Absolute mobility refers to the ability of individuals or families to improve their economic status compared to previous generations, often measured by income or wealth increases. It reflects the overall improvement in living standards and economic opportunities within a society. Discover how absolute mobility impacts your future prospects and shapes social dynamics by reading the rest of the article.
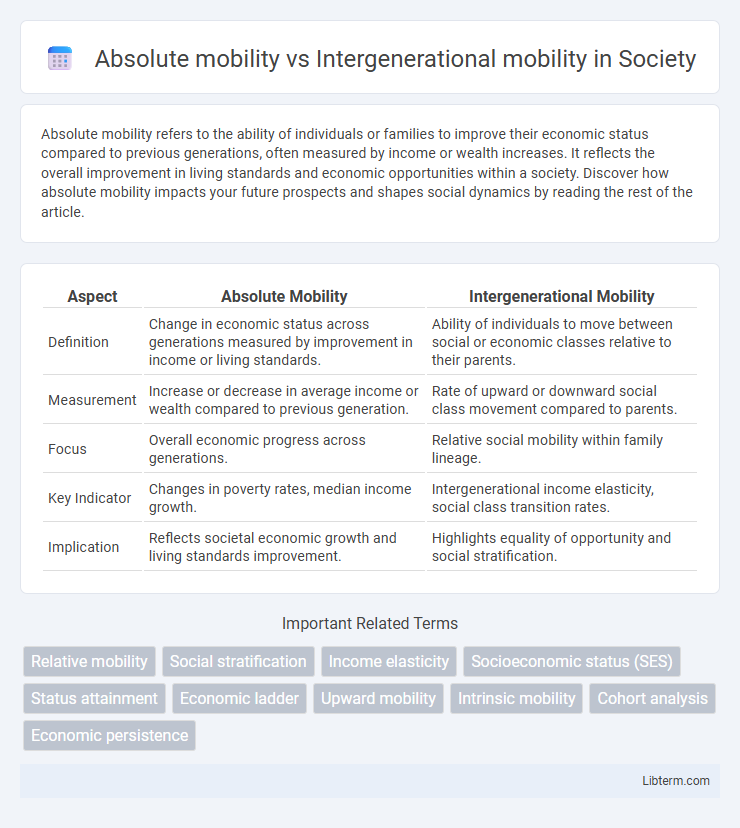
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Absolute Mobility | Intergenerational Mobility |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Change in economic status across generations measured by improvement in income or living standards. | Ability of individuals to move between social or economic classes relative to their parents. |
| Measurement | Increase or decrease in average income or wealth compared to previous generation. | Rate of upward or downward social class movement compared to parents. |
| Focus | Overall economic progress across generations. | Relative social mobility within family lineage. |
| Key Indicator | Changes in poverty rates, median income growth. | Intergenerational income elasticity, social class transition rates. |
| Implication | Reflects societal economic growth and living standards improvement. | Highlights equality of opportunity and social stratification. |
Introduction to Economic Mobility
Economic mobility measures the ability of individuals or families to improve their economic status over time, with absolute mobility tracking overall income growth compared to previous generations. Intergenerational mobility specifically examines changes in economic status from parents to children, highlighting the degree to which economic advantages or disadvantages persist across generations. Understanding these dimensions helps analyze social equity and the impact of policies on reducing income inequality and promoting equal opportunities.
Defining Absolute Mobility
Absolute mobility measures the change in average economic status or income of individuals compared to their parents, reflecting overall improvements in living standards across generations. It captures whether the current generation is better off economically than the previous one, without considering relative position within the income distribution. This metric is essential for assessing economic growth and societal progress over time.
Understanding Intergenerational Mobility
Intergenerational mobility measures changes in socioeconomic status or income from one generation to the next, reflecting opportunities for children to achieve a different economic position than their parents. Absolute mobility refers to the overall improvement in living standards across generations, such as higher income or education levels compared to prior generations. Understanding intergenerational mobility is crucial for assessing equality of opportunity, social stratification, and the persistence of economic advantage or disadvantage within families over time.
Key Differences Between Absolute and Intergenerational Mobility
Absolute mobility measures the overall improvement in living standards or economic status across generations, reflecting whether younger generations achieve higher income or educational levels than their parents. Intergenerational mobility specifically assesses the degree to which individuals' socioeconomic status changes relative to their parents, indicating how family background influences economic outcomes. Key differences lie in absolute mobility's focus on societal progress over time versus intergenerational mobility's emphasis on relative changes and equality of opportunity within family lineages.
Measuring Absolute Mobility: Methods and Metrics
Measuring absolute mobility primarily involves comparing the economic or social status of children directly to that of their parents, often using metrics like income growth rates or attainment of higher education levels. Common methods include longitudinal studies tracking income percentile changes across generations or analyzing shifts in employment sectors and occupational status. Absolute mobility metrics reveal whether each generation achieves a better standard of living than the previous one, providing a clear picture of overall societal progress.
Analyzing Intergenerational Mobility: Tools and Approaches
Analyzing intergenerational mobility involves measuring the extent to which economic status or social class is transmitted from parents to children using tools like income elasticity, transition matrices, and rank-rank correlations. Statistical models and longitudinal data sets are essential for capturing the dynamics of socioeconomic mobility across generations, enabling researchers to differentiate between absolute and relative mobility. Advanced approaches, including multigenerational studies and decomposition techniques, offer deeper insights into barriers and opportunities affecting intergenerational mobility.
Factors Influencing Absolute Mobility
Absolute mobility measures the overall improvement in average income or living standards across generations, while intergenerational mobility assesses the extent to which individuals move up or down the socioeconomic ladder relative to their parents. Factors influencing absolute mobility include economic growth, labor market conditions, education access, demographic changes, and social policies that enhance income opportunities. High absolute mobility often results from sustained economic expansion, increased educational attainment, and effective redistribution measures that raise the general population's income levels over time.
Determinants of Intergenerational Mobility
Intergenerational mobility refers to the degree to which individuals' socioeconomic status differs from that of their parents, influenced by factors such as education accessibility, family background, and social policies. Determinants of intergenerational mobility include parental income, neighborhood quality, school resources, and labor market conditions that shape opportunities for upward movement. Understanding these determinants is crucial for addressing inequalities and promoting equal chances across generations.
Policy Implications: Enhancing Mobility
Policy implications for enhancing mobility emphasize targeted investments in education and workforce development to boost both absolute and intergenerational mobility. Expanding access to quality early childhood programs, vocational training, and higher education reduces economic disparities and promotes upward mobility across generations. Strengthening social safety nets and labor market policies further supports sustained income growth and equal opportunities for disadvantaged populations.
Conclusion: Towards a More Mobile Society
Absolute mobility reflects overall improvements in living standards across generations, while intergenerational mobility measures the ability to move up or down the social ladder compared to one's parents. Enhancing policies that promote equal access to education, healthcare, and economic opportunities can reduce barriers and increase both types of mobility. Fostering a more mobile society requires targeted investments in social infrastructure, enabling individuals to realize their potential regardless of their socioeconomic background.
Absolute mobility Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com