zones or private domains amidst more open, shared environments.
Benefits of Integrated Spaces in Modern Design
Integrated spaces in modern design enhance functionality by promoting fluid movement and maximizing the use of available square footage. These spaces encourage social interaction and create a sense of openness, improving natural light distribution and air circulation. Implementing integrated layouts supports flexibility in furniture arrangement and accommodates multifunctional activities, making it ideal for contemporary living and working environments.
Advantages and Challenges of Enclaved Spaces
Enclaved spaces offer enhanced security and privacy by isolating sensitive activities or data within a controlled environment, reducing exposure to external threats and unauthorized access. These spaces enable focused collaboration among specific groups, minimizing distractions and fostering specialized workflows. However, challenges include potential communication barriers with integrated systems, increased management complexity, and possible duplication of resources that can hinder operational efficiency.
Psychological Effects: Integrated vs Enclaved Environments
Integrated spaces promote psychological well-being by enhancing social interaction, increasing feelings of inclusion, and reducing stress through open, connected layouts. Enclaved spaces provide psychological benefits such as privacy, security, and controlled sensory input, which support concentration and emotional regulation. The balance between integrated and enclaved environments influences cognitive performance, emotional comfort, and overall mental health outcomes.
Functional Implications: Which Space Suits Your Needs?
Integrated space promotes openness and fluidity, enhancing collaboration and social interaction, making it ideal for dynamic work environments and creative hubs. Enclaved space offers privacy and focused concentration, suitable for tasks requiring minimal distractions and confidential activities. Selecting the right spatial design depends on functional needs such as teamwork intensity, noise sensitivity, and privacy requirements.
Design Considerations for Integrating Spaces
Design considerations for integrating spaces focus on creating fluid transitions and maintaining functional coherence between areas, emphasizing open layouts and shared visual connections. Material continuity, consistent lighting, and coordinated color schemes enhance spatial unity while supporting diverse activities within the integrated environment. Balancing privacy with openness through strategic zoning and flexible furniture arrangements optimizes user experience and adaptability.
Privacy and Accessibility: A Comparative Analysis
Integrated space optimizes accessibility by promoting open layouts that facilitate interaction and easy movement while potentially reducing privacy due to shared environments. Enclaved space enhances privacy through physical boundaries and separation, allowing individuals or groups to control their immediate surroundings but often limits accessibility by restricting flow and visibility. Evaluating these spatial designs requires balancing the trade-offs between privacy needs and accessibility demands to suit specific functional and social contexts.
Real-World Examples: Integrated vs Enclaved Spaces
Integrated spaces, such as open-plan offices exemplified by Google's Mountain View campus, promote collaboration and fluid interaction by removing physical barriers between work areas. Enclaved spaces, like the traditional bank branch design or secure data centers, prioritize privacy, security, and controlled access by isolating functions within defined boundaries. These real-world examples highlight how integrated spaces foster transparency and teamwork, while enclaved spaces emphasize protection and focused individual tasks.
Future Trends in Spatial Organization and Design
Future trends in spatial organization emphasize flexibility in integrated space designs, promoting multifunctional areas that foster collaboration and adaptability within residential, commercial, and co-working environments. Enclaved spaces, conversely, evolve to provide personalized, quiet zones that support privacy and mental well-being, leveraging advances in acoustic technology and smart materials. The convergence of IoT and AI-driven environmental controls enhances both integrated and enclaved spaces, enabling seamless transitions and optimized user experiences.
Integrated space Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com