A formal structure defines clear roles, responsibilities, and communication channels within an organization or document, ensuring consistency and professionalism. It supports efficient decision-making and maintains accountability at every level. Explore the rest of the article to understand how applying a formal structure can enhance your workflows and outcomes.
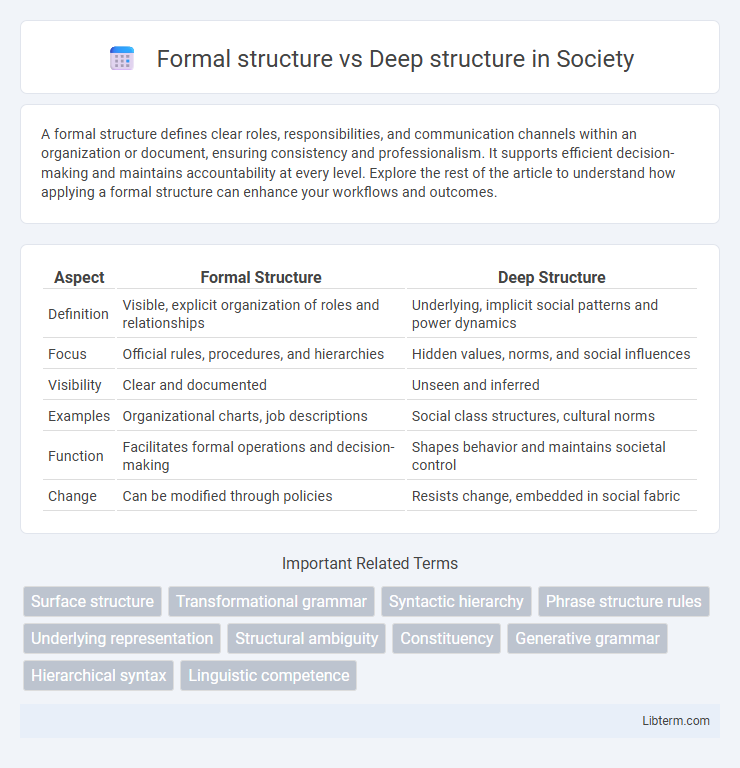
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Formal Structure | Deep Structure |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Visible, explicit organization of roles and relationships | Underlying, implicit social patterns and power dynamics |
| Focus | Official rules, procedures, and hierarchies | Hidden values, norms, and social influences |
| Visibility | Clear and documented | Unseen and inferred |
| Examples | Organizational charts, job descriptions | Social class structures, cultural norms |
| Function | Facilitates formal operations and decision-making | Shapes behavior and maintains societal control |
| Change | Can be modified through policies | Resists change, embedded in social fabric |
Introduction to Formal Structure and Deep Structure
Formal structure in linguistics refers to the specific syntactic arrangement of words within a sentence, emphasizing surface-level grammar rules and phrase order. Deep structure represents the underlying meaning and semantic relationships of a sentence before it is transformed into formal structure through syntactic operations. Understanding the distinction between formal and deep structures is essential for analyzing sentence formation and the interpretation of meaning in generative grammar.
Defining Formal Structure in Linguistics
Formal structure in linguistics refers to the explicit, observable arrangement of elements within a sentence, such as syntax and morphological patterns. It focuses on the surface-level organization of words and phrases based on grammatical rules and hierarchical relationships. This contrasts with deep structure, which represents the underlying semantic meaning and abstract syntactic relationships that govern sentence interpretation.
Understanding Deep Structure: A Semantic Perspective
Deep structure represents the underlying semantic relationships and meaning of a sentence, capturing abstract syntactic forms that convey core ideas beyond surface variations. Understanding deep structure involves analyzing how different sentence forms share common semantic roles and thematic relationships, which supports accurate interpretation and transformation in natural language processing. This semantic perspective highlights the importance of grasping deep structure for tasks such as language translation, ambiguity resolution, and context-aware comprehension.
Key Differences Between Formal and Deep Structures
Formal structure refers to the explicit grammatical framework of a sentence, representing its surface syntax and word order, while deep structure captures the underlying semantic relationships and meaning within a sentence. Formal structure is concerned with how sentences are constructed using syntactic rules, whereas deep structure reveals the fundamental concepts and logical forms that inform sentence interpretation. The key differences lie in formal structure's focus on observable linguistic patterns and deep structure's emphasis on abstract meaning and thematic roles.
Role of Formal Structure in Syntax
Formal structure in syntax provides a systematic framework for representing sentence organization through hierarchical rules and constituent boundaries, enabling precise parsing and syntactic analysis. It governs the arrangement of phrases and the relationships between grammatical elements, ensuring that sentence constructions adhere to language-specific patterns. By defining explicit syntactic configurations, formal structure facilitates the generation and interpretation of well-formed sentences within a given linguistic system.
Deep Structure and Meaning Representation
Deep structure in linguistics represents the underlying syntactic relationships and core semantic content of a sentence, serving as a critical foundation for meaning representation. Unlike formal structure, which deals with surface arrangements and word order, deep structure captures the abstract grammatical relations that inform how meaning is derived. This level of analysis enables semantic interpretation, facilitating natural language understanding and processing in computational linguistics and cognitive science.
Transformational Grammar: Linking Formal and Deep Structures
Transformational Grammar distinguishes between deep structure, representing the core semantic relations of a sentence, and formal structure, which refers to the surface syntactic form after transformations. The process of linking deep structures to formal structures involves syntactic rules that transform abstract representations into concrete sentence forms. This framework enhances understanding of how meaning is encoded and realized in varied sentence constructions.
Applications of Formal and Deep Structures in Language Analysis
Formal structure in language analysis refers to the explicit syntactic arrangement of words and phrases, crucial for parsing sentences and developing natural language processing algorithms. Deep structure captures the underlying semantic meaning and relationships within sentences, enabling applications in machine translation and semantic role labeling. Combining formal and deep structures enhances automated language understanding by bridging syntax with meaning representation.
Challenges in Distinguishing Formal and Deep Structures
Distinguishing formal structure from deep structure presents significant challenges due to their abstract and interconnected nature in linguistic theory. Formal structure refers to the surface syntactic arrangement of words, while deep structure involves the underlying semantic relationships and meaning representations. Ambiguities arise because similar surface forms can correspond to different deep structures, complicating syntax-semantics mapping and requiring sophisticated parsing algorithms and theoretical frameworks to accurately interpret language.
Conclusion: Integrating Formal and Deep Structural Approaches
Integrating formal and deep structural approaches enhances linguistic analysis by combining surface-level syntactic accuracy with underlying semantic interpretations. This synergy allows for more comprehensive understanding of language, capturing both explicit grammatical rules and implicit cognitive representations. Effective language processing benefits from models that align formal syntax with deep semantic structures, improving natural language understanding and generation.
Formal structure Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com