Globalism promotes interconnected economies, cultures, and political systems, fostering cooperation and exchange on a worldwide scale. It drives innovation, trade, and cultural understanding by breaking down national barriers and encouraging global collaboration. Discover how globalism impacts your life and shapes the future by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
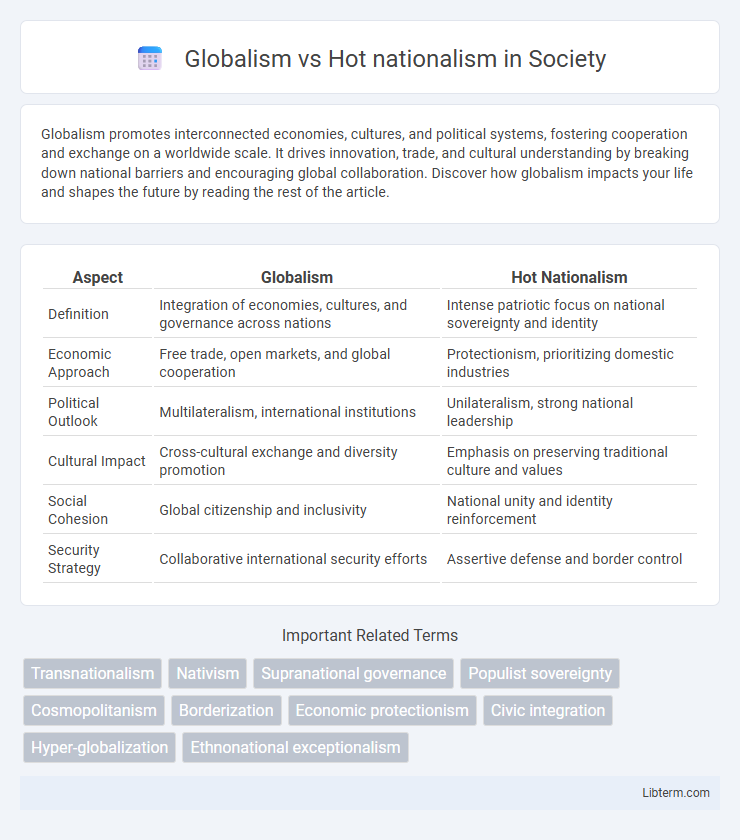
| Aspect | Globalism | Hot Nationalism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integration of economies, cultures, and governance across nations | Intense patriotic focus on national sovereignty and identity |
| Economic Approach | Free trade, open markets, and global cooperation | Protectionism, prioritizing domestic industries |
| Political Outlook | Multilateralism, international institutions | Unilateralism, strong national leadership |
| Cultural Impact | Cross-cultural exchange and diversity promotion | Emphasis on preserving traditional culture and values |
| Social Cohesion | Global citizenship and inclusivity | National unity and identity reinforcement |
| Security Strategy | Collaborative international security efforts | Assertive defense and border control |
Defining Globalism and Hot Nationalism
Globalism emphasizes interconnected economies, cultural exchange, and cooperation among nations to address global challenges such as climate change, trade, and security. Hot nationalism centers on strong national identity, sovereignty, and prioritizing domestic interests over global agreements, often accompanied by cultural preservation and resistance to immigration. The tension between these ideologies shapes contemporary political discourse and policy-making on issues like trade tariffs, border control, and international alliances.
Historical Roots and Evolution
Globalism traces its historical roots to the Age of Exploration in the 15th century, when increased trade and cultural exchanges began connecting continents and fostering interdependence among nations. Hot nationalism emerged in the 19th and 20th centuries as a reaction to imperialism and colonialism, emphasizing intense loyalty to cultural identity, sovereignty, and self-determination. The evolution of globalism promotes interconnected economies and supranational institutions, while hot nationalism resurfaces during periods of political unrest, emphasizing protectionism and ethnonationalist policies.
Key Differences in Ideology
Globalism advocates for interconnected economies, open borders, and multilateral cooperation to address global challenges such as climate change and trade. Hot nationalism emphasizes strong national sovereignty, cultural identity, and protectionist policies to preserve a nation's interests and traditions. The ideological divide centers on global integration versus prioritizing domestic priorities and national unity.
Economic Impacts and Trade Policies
Globalism promotes economic integration through free trade agreements and multilateral institutions, enhancing market access and capital flows across nations. Hot nationalism emphasizes protectionist trade policies and tariffs to safeguard domestic industries, often leading to reduced trade volumes and higher costs for consumers. The economic impact of globalism tends to boost GDP growth and innovation through international cooperation, whereas hot nationalism can trigger trade wars and economic fragmentation.
Cultural Influences and Identity
Globalism promotes cultural exchange and hybrid identities, fostering interconnectedness and diverse cultural influences across nations. Hot nationalism emphasizes preserving unique cultural heritage and strong national identity, often resisting external influences to maintain historical traditions. The tension between these forces shapes contemporary debates on cultural sovereignty and globalization's impact on identity formation.
Political Movements and Leadership
Globalism promotes interconnected political movements emphasizing cooperation across national borders, driven by leaders advocating for international institutions like the United Nations and trade alliances such as the European Union. Hot nationalism centers on fervent patriotic political movements that prioritize sovereignty, cultural identity, and protectionist policies, often led by populist figures who reject globalization and favor strong state control. Leadership styles in globalism tend to be collaborative and multilateral, whereas nationalist leaders adopt assertive, sometimes exclusionary rhetoric to mobilize domestic support.
Social Media’s Role in Shaping Narratives
Social media platforms amplify globalism by fostering cross-cultural exchanges and real-time information sharing, creating interconnected digital communities that transcend national borders. Conversely, these platforms also serve as breeding grounds for hot nationalism, where algorithm-driven echo chambers intensify tribal identities, misinformation, and polarized narratives. The dual role of social media profoundly influences public opinion and political mobilization by shaping how globalism and nationalism are perceived and enacted worldwide.
Case Studies: Globalism vs Hot Nationalism in Action
Case studies like the European Union versus Hungary showcase globalism's emphasis on transnational cooperation and economic integration clashing with hot nationalism's prioritization of sovereignty and cultural identity. Brexit epitomizes hot nationalism, where the UK sought to reclaim national control over immigration and trade policies, directly opposing the EU's globalist agenda. These examples highlight tensions between globalist frameworks promoting interconnectedness and nationalist movements demanding greater autonomy and preservation of national distinctiveness.
Challenges and Criticisms of Both Approaches
Globalism faces challenges such as undermining national sovereignty, economic inequality, and cultural homogenization, raising concerns about loss of local identity and democratic accountability. Hot nationalism often triggers xenophobia, isolationism, and conflicts, undermining international cooperation and global stability. Both approaches struggle to balance inclusive global integration with protecting national interests and social cohesion.
Future Prospects and Possible Resolutions
The future of globalism versus hot nationalism hinges on balancing economic integration with sovereign identity, as rising geopolitical tensions and economic disparities challenge multilateral cooperation. Innovations in technology and diplomacy offer pathways to reconcile global interconnectedness with nationalist aspirations by promoting inclusive policies and equitable resource distribution. Sustainable resolutions will require adaptive governance models that address both global challenges like climate change and local demands for cultural preservation and autonomy.
Globalism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com