Community-based care focuses on delivering healthcare services directly within local settings, promoting accessibility and personalized support. Emphasizing collaboration among healthcare providers, patients, and community organizations enhances overall well-being and resource efficiency. Discover how your community can benefit from these innovative care models in the following article.
Table of Comparison
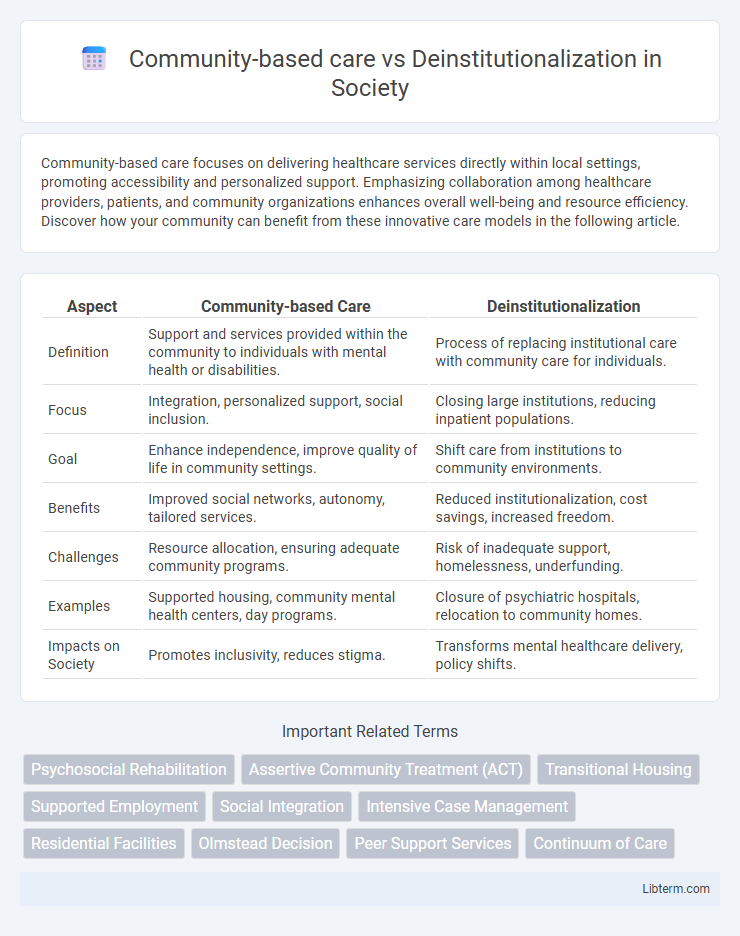
| Aspect | Community-based Care | Deinstitutionalization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Support and services provided within the community to individuals with mental health or disabilities. | Process of replacing institutional care with community care for individuals. |
| Focus | Integration, personalized support, social inclusion. | Closing large institutions, reducing inpatient populations. |
| Goal | Enhance independence, improve quality of life in community settings. | Shift care from institutions to community environments. |
| Benefits | Improved social networks, autonomy, tailored services. | Reduced institutionalization, cost savings, increased freedom. |
| Challenges | Resource allocation, ensuring adequate community programs. | Risk of inadequate support, homelessness, underfunding. |
| Examples | Supported housing, community mental health centers, day programs. | Closure of psychiatric hospitals, relocation to community homes. |
| Impacts on Society | Promotes inclusivity, reduces stigma. | Transforms mental healthcare delivery, policy shifts. |
Understanding Community-Based Care
Community-based care emphasizes providing healthcare and social support services within local communities, promoting accessibility, personalized treatment, and social inclusion for individuals with mental health or developmental challenges. This approach integrates multidisciplinary teams, such as psychologists, social workers, and medical professionals, to deliver tailored care plans that address patients' unique needs outside of institutional settings. By fostering independence and community integration, community-based care aims to improve quality of life and reduce hospital readmissions compared to traditional institutional care models.
Defining Deinstitutionalization
Deinstitutionalization refers to the systematic process of reducing reliance on large psychiatric hospitals by discharging patients into community-based settings. This movement emphasizes integrating individuals with mental health challenges into society, promoting autonomy and access to local support services. The core goal is to replace institutional care with personalized, community-oriented treatment options that enhance quality of life and social inclusion.
Historical Context and Evolution
Deinstitutionalization began in the mid-20th century as a response to the overcrowding and often inhumane conditions of large psychiatric hospitals, promoting the closure of institutions and transition of patients to community-based care settings. Community-based care evolved to provide more personalized support integrating individuals with mental illnesses or disabilities into society, emphasizing rehabilitation, social inclusion, and access to local resources. Over time, these approaches have shifted mental health treatment paradigms from isolation in institutions to a focus on empowerment and outpatient services within community environments.
Key Principles of Community-Based Care
Community-based care prioritizes personalized support within familiar environments, emphasizing accessibility, integration, and empowerment for individuals with mental health or developmental challenges. Key principles include collaboration among multidisciplinary teams, respect for cultural diversity, and promoting independence through tailored interventions that enhance quality of life. This approach contrasts with deinstitutionalization by focusing on sustained community integration rather than merely relocating individuals from institutional settings.
Goals and Motivations of Deinstitutionalization
Deinstitutionalization aims to transition individuals with mental health conditions from large, isolated psychiatric hospitals to community-based care settings to promote integration, autonomy, and improved quality of life. The primary goals include reducing social stigma, enabling access to personalized support, and fostering independent living within society. Motivations behind this shift involve addressing human rights concerns, minimizing institutional abuses, and improving outcomes through localized, holistic care models.
Impact on Patient Outcomes
Community-based care improves patient outcomes by promoting social integration, personalized treatment, and continuous support, which reduces relapse rates and hospital readmissions. Deinstitutionalization aimed to shift patients from large psychiatric hospitals to less restrictive environments but often resulted in inadequate community resources, leading to homelessness and increased emergency room visits for many patients. Effective community-based care requires coordinated services and sufficient funding to ensure sustainable improvements in mental health recovery and quality of life.
Challenges and Barriers in Community-Based Settings
Community-based care faces significant challenges including limited funding, inadequate staffing, and insufficient training for healthcare providers, which impede the delivery of comprehensive support services. Barriers such as fragmented coordination between agencies, lack of accessible facilities, and social stigma further restrict effective integration of individuals transitioning from deinstitutionalization. These issues contribute to gaps in continuity of care, posing risks to patients' mental health stability and community reintegration success.
Comparing Cost-Effectiveness
Community-based care often demonstrates greater cost-effectiveness than deinstitutionalization by reducing long-term hospitalization expenses and minimizing reliance on costly institutional infrastructure. Studies indicate that shifting resources to community mental health services leads to lower per capita costs while improving quality of life and social integration for patients. Investment in local support networks and outpatient care significantly decreases the financial burden on public health systems compared to maintaining large institutional facilities.
Policy and Advocacy Considerations
Community-based care policies emphasize localized support systems, promoting integration and autonomy for individuals with mental health conditions. Deinstitutionalization advocates prioritize the closure of large psychiatric hospitals, reallocating resources to outpatient and residential services tailored to community needs. Effective advocacy requires policies that balance funding, ensure service accessibility, and incorporate stakeholder input to sustain long-term care quality and social inclusion.
Future Directions in Mental Health Care
Future directions in mental health care emphasize integrating community-based care models that prioritize personalized support, social inclusion, and recovery-oriented services, which have shown improved outcomes compared to traditional institutional settings. Advances in telepsychiatry, peer support networks, and mobile crisis intervention teams enhance accessibility and continuity of care within community frameworks. Investment in training mental health professionals and expanding housing and employment opportunities remain critical to sustaining deinstitutionalization efforts and reducing hospital readmissions.
Community-based care Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com