Cultural acceptance fosters understanding and respect among diverse communities, promoting harmony in social and professional environments. It encourages open-mindedness, reduces stereotypes, and enhances collaboration across different cultural backgrounds. Discover how embracing cultural acceptance can enrich your life and relationships by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
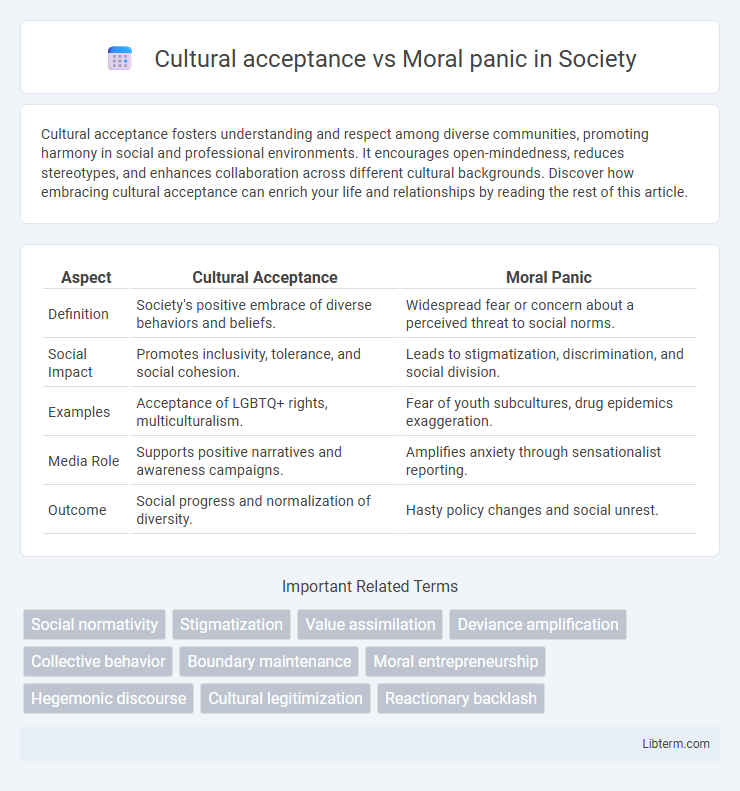
| Aspect | Cultural Acceptance | Moral Panic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Society's positive embrace of diverse behaviors and beliefs. | Widespread fear or concern about a perceived threat to social norms. |
| Social Impact | Promotes inclusivity, tolerance, and social cohesion. | Leads to stigmatization, discrimination, and social division. |
| Examples | Acceptance of LGBTQ+ rights, multiculturalism. | Fear of youth subcultures, drug epidemics exaggeration. |
| Media Role | Supports positive narratives and awareness campaigns. | Amplifies anxiety through sensationalist reporting. |
| Outcome | Social progress and normalization of diversity. | Hasty policy changes and social unrest. |
Understanding Cultural Acceptance
Cultural acceptance involves recognizing and respecting diverse cultural identities, practices, and values without prejudice or discrimination. It promotes social cohesion by encouraging open-mindedness and empathy towards different cultural expressions, fostering inclusivity in multicultural societies. Understanding cultural acceptance requires examining historical contexts, societal structures, and the impact of globalization on cultural integration and identity preservation.
Defining Moral Panic
Moral panic refers to a widespread feeling of fear and concern among a population that certain behaviors, groups, or events pose a significant threat to societal norms and values. Rooted in media amplification and social reactions, moral panic often leads to exaggerated perceptions of danger and demands for increased control or regulation. This phenomenon contrasts with cultural acceptance, which embraces diversity and change without undue fear or stigmatization.
Historical Examples of Moral Panic
Historical examples of moral panic include the Salem witch trials of 1692, where fear of witchcraft led to widespread hysteria and wrongful executions. The Red Scare in the 1950s exemplifies political paranoia about communist infiltration, resulting in blacklists and lost careers. These instances contrast sharply with cultural acceptance, demonstrating how societal fears can escalate into disproportionate reactions rather than embracing diversity or differing beliefs.
Societal Benefits of Cultural Acceptance
Cultural acceptance fosters social cohesion, enhances mutual understanding, and reduces discrimination, contributing to a more inclusive and harmonious society. Embracing diverse cultural perspectives enriches innovation, creativity, and economic growth by leveraging varied talents and experiences. Societal benefits include improved mental health outcomes and stronger community resilience, as acceptance mitigates fear-driven moral panics that often lead to social division and marginalization.
Triggers and Drivers of Moral Panic
Moral panic arises from triggers such as perceived threats to societal norms, often amplified by media sensationalism and political rhetoric, which frame certain groups or behaviors as deviant or dangerous. Drivers include social anxiety during periods of rapid change, economic instability, and identity crises, prompting collective fear and condemnation. Cultural acceptance, in contrast, is facilitated by increased exposure, education, and intercultural dialogue that challenge stereotypes and reduce exaggerated fears.
Media’s Role in Shaping Perceptions
Media plays a pivotal role in shaping public perceptions by amplifying cultural acceptance or fueling moral panic through selective framing and sensationalism. News outlets, social media platforms, and entertainment channels influence societal attitudes by highlighting specific narratives, often emphasizing fear or controversy to attract attention and engagement. This dynamic shapes collective understanding, either normalizing diverse cultural practices or triggering widespread alarm and resistance.
Cultural Change and Resistance
Cultural acceptance reflects societal adaptation to evolving norms, values, and behaviors, fostering inclusivity and diversity, while moral panic emerges from heightened fear and exaggerated reactions to perceived threats against traditional cultural frameworks. Cultural change often encounters resistance rooted in moral panic, as groups strive to preserve established social orders and identity through amplified concerns over social deviance. Understanding the dynamics between cultural acceptance and moral panic reveals the mechanisms by which societies negotiate transformation and maintain cohesion amidst shifting cultural landscapes.
Impacts of Moral Panic on Policy
Moral panic significantly influences policy by prompting lawmakers to enact restrictive regulations and punitive measures aimed at addressing perceived social threats, often leading to disproportionate responses. These policies can marginalize targeted groups, perpetuating stigma and social exclusion rather than fostering understanding or inclusion. The resulting legal frameworks may prioritize control and surveillance over cultural acceptance, undermining social cohesion and progress.
Navigating Between Fear and Tolerance
Cultural acceptance embraces diversity by fostering understanding and inclusion, while moral panic arises from exaggerated fears that threaten social cohesion. Navigating between fear and tolerance requires critical analysis of media narratives and empirical evidence to counteract misinformation and stereotypes. Building resilience through education and dialogue promotes a balanced response that respects cultural differences without succumbing to irrational fears.
Pathways to Promoting Acceptance
Pathways to promoting cultural acceptance involve education, open dialogue, and exposure to diverse perspectives, fostering empathy and reducing fear. Implementing inclusive policies and community programs helps normalize differences and counteract misinformation that fuels moral panic. Supporting grassroots initiatives and media representation further strengthens understanding and resilience against societal stigmatization.
Cultural acceptance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com