Social exclusion isolates individuals or groups from meaningful participation in economic, social, and political life, leading to adverse impacts on mental health, self-esteem, and access to opportunities. It disproportionately affects marginalized communities, creating cycles of poverty and inequality that hinder societal progress. Discover how social exclusion shapes your world and what can be done to foster inclusion by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
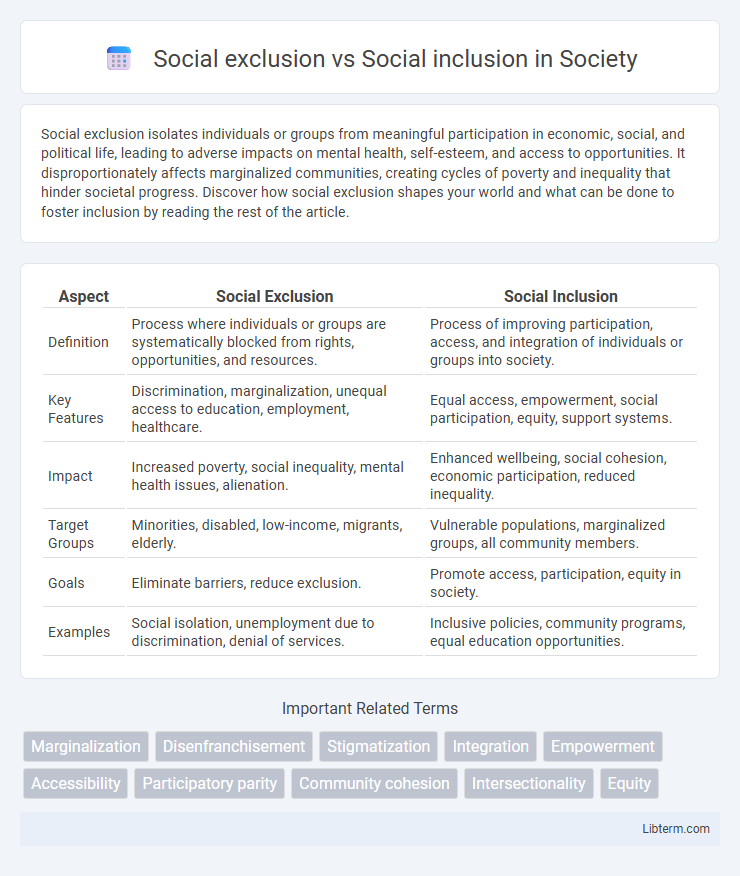
| Aspect | Social Exclusion | Social Inclusion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process where individuals or groups are systematically blocked from rights, opportunities, and resources. | Process of improving participation, access, and integration of individuals or groups into society. |
| Key Features | Discrimination, marginalization, unequal access to education, employment, healthcare. | Equal access, empowerment, social participation, equity, support systems. |
| Impact | Increased poverty, social inequality, mental health issues, alienation. | Enhanced wellbeing, social cohesion, economic participation, reduced inequality. |
| Target Groups | Minorities, disabled, low-income, migrants, elderly. | Vulnerable populations, marginalized groups, all community members. |
| Goals | Eliminate barriers, reduce exclusion. | Promote access, participation, equity in society. |
| Examples | Social isolation, unemployment due to discrimination, denial of services. | Inclusive policies, community programs, equal education opportunities. |
Understanding Social Exclusion: Definition and Key Concepts
Social exclusion refers to the process by which individuals or groups are systematically blocked from rights, opportunities, and resources that are normally available to members of society, leading to marginalization and reduced social participation. Key concepts include economic disadvantage, lack of access to education and healthcare, and social isolation, which contribute to inequality and hinder social cohesion. Understanding social exclusion involves recognizing the multidimensional nature of deprivation and the structural barriers that prevent full social inclusion.
What Is Social Inclusion? Core Principles and Benefits
Social inclusion is the process of improving the terms for individuals and groups to take part in society, fostering equality, respect, and access to resources and opportunities. Core principles include equal access, participation, and removal of barriers related to discrimination, poverty, and social isolation. Benefits of social inclusion comprise enhanced well-being, economic growth, stronger communities, and reduced inequality.
Historical Perspectives on Social Exclusion and Inclusion
Historical perspectives on social exclusion reveal patterns of marginalization based on race, class, gender, and caste, deeply rooted in colonialism, slavery, and segregation policies. Social inclusion efforts emerged as responses during the Enlightenment and civil rights movements, emphasizing equality, human rights, and access to education and employment. Understanding these historical contexts is crucial to addressing contemporary inequalities and promoting inclusive social policies worldwide.
Causes and Drivers of Social Exclusion
Social exclusion arises from factors such as poverty, discrimination, lack of education, and unequal access to resources, which marginalize individuals or groups from participating fully in society. Structural inequalities, including systemic racism, gender bias, and economic disparity, serve as primary drivers perpetuating social exclusion. Addressing these causes requires targeted policies promoting equal opportunities, social protection, and inclusive community engagement to foster social inclusion.
Impact of Social Exclusion on Individuals and Communities
Social exclusion significantly impacts individuals by limiting access to essential resources such as education, employment, and healthcare, leading to increased poverty and mental health issues. Communities experiencing high levels of social exclusion often face heightened social tensions, reduced economic growth, and weakened social cohesion. Addressing social exclusion is crucial for fostering social inclusion, which promotes equal opportunities, community engagement, and overall well-being.
Pathways to Achieve Social Inclusion
Pathways to achieve social inclusion involve creating equitable access to education, employment, and healthcare services, ensuring marginalized groups can participate fully in society. Implementing community-based programs and policies that promote diversity, respect, and empowerment helps dismantle barriers associated with social exclusion. Strengthening social networks and fostering inclusive environments within schools, workplaces, and public services also contribute significantly to reducing social isolation and enhancing cohesion.
Social Exclusion vs Social Inclusion: Key Differences
Social exclusion involves the systematic marginalization of individuals or groups from essential social, economic, and political opportunities, leading to limited access to resources and diminished participation in society. Social inclusion emphasizes ensuring equal access to rights, opportunities, and resources, promoting active engagement and full integration within communities. Key differences lie in the outcomes where social exclusion results in isolation and inequality, whereas social inclusion fosters cohesion, empowerment, and social justice.
Barriers to Social Inclusion in Modern Societies
Barriers to social inclusion in modern societies include systemic inequalities, such as unequal access to education, employment, and healthcare, which perpetuate social exclusion for marginalized groups. Discrimination based on race, gender, disability, and socioeconomic status limits opportunities and reinforces isolation. Cultural stigmas and inadequate policy frameworks further restrict participation in social, economic, and political life, deepening social divides.
Strategies and Policies Promoting Social Inclusion
Strategies promoting social inclusion emphasize equitable access to education, healthcare, and employment opportunities, designed to dismantle barriers faced by marginalized groups. Policies such as affirmative action, community development programs, and anti-discrimination laws foster environments where diverse populations can participate fully in social, economic, and political life. Governments and organizations deploy targeted interventions like social safety nets and inclusive urban planning to reduce social exclusion and enhance cohesion.
Future Directions: Building Inclusive Societies
Future directions for building inclusive societies emphasize the integration of marginalized groups through equitable access to education, employment, and healthcare. Innovative policies leveraging digital technology and community-driven approaches can dismantle systemic barriers to social participation. Effective collaboration among governments, NGOs, and local communities is essential to promote social cohesion and sustainable inclusion.
Social exclusion Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com