Race shapes cultural identities and influences social dynamics across communities worldwide. Understanding the historical context and ongoing challenges related to race is essential for fostering empathy and promoting equality. Explore the full article to deepen your insight into how race impacts society and your interactions.
Table of Comparison
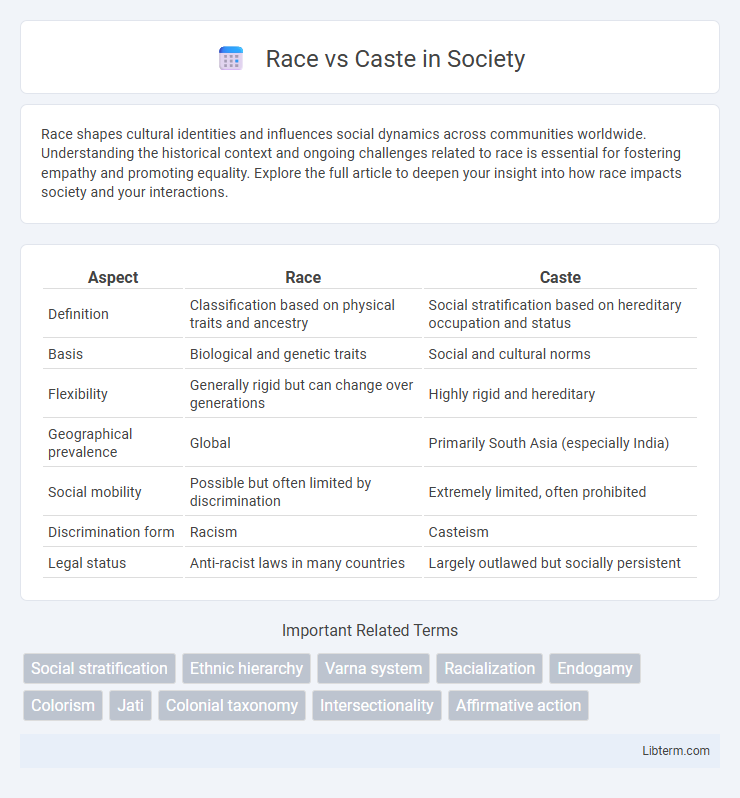
| Aspect | Race | Caste |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Classification based on physical traits and ancestry | Social stratification based on hereditary occupation and status |
| Basis | Biological and genetic traits | Social and cultural norms |
| Flexibility | Generally rigid but can change over generations | Highly rigid and hereditary |
| Geographical prevalence | Global | Primarily South Asia (especially India) |
| Social mobility | Possible but often limited by discrimination | Extremely limited, often prohibited |
| Discrimination form | Racism | Casteism |
| Legal status | Anti-racist laws in many countries | Largely outlawed but socially persistent |
Understanding Race and Caste: Foundational Definitions
Race is a socially constructed classification based primarily on physical characteristics such as skin color, often used to categorize and differentiate groups of people. Caste refers to a rigid social stratification system, particularly in South Asia, defined by hereditary occupation and social status rather than physical traits. Understanding race involves examining historical and political contexts shaping identity, while caste requires analysis of entrenched social hierarchy and religious codification.
Historical Origins of Race and Caste Systems
Race systems originated primarily from European colonial expansion during the 15th century, using physical characteristics to justify social hierarchies and imperial domination. Caste systems, deeply rooted in ancient South Asian societies such as the Indian subcontinent, emerged from religious texts like the Manusmriti, establishing hereditary social orders based on occupation and ritual purity. Both systems institutionalized inequality, but race is largely based on perceived biological differences while caste revolves around socio-religious status and endogamy.
Key Differences Between Race and Caste
Race is primarily a social construct based on physical characteristics such as skin color and facial features, while caste is a hereditary social stratification system rooted in occupation and social status. Race categories are often fluid and influenced by sociology and genetics, whereas caste systems are rigid, traditionally linked to birth and religious customs, especially prominent in South Asia. Unlike race, caste determines social mobility and access to resources within a community, often enforced by cultural and legal practices.
Social Hierarchies: How Race and Caste Shape Societies
Race and caste both establish rigid social hierarchies that dictate individuals' access to resources, status, and power across societies. Racial hierarchies, often based on physical characteristics like skin color, underpin systemic discrimination and segregation in many countries, reinforcing economic and political inequalities. Caste systems, notably in South Asia, assign social roles and privileges based on hereditary status, perpetuating social exclusion and intergenerational disparities within communities.
Mechanisms of Discrimination in Race and Caste
Discrimination in race operates primarily through systemic racism, including segregation, unequal access to education, and institutional biases embedded in law enforcement and employment practices. In contrast, caste discrimination is enforced through hereditary social stratification, rigid endogamy, and denial of resources based on birth within specific hierarchical groups. Both mechanisms perpetuate exclusion and socioeconomic disparities but differ in their historical, cultural, and legal foundations.
Race and Caste in the Modern World
Race and caste both shape social identities but differ fundamentally: race is often linked to physical traits and perceived biological differences, whereas caste is a rigid social hierarchy typically based on birth and occupation. In the modern world, race remains a critical factor in systemic inequality, influencing access to resources and social mobility, while caste continues to impact social status, especially in regions like India, despite legal measures against discrimination. Understanding the distinct yet intersecting roles of race and caste is essential for addressing global social justice challenges effectively.
Intersectionality: When Race and Caste Overlap
Race and caste systems intersect to compound social inequalities, with marginalized groups often experiencing layered discrimination based on both racial and caste identities. Intersectionality highlights how individuals at this overlap face unique barriers in access to education, employment, and social mobility. Understanding this intersection is crucial for creating comprehensive social justice policies that address the multifaceted nature of systemic oppression.
Policies and Movements Addressing Race and Caste Inequality
Policies addressing race and caste inequality include affirmative action and reservation systems implemented in countries like the United States and India to promote educational and employment opportunities for marginalized groups. Movements such as the Civil Rights Movement in the US and the Dalit Rights Movement in India have played pivotal roles in challenging systemic discrimination and advocating for social justice reforms. Legal frameworks like the Civil Rights Act and India's Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes (Prevention of Atrocities) Act are instrumental in combating racial and caste-based discrimination.
Global Perspectives: Race and Caste Across Cultures
Race and caste systems manifest differently across global cultures, reflecting distinct social hierarchies and historical contexts. In South Asia, caste operates as a rigid hereditary system defining social status and occupation, while in many Western societies, race often shapes identity and experiences through constructed racial categories linked to ancestry and physical traits. Comparative studies reveal that both frameworks perpetuate inequality, yet their cultural logics, mechanisms of discrimination, and socio-political implications vary significantly worldwide.
The Future of Social Stratification: Rethinking Race and Caste
The future of social stratification demands a critical reevaluation of race and caste as interconnected systems shaping inequality. Emerging research emphasizes the fluidity of social identities and the need to dismantle structural barriers rooted in both racial discrimination and caste hierarchies. Policy development must prioritize intersectional approaches to achieve equitable social mobility and inclusive governance.
Race Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com