Nonprofit organizations play a vital role in addressing social, environmental, and community issues by reinvesting resources into mission-driven initiatives rather than profit distribution. They rely on donations, grants, and volunteer support to sustain their programs and create meaningful impact. Discover how your involvement can strengthen these organizations and contribute to positive change throughout the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
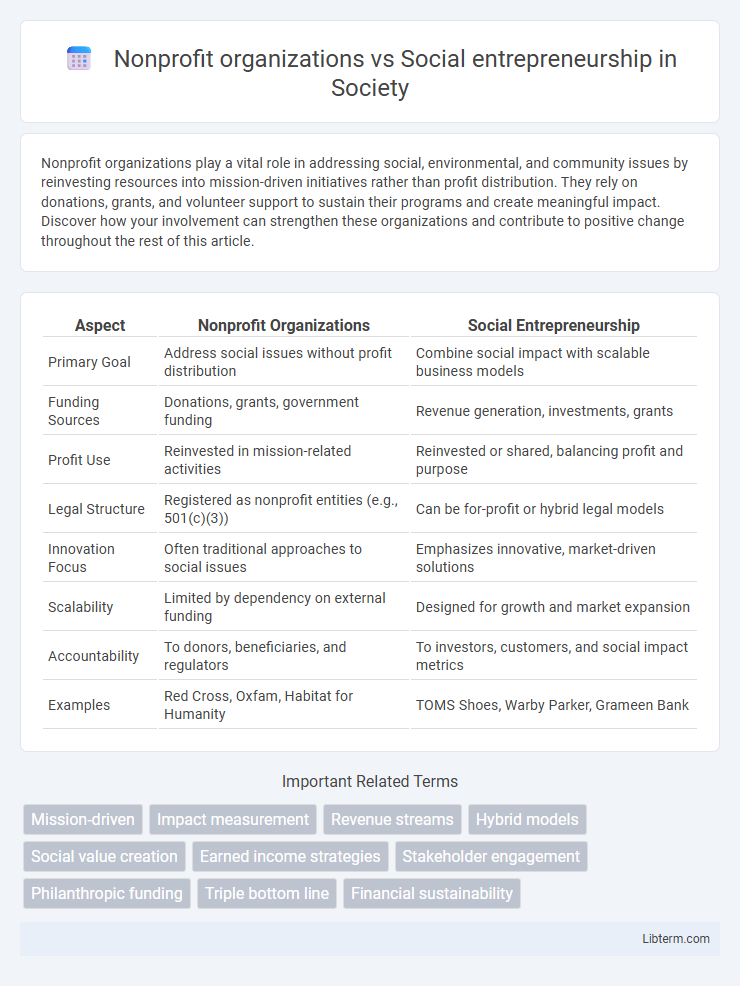
| Aspect | Nonprofit Organizations | Social Entrepreneurship |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Address social issues without profit distribution | Combine social impact with scalable business models |
| Funding Sources | Donations, grants, government funding | Revenue generation, investments, grants |
| Profit Use | Reinvested in mission-related activities | Reinvested or shared, balancing profit and purpose |
| Legal Structure | Registered as nonprofit entities (e.g., 501(c)(3)) | Can be for-profit or hybrid legal models |
| Innovation Focus | Often traditional approaches to social issues | Emphasizes innovative, market-driven solutions |
| Scalability | Limited by dependency on external funding | Designed for growth and market expansion |
| Accountability | To donors, beneficiaries, and regulators | To investors, customers, and social impact metrics |
| Examples | Red Cross, Oxfam, Habitat for Humanity | TOMS Shoes, Warby Parker, Grameen Bank |
Introduction: Understanding Nonprofit Organizations and Social Entrepreneurship
Nonprofit organizations operate primarily to serve public or community interests without profit distribution, relying on donations, grants, and volunteers to achieve social missions. Social entrepreneurship merges innovative business strategies with social impact goals, creating sustainable ventures that address societal challenges while generating revenue. Both models prioritize social change, yet differ in funding mechanisms, operational structures, and scalability approaches.
Defining Nonprofit Organizations
Nonprofit organizations are legally structured entities dedicated to advancing social causes without profit distribution to members or leaders, typically reinvesting all surplus funds into their mission-driven activities. These organizations rely heavily on donations, grants, and volunteer support to provide services or advocacy in areas such as education, health, and environmental protection. Distinct from social entrepreneurship, nonprofits emphasize charitable objectives and public benefit rather than innovative business models generating sustainable revenue streams.
Defining Social Entrepreneurship
Social entrepreneurship involves creating innovative solutions to address social, cultural, or environmental issues through sustainable business models, blending mission-driven goals with market-based strategies. Unlike traditional nonprofit organizations, which primarily rely on donations and grants to fund their activities, social enterprises generate revenue by delivering products or services while pursuing social impact. This approach enables social entrepreneurs to scale their initiatives and achieve long-term sustainability by reinvesting profits into their social missions.
Key Differences Between Nonprofits and Social Enterprises
Nonprofit organizations primarily rely on donations, grants, and fundraising to support their missions, whereas social enterprises generate revenue through business activities aimed at achieving social impact. Nonprofits reinvest surplus funds into their programs without distributing profits to stakeholders, while social enterprises balance profit-making with social goals, often distributing profits or reinvesting them to scale impact. Governance structures also differ, with nonprofits governed by boards focused on mission-driven oversight, and social enterprises blending business management with social accountability.
Funding Models: Grants vs. Revenue-Generating Activities
Nonprofit organizations predominantly rely on grants, donations, and government funding to sustain their operations, which can limit financial flexibility and scalability. Social entrepreneurship leverages revenue-generating activities alongside grants, enabling a hybrid funding model that supports innovation and long-term sustainability. This approach allows social enterprises to reinvest profits into their mission-driven projects while reducing dependency on external funding sources.
Mission and Impact: Social Goals and Measurement
Nonprofit organizations prioritize social missions by reinvesting all surplus revenues into their programs to maximize community impact, often relying on traditional metrics like service delivery volume and beneficiary outcomes to measure success. Social entrepreneurship integrates innovative business models with social goals, balancing financial sustainability with scalable impact, utilizing metrics such as social return on investment (SROI) and impact performance indicators to evaluate both economic viability and social change. Mission-driven focus in nonprofits centers on long-term social value creation, while social entrepreneurs emphasize adaptive strategies to generate measurable and sustainable social impact.
Organizational Structures and Legal Status
Nonprofit organizations typically operate under a legal status that prioritizes charitable purposes, qualifying for tax-exempt benefits under IRS code 501(c)(3) or similar regulations, with organizational structures centered around boards of directors and strict compliance with nonprofit governance. Social entrepreneurship ventures blend business strategies with social missions, often adopting for-profit or hybrid organizational structures such as benefit corporations (B Corps) or low-profit limited liability companies (L3Cs), which allow for greater operational flexibility and profit generation while addressing social issues. Legal distinctions impact funding options, accountability, and resource allocation, with nonprofits relying heavily on grants and donations, whereas social enterprises attract investments and revenue streams aligned with social impact goals.
Sustainability and Scalability Challenges
Nonprofit organizations often face sustainability challenges due to reliance on donations and grants, which can fluctuate and limit long-term impact. Social entrepreneurship emphasizes scalable business models that generate revenue while addressing social issues, enhancing financial independence and growth potential. However, social enterprises must balance profit goals with mission-driven outcomes, presenting unique challenges in maintaining both sustainability and social impact.
Collaboration and Competition in the Social Sector
Nonprofit organizations and social entrepreneurship both play crucial roles in the social sector, emphasizing collaboration to leverage resources and amplify impact. Nonprofits often collaborate through partnerships and alliances to address complex social issues, while social entrepreneurs introduce innovative, competitive strategies to drive systemic change. The dynamic interplay between cooperation and competition fosters a vibrant ecosystem that accelerates social innovation and maximizes community benefits.
Future Trends: Blurring Lines Between Nonprofit and Social Entrepreneurship
Future trends reveal an increasing convergence between nonprofit organizations and social entrepreneurship, driven by shared goals of social impact and sustainable solutions. Hybrid models combining profit-driven approaches with mission-focused objectives are gaining momentum, enabling resource diversification and innovative funding strategies. This blurring of lines fosters a collaborative ecosystem that leverages business principles to enhance social value while maintaining community-centric priorities.
Nonprofit organizations Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com