Social cohesion strengthens communities by fostering trust, shared values, and active participation among members. High social cohesion reduces crime rates, boosts economic development, and enhances overall well-being. Discover how your community can benefit from improved social cohesion by reading the rest of the article.
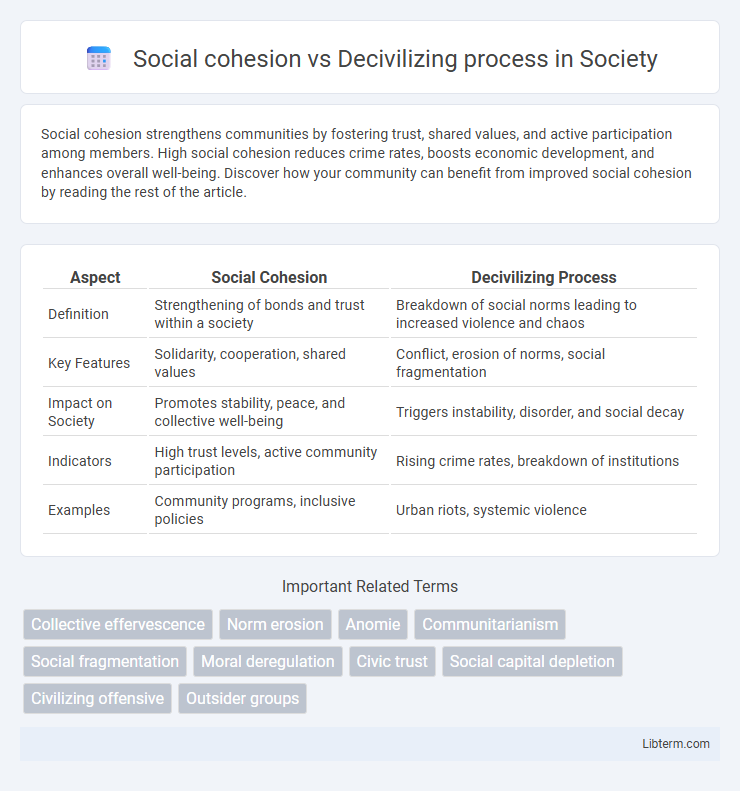
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Social Cohesion | Decivilizing Process |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Strengthening of bonds and trust within a society | Breakdown of social norms leading to increased violence and chaos |
| Key Features | Solidarity, cooperation, shared values | Conflict, erosion of norms, social fragmentation |
| Impact on Society | Promotes stability, peace, and collective well-being | Triggers instability, disorder, and social decay |
| Indicators | High trust levels, active community participation | Rising crime rates, breakdown of institutions |
| Examples | Community programs, inclusive policies | Urban riots, systemic violence |
Understanding Social Cohesion
Social cohesion refers to the strength of relationships and the sense of solidarity among members of a community, which fosters cooperation, trust, and shared values. Understanding social cohesion involves analyzing factors such as social inclusion, mutual respect, and the integration of diverse groups to maintain societal stability. In contrast, the decivilizing process highlights the breakdown of these bonds through increased violence, social fragmentation, and the erosion of norms that undermine collective well-being.
The Concept of the Decivilizing Process
The concept of the decivilizing process, developed by Norbert Elias, explores the erosion of social norms and self-restraint that leads to increased violence and social fragmentation, contrasting sharply with social cohesion, which emphasizes integration, mutual trust, and collective well-being. Decivilizing processes often arise from weakened institutions, rising inequality, and cultural conflicts that undermine shared values and disrupt societal order. Understanding this concept is crucial for addressing challenges to social cohesion in modern, complex societies facing polarization and resource competition.
Historical Perspectives on Social Cohesion
Historical perspectives on social cohesion reveal fluctuating patterns driven by political, economic, and cultural shifts that either strengthen or undermine societal bonds. Decivilizing processes, as theorized by Norbert Elias, describe periods marked by increased violence, social fragmentation, and weakening norms, which historically coincide with times of crisis such as wars, revolutions, or economic depressions. Examining these dynamics offers insight into how societies transition between stability and disorder, highlighting the fragile balance underpinning collective identity and cooperation.
Factors Promoting Social Cohesion
Factors promoting social cohesion include shared values, trust, inclusive institutions, and effective communication within communities. Economic equality, social inclusion, and participatory governance enhance collective identity and cooperation, counteracting the fragmentation seen in decivilizing processes. Strengthening social networks and fostering mutual respect contribute significantly to resilient and harmonious societies.
Drivers Behind the Decivilizing Process
The decivilizing process is driven by factors such as social inequality, political instability, and erosion of shared values, which undermine social cohesion. Economic disparities and cultural polarization intensify mistrust among communities, leading to weakened social bonds and increasing conflict. Breakdown in institutional trust and failures in governance exacerbate these drivers, accelerating societal fragmentation.
Social Cohesion vs. Social Fragmentation
Social cohesion strengthens community bonds through shared values, trust, and cooperation, fostering social stability and collective well-being. In contrast, social fragmentation, often driven by decivilizing processes such as rising inequality, polarization, and eroding institutions, leads to weakened social bonds and increased conflict. Understanding the dynamics between social cohesion and fragmentation is crucial for addressing societal challenges and promoting inclusive development.
Impacts of Decivilizing Trends on Communities
Decivilizing processes erode social cohesion by fostering mistrust, violence, and fragmentation within communities. These trends increase social polarization, weaken community bonds, and diminish collective action needed for effective governance and mutual support. The resulting instability impairs economic development, mental health, and overall quality of life for residents.
Strategies to Strengthen Social Cohesion
Strategies to strengthen social cohesion center on fostering inclusive community engagement, promoting equitable access to resources, and enhancing trust through transparent governance. Initiatives such as participatory decision-making, conflict resolution programs, and educational campaigns addressing diversity reduce fragmentation and counteract decivilizing processes. Emphasizing shared values and social solidarity helps to rebuild social fabric and prevent societal breakdown.
Case Studies: Cohesion and Decivilization in Practice
Case studies on social cohesion often highlight successful community-building initiatives that foster trust, cooperation, and shared norms, while decivilizing processes reveal the breakdown of these elements through increased conflict, social fragmentation, and erosion of institutional norms. For example, urban neighborhoods experiencing gentrification may demonstrate shifting social cohesion as economic disparities strain traditional community bonds, whereas conflict zones illustrate decivilized environments where violence and breakdown of social order prevail. Research on these cases emphasizes the importance of strong social institutions and inclusive policies to maintain cohesion and prevent decivilization dynamics.
Future Challenges and Opportunities for Social Integration
Future challenges for social cohesion include rising polarization and inequality, which may intensify decivilizing processes characterized by erosion of trust and social norms. Opportunities for social integration lie in leveraging digital platforms to foster inclusive dialogue and implementing policies that promote equity and community engagement. Strengthening education and civic participation can counteract fragmentation and build resilience against social decay.
Social cohesion Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com