Technocracy emphasizes governance by experts and technical professionals, prioritizing data-driven decision-making and scientific methods over political influence. This approach can enhance efficiency and innovation in public administration but may face challenges related to democratic representation and public accountability. Explore the article to understand how technocracy impacts modern governance and what it means for your role in a technology-driven society.
Table of Comparison
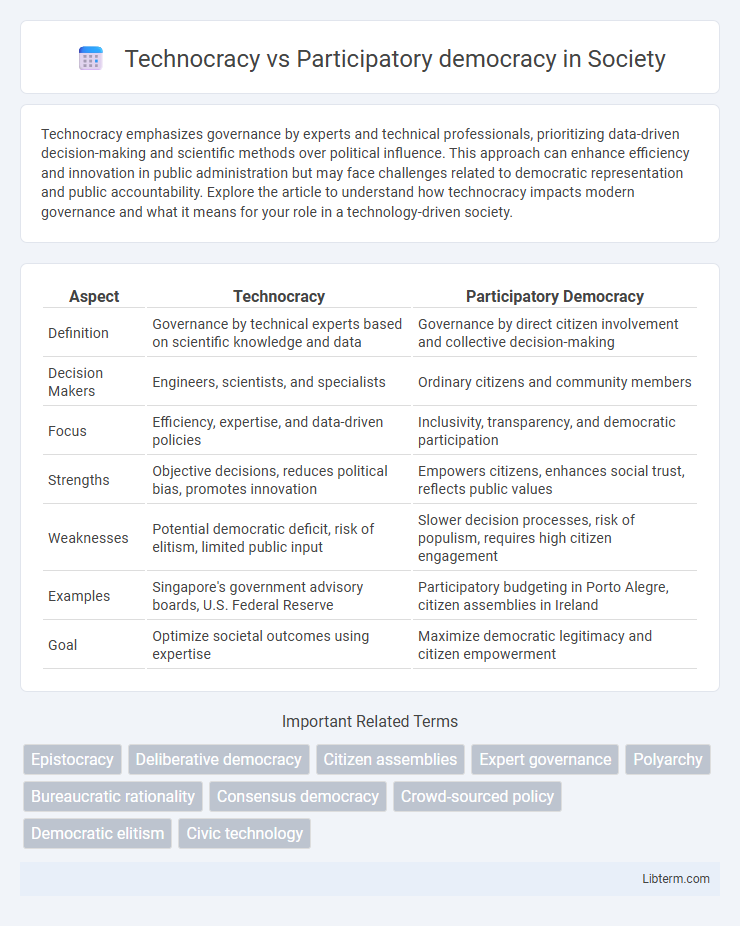
| Aspect | Technocracy | Participatory Democracy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Governance by technical experts based on scientific knowledge and data | Governance by direct citizen involvement and collective decision-making |
| Decision Makers | Engineers, scientists, and specialists | Ordinary citizens and community members |
| Focus | Efficiency, expertise, and data-driven policies | Inclusivity, transparency, and democratic participation |
| Strengths | Objective decisions, reduces political bias, promotes innovation | Empowers citizens, enhances social trust, reflects public values |
| Weaknesses | Potential democratic deficit, risk of elitism, limited public input | Slower decision processes, risk of populism, requires high citizen engagement |
| Examples | Singapore's government advisory boards, U.S. Federal Reserve | Participatory budgeting in Porto Alegre, citizen assemblies in Ireland |
| Goal | Optimize societal outcomes using expertise | Maximize democratic legitimacy and citizen empowerment |
Understanding Technocracy: Definition and Principles
Technocracy is a system of governance where decision-making authority is vested in experts and technical specialists based on knowledge and efficiency rather than elected representatives. Its core principles emphasize meritocracy, scientific management, and the prioritization of data-driven policies to optimize social and economic outcomes. Unlike participatory democracy, which values broad citizen involvement and direct input, technocracy centers on expertise and rational problem-solving to guide public administration.
What is Participatory Democracy? Core Concepts
Participatory democracy emphasizes direct involvement of citizens in decision-making processes, ensuring that people have a meaningful voice beyond just voting in elections. Core concepts include empowerment, transparency, and grassroots engagement, fostering collective deliberation and shared responsibility. This model contrasts with technocracy, where experts and specialists primarily influence policy based on technical knowledge rather than popular input.
Historical Evolution of Technocracy
The historical evolution of technocracy traces back to the early 20th century, with roots in the Industrial Revolution and the Progressive Era, emphasizing governance by experts and engineers to optimize efficiency. Prominent during the 1930s, technocracy gained traction amid economic crises, proposing scientific management and decision-making based on technical expertise rather than political lobbying. This model contrasted with participatory democracy, which evolved through grassroots movements and expanded suffrage, advocating for broad citizen engagement and decentralized political power over time.
The Rise and Impact of Participatory Democracy
Participatory democracy has risen as a powerful alternative to technocracy, emphasizing direct citizen involvement in decision-making processes rather than relying solely on experts and bureaucrats. This model fosters greater transparency, accountability, and inclusivity, enabling communities to influence policies that affect their daily lives. The impact of participatory democracy is evident in enhanced civic engagement, improved governance outcomes, and strengthened social cohesion.
Decision-Making: Experts vs. Citizens
Technocracy centers decision-making in the hands of experts and specialists who apply technical knowledge and data-driven analysis to address complex societal issues. Participatory democracy emphasizes the direct involvement of citizens in decision-making processes, fostering inclusive dialogue and collective problem-solving. The contrast lies in technocracy's reliance on specialized expertise versus participatory democracy's emphasis on broad citizen engagement for legitimacy and responsiveness.
Efficiency and Accountability in Governance
Technocracy prioritizes efficiency by entrusting decision-making to experts with specialized knowledge, enabling swift implementation of policies based on data-driven analysis. In contrast, participatory democracy emphasizes accountability by involving citizens directly in governance, ensuring that diverse perspectives shape policies and leaders remain answerable to the public. Balancing technocratic efficiency with participatory accountability can optimize governance outcomes by integrating expert insights and citizen legitimacy.
Inclusivity and Representation in Both Models
Technocracy emphasizes governance by experts and specialists, which can limit inclusivity by prioritizing technical knowledge over diverse societal perspectives. Participatory democracy prioritizes broad citizen involvement, ensuring higher representation by actively including various social groups in decision-making processes. Balancing expert input with widespread public engagement enhances legitimacy and responsiveness in governance models.
Case Studies: Real-World Applications
Technocracy in Singapore demonstrates efficient governance by leveraging expert-driven policies to achieve rapid economic growth and urban development, while participatory democracy in Switzerland showcases direct citizen involvement through frequent referendums that influence legislation and public decisions. In China, technocratic leadership under the Communist Party has enabled large-scale infrastructure projects and economic reforms, contrasting with participatory practices in Scandinavian countries like Denmark, where citizens actively shape social policies via local councils and public consultations. These case studies highlight how technocracy prioritizes expertise and centralized decision-making, whereas participatory democracy emphasizes citizen engagement and decentralized governance for policy legitimacy.
Strengths and Weaknesses Compared
Technocracy offers decision-making based on expertise and data-driven policies, which can enhance efficiency and reduce populist influence but may suffer from a lack of public accountability and democratic legitimacy. Participatory democracy encourages inclusive citizen involvement and diverse perspectives, promoting transparency and social equity, yet it risks slower decision processes and potential dominance by vocal minorities. Balancing technocratic efficiency with participatory inclusiveness remains a critical challenge for effective governance systems.
Future Prospects: Hybrid Approaches and Innovations
Hybrid governance models combining technocracy and participatory democracy are gaining traction as future-focused solutions to complex societal challenges. Integrating data-driven decision-making with citizen engagement platforms enhances policy effectiveness and democratic legitimacy. Innovations such as AI-assisted deliberation tools and blockchain-based voting systems promise increased transparency, efficiency, and inclusivity in governance structures.
Technocracy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com