Temporary status grants you limited permission to stay in a country for a specific period, often tied to work, study, or humanitarian grounds. Understanding the rights and restrictions associated with your temporary status is crucial to ensure compliance with local laws and avoid potential penalties. Discover essential insights in the rest of the article to navigate your temporary status confidently.
Table of Comparison
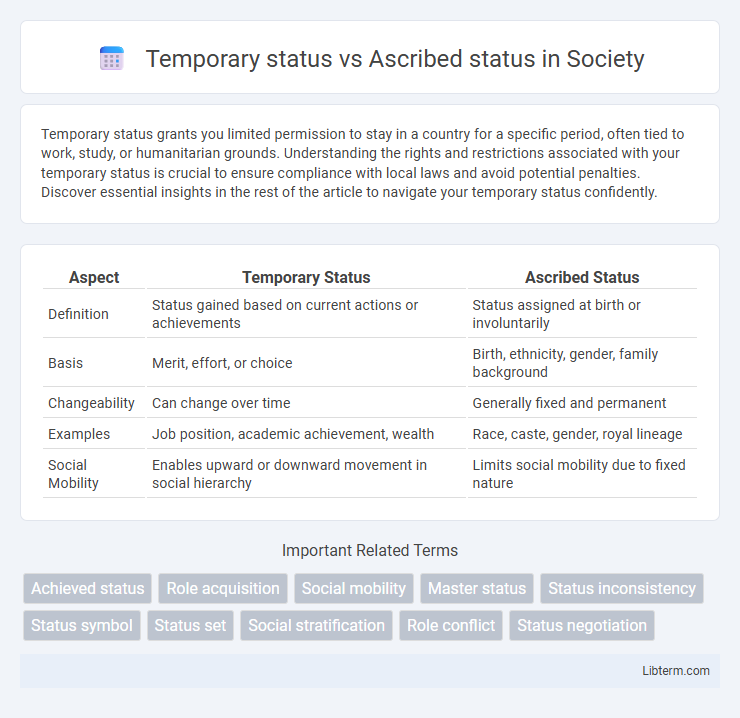
| Aspect | Temporary Status | Ascribed Status |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Status gained based on current actions or achievements | Status assigned at birth or involuntarily |
| Basis | Merit, effort, or choice | Birth, ethnicity, gender, family background |
| Changeability | Can change over time | Generally fixed and permanent |
| Examples | Job position, academic achievement, wealth | Race, caste, gender, royal lineage |
| Social Mobility | Enables upward or downward movement in social hierarchy | Limits social mobility due to fixed nature |
Definition of Temporary Status
Temporary status refers to a social position assigned to an individual for a limited period, often based on specific roles or situations, such as student, intern, or seasonal worker. This status contrasts with ascribed status, which is assigned at birth or involuntarily based on inherent characteristics like ethnicity, gender, or family background. Temporary status is dynamic and subject to change, reflecting an individual's current social function rather than fixed identity traits.
Definition of Ascribed Status
Ascribed status refers to the social position assigned to an individual at birth or assumed involuntarily later in life, based on attributes such as race, ethnicity, gender, or family heritage. This status contrasts with temporary status, which is a social position held for a limited period or under specific circumstances, often based on achievements or roles like student or employee. Understanding ascribed status is essential in sociology because it influences opportunities, social interactions, and identity formation independent of personal effort.
Key Differences Between Temporary and Ascribed Status
Temporary status refers to an individual's social position based on roles or circumstances that change over time, such as being a student or employee. Ascribed status is assigned at birth or involuntarily and remains stable, exemplified by ethnicity, gender, or family background. Key differences include the flexibility of temporary status versus the permanence of ascribed status, and the influence of personal choice in temporary roles compared to the predetermined nature of ascribed characteristics.
Examples of Temporary Status in Society
Temporary status in society refers to roles or positions held for a limited period, such as a student, intern, or seasonal worker, which depend on situational contexts rather than inherent traits. Examples include a college student engaged in a four-year educational program, a temporary employee hired for a summer project, or a guest attending a cultural festival. These statuses contrast with ascribed status, which is assigned at birth and remains relatively fixed, like ethnicity or royalty.
Examples of Ascribed Status in Society
Ascribed status refers to social positions assigned at birth or involuntarily later in life, such as race, gender, ethnicity, or family heritage. Examples include a royal title inherited through lineage, caste membership in societies like India, or gender roles traditionally prescribed at birth. These statuses often influence an individual's opportunities and social interactions independent of personal achievements or choices.
Factors Influencing Temporary Status
Temporary status is influenced by situational factors such as job assignments, educational enrollment, or travel visas that grant short-term privileges or roles. These positions are often shaped by external conditions like organizational needs, legal frameworks, or specific time-bound projects. Unlike ascribed status, which is determined by inherent traits such as ethnicity, gender, or family heritage, temporary status fluctuates based on changing circumstances and decisions.
Factors Influencing Ascribed Status
Ascribed status is determined by factors beyond individual control such as age, gender, ethnicity, and family heritage, which are assigned at birth and remain relatively fixed throughout life. In contrast, temporary status results from roles or positions achieved or assumed for a limited duration, often influenced by situational changes or personal actions. Understanding how social structures and cultural norms reinforce ascribed status illuminates persistent inequalities in societies based on inherited characteristics.
Social Implications of Temporary Status
Temporary status often results in limited social mobility and access to resources, reinforcing socio-economic disparities and social exclusion. Individuals with temporary status may face stigma, reduced legal protections, and restricted opportunities for community participation, affecting their integration and well-being. The social implications include heightened vulnerability to exploitation, marginalization, and challenges in forming stable social identities compared to ascribed status, which is typically fixed and linked to inherited characteristics.
Social Implications of Ascribed Status
Ascribed status, assigned at birth based on traits such as race, gender, and family background, significantly shapes social identities and access to resources, often perpetuating systemic inequalities. Unlike temporary status, which can change through personal effort or circumstance, ascribed status rigidly influences social roles, expectations, and power dynamics within communities. The social implications include reinforced social stratification and limited social mobility, affecting opportunities in education, employment, and political participation.
Impact on Identity and Social Mobility
Temporary status, often acquired through achievements or roles, allows individuals to modify their social identity and enhances social mobility by providing opportunities for upward movement. In contrast, ascribed status is assigned at birth based on characteristics like race, gender, or family background, deeply influencing identity formation and often restricting social mobility due to entrenched societal norms. The rigidity of ascribed status limits personal agency, whereas the fluidity of temporary status enables dynamic identity shifts and greater access to diverse social positions.
Temporary status Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com