Personal autonomy empowers individuals to make decisions aligned with their values and beliefs, fostering a sense of control and self-determination. It is essential for mental well-being and personal growth, enabling you to navigate life's challenges confidently. Explore the full article to understand how to cultivate and maintain your autonomy effectively.
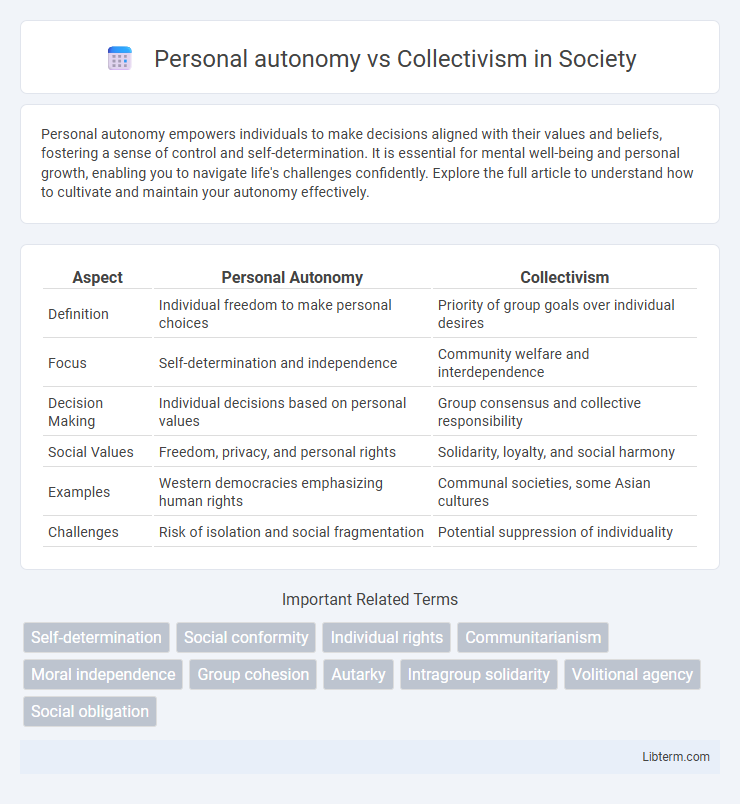
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Personal Autonomy | Collectivism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Individual freedom to make personal choices | Priority of group goals over individual desires |
| Focus | Self-determination and independence | Community welfare and interdependence |
| Decision Making | Individual decisions based on personal values | Group consensus and collective responsibility |
| Social Values | Freedom, privacy, and personal rights | Solidarity, loyalty, and social harmony |
| Examples | Western democracies emphasizing human rights | Communal societies, some Asian cultures |
| Challenges | Risk of isolation and social fragmentation | Potential suppression of individuality |
Defining Personal Autonomy and Collectivism
Personal autonomy emphasizes individual freedom, self-governance, and the ability to make independent decisions without external coercion. Collectivism prioritizes the group's needs, social cohesion, and interdependence, often valuing collective goals over individual desires. Defining personal autonomy involves rights, self-determination, and individual agency, while collectivism centers on communal responsibility, shared values, and social harmony.
Historical Evolution of Autonomy and Collectivist Ideals
The historical evolution of personal autonomy and collectivist ideals reflects shifting societal values from ancient communal tribes to modern individualistic democracies. Enlightenment thinkers emphasized individual rights and self-governance, fueling autonomy's rise against traditional collective hierarchies. Industrialization and socialism later reinforced collectivist ideals, advocating for social welfare and shared responsibility within increasingly complex societies.
Cultural Perspectives on Individualism vs Collectivism
Cultural perspectives on individualism versus collectivism highlight how societies prioritize personal autonomy or group loyalty. In individualistic cultures, such as the United States and Western Europe, personal goals and independence are emphasized, promoting self-expression and individual rights. Conversely, collectivist cultures like Japan and India value social harmony and community interdependence, encouraging individuals to prioritize the needs of the group over personal desires.
Psychological Foundations of Personal Freedom
Personal autonomy is rooted in the psychological foundation of self-determination theory, emphasizing intrinsic motivation and the need for competence, relatedness, and autonomy to achieve personal freedom. Collectivism prioritizes group goals and interconnectedness, influencing individuals to align their behaviors with community norms and shared values. The balance between personal autonomy and collectivism shapes psychological well-being by mediating the tension between individual desires and social obligations.
Social Benefits of Collective Approaches
Collectivism emphasizes social benefits by promoting shared resources, community support, and mutual aid, leading to stronger social cohesion and reduced inequality. Collective approaches enable effective public goods provision, such as healthcare and education, which are often underfunded or inaccessible in highly individualistic societies. These systems foster social trust and collaboration, enhancing overall well-being and resilience in times of crisis.
Autonomy in Decision-Making: Pros and Cons
Personal autonomy in decision-making empowers individuals to make choices based on their values and preferences, fostering creativity and personal growth. However, excessive autonomy can lead to fragmented social cohesion and may overlook community welfare or collective responsibilities. Balancing autonomy with collective interests ensures that personal freedoms do not undermine societal harmony or shared goals.
Collectivism in Modern Communities and Institutions
Collectivism in modern communities and institutions prioritizes group goals, social cohesion, and shared responsibilities over individual desires, promoting collaboration and mutual support across diverse populations. Institutions such as cooperatives, social movements, and community organizations embody collectivist principles by fostering inclusive decision-making processes and equitable resource distribution. This framework enhances societal resilience and addresses collective challenges by emphasizing interdependence and communal well-being.
Balancing Individual Rights with Group Responsibilities
Balancing individual rights with group responsibilities requires recognizing personal autonomy while fostering social cohesion through shared values and mutual support. Emphasizing personal freedoms empowers decision-making and self-expression, whereas collectivism promotes cooperative efforts vital for community well-being and stability. Effective governance and social policies integrate respect for individual liberties with collective goals, ensuring equitable participation and accountability within diverse societies.
Real-World Conflicts: Case Studies of Autonomy vs Collectivism
Real-world conflicts between personal autonomy and collectivism are evident in case studies like the COVID-19 pandemic, where individual freedoms clashed with public health mandates requiring collective action. Another example is the debate over indigenous land rights, highlighting tensions between community governance and national or corporate interests prioritizing development. These conflicts underscore the challenges in balancing individual rights with collective responsibilities in policymaking and social governance.
Navigating the Future: Harmonizing Autonomy and Collectivism
Navigating the future demands a balance between personal autonomy and collectivism, where individual freedoms coexist with communal responsibilities to foster societal progress. Emphasizing ethical governance and inclusive decision-making can harmonize diverse interests, enabling sustainable development and social cohesion. Technological advancements and global interconnectedness further challenge societies to integrate autonomy with collective well-being effectively.
Personal autonomy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com