Horizontal mobility refers to the movement of individuals or groups within the same social class or occupational level, without significant changes in status or income. This type of mobility often involves job changes or shifts in roles that maintain a similar social standing. Explore the article to understand how horizontal mobility impacts your career and social dynamics.
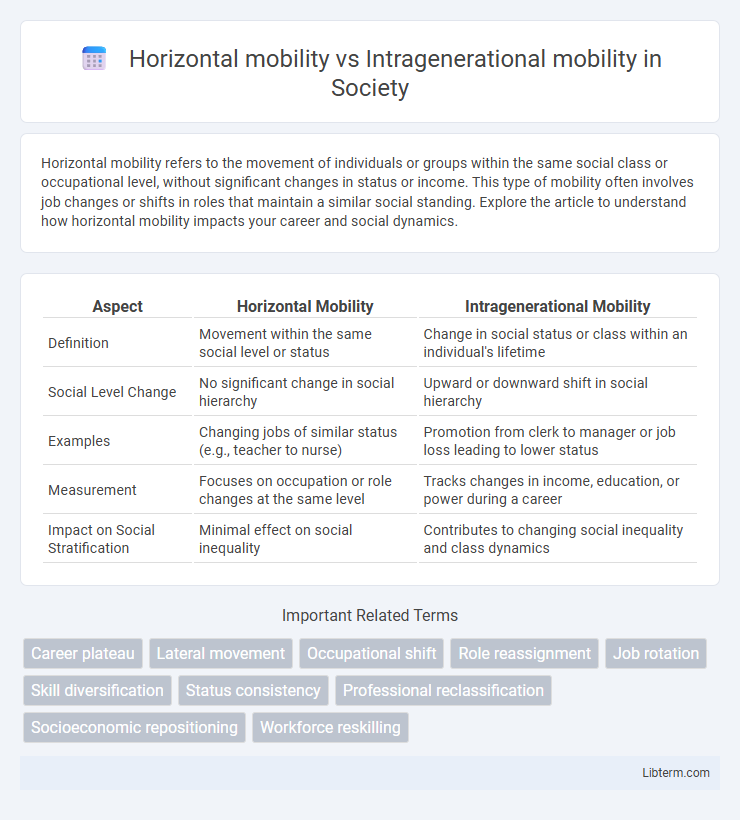
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Horizontal Mobility | Intragenerational Mobility |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Movement within the same social level or status | Change in social status or class within an individual's lifetime |
| Social Level Change | No significant change in social hierarchy | Upward or downward shift in social hierarchy |
| Examples | Changing jobs of similar status (e.g., teacher to nurse) | Promotion from clerk to manager or job loss leading to lower status |
| Measurement | Focuses on occupation or role changes at the same level | Tracks changes in income, education, or power during a career |
| Impact on Social Stratification | Minimal effect on social inequality | Contributes to changing social inequality and class dynamics |
Understanding Social Mobility: Key Concepts
Horizontal mobility refers to a change in an individual's social position without altering their social status or class, such as switching jobs within the same occupational level. Intragenerational mobility captures the movement of an individual within their own lifetime, reflecting upward or downward shifts in social standing across economic or occupational tiers. Understanding these distinctions is essential for analyzing social mobility patterns, as horizontal mobility highlights positional changes without economic advancement, whereas intragenerational mobility emphasizes the dynamic nature of social status during one's career.
What is Horizontal Mobility?
Horizontal mobility refers to the movement of individuals or groups within the same social stratum or economic level, involving changes in occupation or role without altering their overall social status. This type of mobility contrasts with intragenerational mobility, which tracks changes in social status or class over an individual's lifetime, including upward or downward shifts. Horizontal mobility emphasizes shifts within a social category rather than transitions across different social hierarchies.
Defining Intragenerational Mobility
Intragenerational mobility refers to the changes in an individual's social status or class within their lifetime, reflecting upward or downward movements based on occupation, income, or education. Horizontal mobility involves shifts within the same social level, such as changing jobs without altering social standing. Understanding intragenerational mobility highlights the dynamic nature of social stratification and the opportunities or barriers individuals face during their career trajectories.
Differences Between Horizontal and Intragenerational Mobility
Horizontal mobility involves a change in social position without a significant shift in social status or class, such as switching jobs within the same occupational level. Intragenerational mobility refers to changes in social status occurring within an individual's lifetime, encompassing both upward and downward movements across different social strata. The key difference lies in horizontal mobility's lateral shift within the same social level, whereas intragenerational mobility highlights vertical mobility reflecting changes in socioeconomic status during one's career.
Real-Life Examples of Horizontal Mobility
Horizontal mobility occurs when individuals change positions within the same social class, such as a teacher moving to a school in another district without a change in status or income. Real-life examples include a nurse transferring hospitals or a software developer switching companies while maintaining a similar role and salary level. These instances highlight mobility without vertical advancement or decline, reflecting stability within the middle or working class.
Illustrative Cases of Intragenerational Mobility
Intragenerational mobility refers to the changes in social status or class experienced by an individual within their lifetime, contrasting with horizontal mobility, which involves shifts within the same social stratum. Illustrative cases of intragenerational mobility include a factory worker who becomes a business executive or a teacher who transitions to a corporate trainer role, demonstrating upward or downward mobility across different occupational sectors. Such cases highlight the dynamic nature of social stratification and emphasize individual career trajectories influencing socioeconomic status over time.
Factors Influencing Horizontal Mobility
Horizontal mobility refers to the movement of individuals or groups within the same social stratum, such as changing jobs without altering socioeconomic status, while intragenerational mobility encompasses all changes in social status over a person's lifetime. Factors influencing horizontal mobility include occupational shifts without income variation, geographical relocation, education that enhances skills without raising social class, and changes in industry demand that affect job positions equivalently within a social layer. Understanding labor market conditions, professional networks, and regional economic opportunities is crucial in analyzing horizontal mobility patterns.
Causes and Drivers of Intragenerational Mobility
Intragenerational mobility, driven primarily by factors such as changes in occupational status, educational attainment, and shifts within labor markets, reflects an individual's movement across socioeconomic positions within their own lifetime. Economic fluctuations, technological advancements, and access to professional development opportunities serve as significant catalysts for upward or downward mobility. In contrast, horizontal mobility involves a change in position without altering the individual's overall social status, often influenced by lateral job changes or geographic relocation.
Impacts on Individuals and Society
Horizontal mobility involves changes in occupation or social status without altering an individual's overall socioeconomic position, which can maintain stability but may limit personal economic growth and societal inequality reduction. Intragenerational mobility, referring to significant shifts in social status within an individual's lifetime, can enhance economic diversity, promote social equity, and impact mental health by influencing self-esteem and stress levels. The extent and nature of these mobilities affect societal cohesion, opportunity structures, and the distribution of resources within communities.
Analyzing the Importance of Mobility Types in Social Structure
Horizontal mobility involves changing positions within the same social stratum, maintaining a relatively stable socioeconomic status, whereas intragenerational mobility refers to shifts in social status occurring within an individual's lifetime, often measured by changes in income, occupation, or education. Analyzing these mobility types reveals their distinct roles in social structure dynamics: horizontal mobility emphasizes role adaptability without altering social hierarchy, while intragenerational mobility highlights individual social advancement or decline. Understanding these mobility patterns is crucial for assessing social stratification, inequality persistence, and the potential for social change within societies.
Horizontal mobility Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com