Symbolic interactionism explores how individuals create meaning through social interactions by using symbols such as language, gestures, and objects. This theory highlights the fluid and dynamic nature of self-identity and social reality as continuously negotiated through daily exchanges. Discover how symbolic interactionism shapes your understanding of human behavior in the following article.
Table of Comparison
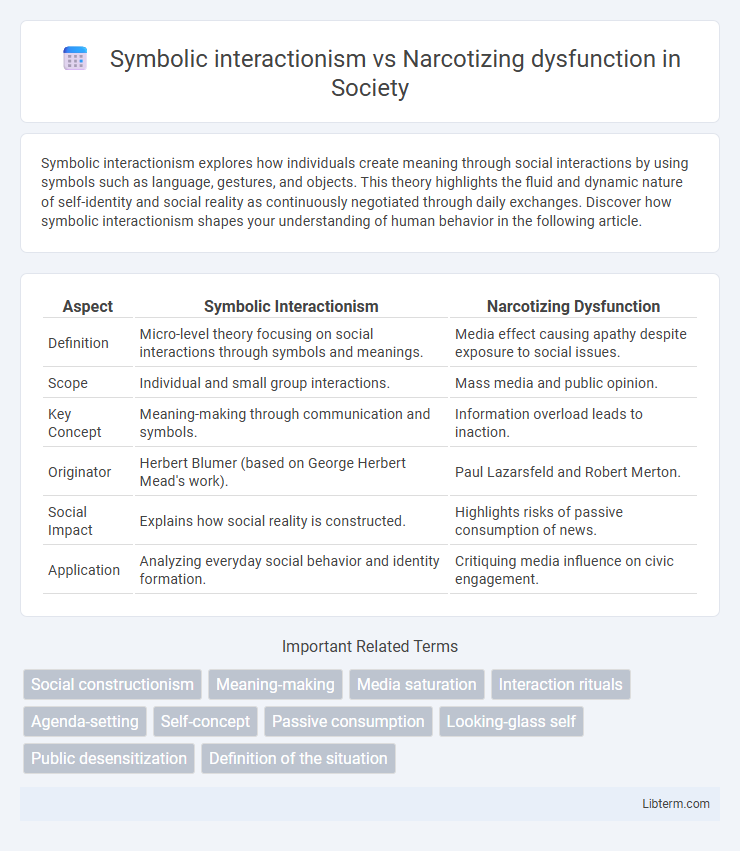
| Aspect | Symbolic Interactionism | Narcotizing Dysfunction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Micro-level theory focusing on social interactions through symbols and meanings. | Media effect causing apathy despite exposure to social issues. |
| Scope | Individual and small group interactions. | Mass media and public opinion. |
| Key Concept | Meaning-making through communication and symbols. | Information overload leads to inaction. |
| Originator | Herbert Blumer (based on George Herbert Mead's work). | Paul Lazarsfeld and Robert Merton. |
| Social Impact | Explains how social reality is constructed. | Highlights risks of passive consumption of news. |
| Application | Analyzing everyday social behavior and identity formation. | Critiquing media influence on civic engagement. |
Introduction to Symbolic Interactionism
Symbolic Interactionism focuses on how individuals create meaning through social interactions using symbols, emphasizing the subjective interpretation of reality. In contrast, Narcotizing Dysfunction describes how excessive media consumption can numb public awareness and reduce active engagement in social issues. Understanding Symbolic Interactionism provides insight into how personal meanings shape behavior, highlighting the dynamic process of social communication.
Understanding Narcotizing Dysfunction
Narcotizing dysfunction describes how extensive media exposure can lead to public apathy by overwhelming individuals with information, causing passive consumption rather than active engagement. This theory contrasts with symbolic interactionism, which emphasizes the importance of personal interactions and meaning-making in shaping social realities. Understanding narcotizing dysfunction reveals the media's role in numbing public response, highlighting challenges in mobilizing collective action despite heightened awareness.
Core Principles of Symbolic Interactionism
Symbolic interactionism emphasizes the core principles of meaning, language, and thought, where individuals create social reality through interactions and the exchange of symbols. This theory highlights how meanings are negotiated and modified through communication, shaping behavior and social roles. In contrast, narcotizing dysfunction describes media saturation leading to passive consumption, reducing critical engagement despite exposure to information.
Key Features of Narcotizing Dysfunction
Narcotizing dysfunction describes a phenomenon where excessive media consumption leads individuals to become apathetic and passive rather than actively engaged in social issues. Key features include the illusion of informed engagement, where people feel knowledgeable simply by being exposed to information, and the resulting decrease in genuine participation or action within society. Unlike symbolic interactionism, which emphasizes personal interactions and meaning-making, narcotizing dysfunction focuses on the numbing effect mass media has on public responsiveness.
Historical Origins and Development
Symbolic interactionism originated in the early 20th century, primarily developed by sociologists George Herbert Mead and Herbert Blumer, emphasizing the creation of meaning through social interaction and symbols. Narcotizing dysfunction was introduced by Paul Lazarsfeld and Robert Merton in the mid-20th century as a critique of mass media, highlighting how excessive media consumption leads to apathy and diminished public engagement. Both theories emerged during significant societal changes, with symbolic interactionism rooted in pragmatist philosophy and narcotizing dysfunction arising from concerns about media's influence on democratic participation.
Communication and Meaning-Making Differences
Symbolic interactionism emphasizes communication as an interactive process where individuals create and negotiate meaning through symbols in social interactions. Narcotizing dysfunction describes how excessive media consumption leads to passive acceptance of information, diminishing active engagement and critical communication. While symbolic interactionism highlights dynamic meaning-making, narcotizing dysfunction underscores the communication breakdown caused by information overload and apathy.
Media Influence: Interactionism vs Dysfunction
Symbolic interactionism emphasizes how individuals interpret and negotiate media messages through social interactions, shaping personal and collective meanings. Narcotizing dysfunction suggests that excessive media consumption leads to passive audiences, where information overload results in apathy rather than action. These contrasting perspectives highlight media's dual role in both fostering active social engagement and contributing to societal disengagement.
Social Behavior and Public Perception
Symbolic interactionism emphasizes how individuals interpret and give meaning to social symbols through face-to-face interactions, shaping social behavior based on those shared meanings. Narcotizing dysfunction describes how repeated exposure to media content can lead to public apathy, where individuals become passive consumers rather than active participants in social issues. Together, these theories explain how micro-level social interactions influence personal behavior, while mass media impact broader public perception and engagement in society.
Critiques and Limitations of Both Theories
Symbolic interactionism faces critiques for its narrow focus on micro-level interactions, often neglecting larger social structures and power dynamics that shape individual behavior. Narcotizing dysfunction is limited by its assumption that media exposure uniformly leads to passivity, failing to account for varied individual and cultural responses to media content. Both theories struggle with empirical testing, as symbolic interactionism is criticized for subjective interpretations while narcotizing dysfunction lacks robust quantitative evidence linking media consumption directly to diminished social activism.
Contemporary Relevance in Today’s Society
Symbolic interactionism remains relevant in analyzing how social identities and meanings are constructed through everyday interactions, shaping individual behavior and group dynamics in contemporary digital communication platforms. Narcotizing dysfunction highlights the paradox where excessive media exposure leads to public apathy and disengagement from social issues despite increased awareness, particularly evident in the age of social media saturation. Understanding both concepts is crucial for addressing challenges in civic engagement and fostering active participation in today's interconnected society.
Symbolic interactionism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com