In-group dynamics influence social interactions by fostering a sense of belonging and shared identity among members. Understanding in-group behavior helps you navigate relationships and avoid conflicts rooted in favoritism or exclusion. Explore the rest of the article to discover how in-groups shape personal and professional environments.
Table of Comparison
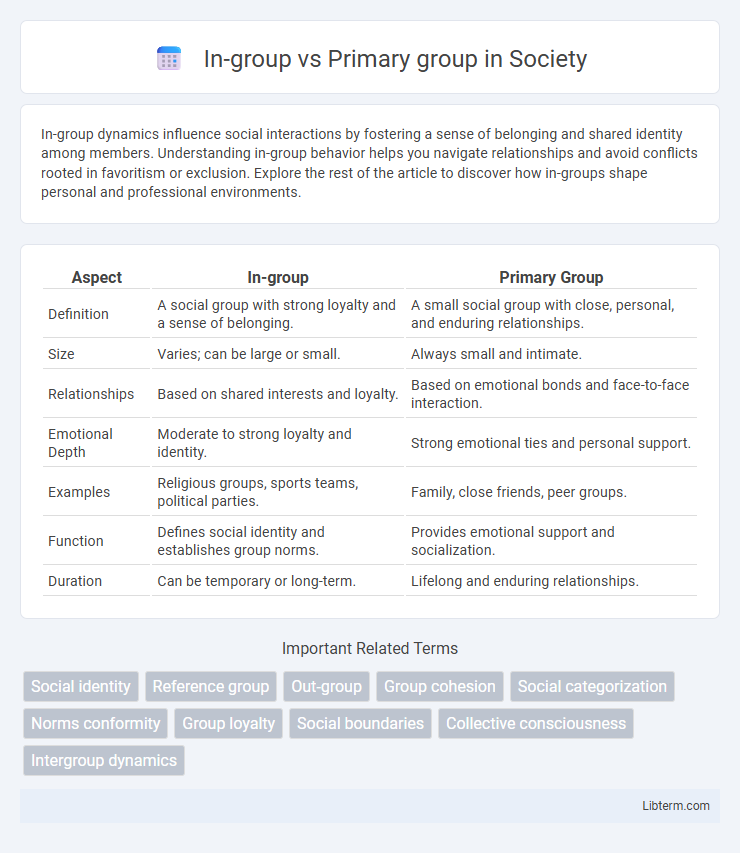
| Aspect | In-group | Primary Group |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A social group with strong loyalty and a sense of belonging. | A small social group with close, personal, and enduring relationships. |
| Size | Varies; can be large or small. | Always small and intimate. |
| Relationships | Based on shared interests and loyalty. | Based on emotional bonds and face-to-face interaction. |
| Emotional Depth | Moderate to strong loyalty and identity. | Strong emotional ties and personal support. |
| Examples | Religious groups, sports teams, political parties. | Family, close friends, peer groups. |
| Function | Defines social identity and establishes group norms. | Provides emotional support and socialization. |
| Duration | Can be temporary or long-term. | Lifelong and enduring relationships. |
Understanding In-Group and Primary Group Concepts
In-group refers to a social group with which an individual identifies strongly, fostering a sense of belonging and loyalty often based on shared interests or values. Primary groups are characterized by close, personal, and enduring relationships, typically found in family or close friend networks where emotional depth and intimacy are high. Understanding these concepts highlights how in-groups emphasize social identity and exclusivity, while primary groups prioritize intimate, supportive bonds essential for personal development and socialization.
Defining In-Group: Meaning and Characteristics
An in-group is a social group with which an individual identifies strongly, characterized by shared values, norms, and a sense of belonging. Members of an in-group often exhibit loyalty, trust, and favoritism toward each other, distinguishing themselves from out-groups. This group dynamic influences social identity and reinforces cohesion through common interests and emotional connections.
Primary Group: Definition and Key Features
Primary groups are small social groups characterized by close, personal, and enduring relationships, often including family members and close friends. These groups provide emotional support, social identity, and a sense of belonging, playing a crucial role in the development of an individual's social self. Key features of primary groups include face-to-face interaction, strong emotional ties, and long-lasting bonds that significantly influence socialization and personal growth.
Core Differences Between In-Group and Primary Group
In-groups consist of individuals who share a strong sense of identity and loyalty, often defined by social boundaries and membership criteria, while primary groups are characterized by close, personal, and enduring relationships typically found among family and close friends. The core difference lies in the nature of interaction: in-groups emphasize social identity and group cohesion, whereas primary groups focus on intimate, face-to-face connections and emotional support. In-groups can be larger and more formal, whereas primary groups are smaller and more informal, fostering deep interpersonal bonds.
Social Functions of In-Groups
In-groups serve crucial social functions by fostering a strong sense of identity and belonging among members, which enhances social cohesion and collective solidarity. These groups establish norms and values that guide behavior, providing members with emotional support and security in social interactions. In contrast to primary groups, which emphasize intimate, long-term relationships, in-groups often focus on shared goals and social categorization that influence group dynamics and social influence.
The Role of Primary Groups in Socialization
Primary groups play a crucial role in socialization by providing individuals with emotional support, language development, and the internalization of cultural norms. Unlike in-groups that emphasize group identity and competition, primary groups offer close, enduring relationships essential for shaping self-concept and moral values. These intimate interactions foster trust, cooperation, and the foundational skills necessary for participation in broader society.
Emotional Bonds: In-Group vs Primary Group
In-group emotional bonds are often characterized by shared identities and mutual support based on common interests or social categories, creating a sense of belonging and loyalty. Primary groups, such as family and close friends, exhibit stronger emotional ties marked by intimate, face-to-face interactions and long-lasting relationships that provide significant emotional support. The intensity of emotional bonds in primary groups typically surpasses those in in-groups due to the deeper personal connections and enduring nature of these relationships.
Examples of In-Groups and Primary Groups
In-groups include social circles like sports teams, political parties, and ethnic or religious communities that create a strong sense of identity and belonging. Primary groups consist of family members, close friends, and intimate peer groups where emotional support and long-term relationships are central. Examples of primary groups often emphasize deep personal connections, while in-groups highlight shared interests or common goals within larger social structures.
Influence on Individual Identity and Behavior
In-group membership significantly shapes individual identity by fostering a sense of belonging and shared values, which influence perceptions and behaviors aligned with group norms. Primary groups, characterized by close, personal relationships, have a profound impact on behavior through emotional support and direct social interactions that reinforce identity. Both group types shape individual actions, but primary groups exert more intimate and consistent influence on daily decision-making and self-concept.
Significance in Modern Society
In-group and primary group dynamics significantly impact social identity and cohesion in modern society, shaping individuals' self-concept and social interactions. In-groups foster a sense of belonging and influence social norms, while primary groups, such as family and close friends, provide emotional support and stability essential for mental health. Understanding these groupings helps address issues like social exclusion, prejudice, and enhances community building in diverse urban environments.
In-group Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com