Sexism refers to prejudice or discrimination based on a person's sex or gender, often resulting in unequal treatment in social, professional, and personal contexts. It manifests in various forms including wage gaps, stereotyping, and exclusion from opportunities, significantly impacting individuals' rights and societal dynamics. Discover how recognizing and addressing sexism can empower your perspective and promote equality by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
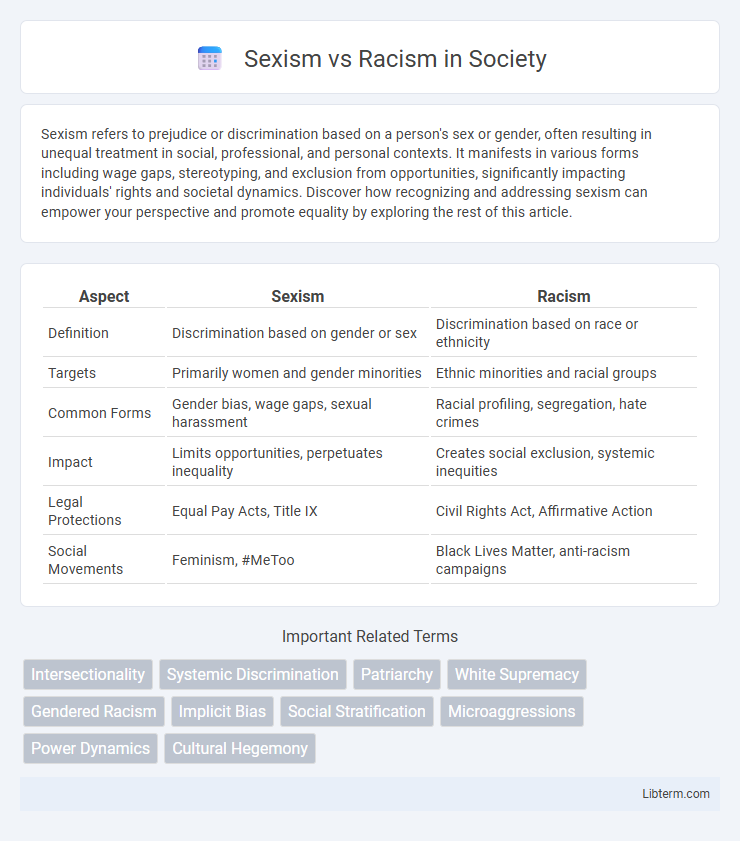
| Aspect | Sexism | Racism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Discrimination based on gender or sex | Discrimination based on race or ethnicity |
| Targets | Primarily women and gender minorities | Ethnic minorities and racial groups |
| Common Forms | Gender bias, wage gaps, sexual harassment | Racial profiling, segregation, hate crimes |
| Impact | Limits opportunities, perpetuates inequality | Creates social exclusion, systemic inequities |
| Legal Protections | Equal Pay Acts, Title IX | Civil Rights Act, Affirmative Action |
| Social Movements | Feminism, #MeToo | Black Lives Matter, anti-racism campaigns |
Defining Sexism: Origins and Impact
Sexism originates from deeply ingrained cultural norms and historical power imbalances that privilege one gender over others, primarily disadvantaging women. It manifests through systemic discrimination in workplaces, education, and social settings, perpetuating unequal opportunities and reinforcing gender stereotypes. The impact of sexism extends beyond individual experiences, contributing to widespread social inequalities and limiting societal progress toward gender equity.
Understanding Racism: Historical and Modern Contexts
Racism has deep historical roots shaped by colonialism, slavery, and segregation, influencing social hierarchies and systemic discrimination worldwide. Modern racism persists through institutional policies, implicit biases, and socioeconomic disparities that disproportionately affect marginalized racial groups. Understanding these contexts highlights the ongoing need for equity-driven reforms and cultural awareness to dismantle entrenched racial prejudices.
Commonalities Between Sexism and Racism
Sexism and racism both involve systemic discrimination rooted in stereotypes and power imbalances that marginalize specific groups based on gender or race. Both forms of bias operate through institutional practices and social norms that perpetuate inequality in areas such as employment, education, and legal treatment. Understanding their commonalities reveals how intersecting oppressions exacerbate the challenges faced by individuals experiencing multiple forms of discrimination.
Key Differences: Sexism vs Racism
Sexism involves discrimination based on an individual's gender, often targeting women and reinforcing unequal power dynamics in social, economic, and political contexts. Racism is the belief in racial superiority that results in systemic inequality and prejudice against people based on race or ethnicity. Key differences include the axes of identity they target--sex or gender in sexism, and race or ethnicity in racism--each with distinct historical and cultural origins shaping their manifestations and impacts.
Intersectionality: When Sexism and Racism Overlap
Sexism and racism intersect in complex ways, creating unique experiences of discrimination for individuals facing both gender and racial biases. Intersectionality highlights how Black women, Indigenous women, and women of color encounter systemic barriers that cannot be understood fully through sexism or racism alone. This overlapping oppression affects access to education, employment, healthcare, and justice, demanding intersectional approaches in policy and activism.
Societal Consequences of Sexism and Racism
Sexism and racism both contribute to systemic inequality, limiting opportunities and access to resources for marginalized groups. Societal consequences of sexism include wage gaps, occupational segregation, and underrepresentation of women in leadership roles, which perpetuate economic disparities and hinder social progress. Racism fosters social exclusion, educational disparities, and unequal treatment in the justice system, reinforcing cycles of poverty and social division.
Media Representation: Sexism vs Racism
Media representation often perpetuates sexism by reinforcing gender stereotypes, portraying women in limited roles such as caregivers or objects of desire, which restricts their visibility and influence. In contrast, racism in media frequently manifests through underrepresentation or negative stereotyping of racial minorities, contributing to societal biases and systemic discrimination. Both sexism and racism in media contribute to skewed public perceptions, hindering progress toward equality and inclusion.
Legal Approaches to Combat Sexism and Racism
Legal approaches to combat sexism and racism include robust anti-discrimination laws such as the Civil Rights Act in the United States, which prohibits employment discrimination based on race, color, sex, or national origin. Enforcement agencies like the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) play a critical role in investigating complaints and ensuring compliance. Court rulings and affirmative action policies further strengthen protections, promoting equality and addressing systemic biases in education, employment, and housing.
Activism and Advocacy: Fighting Sexism and Racism
Activism and advocacy efforts targeting sexism and racism prioritize intersectional approaches to address overlapping systems of oppression. Campaigns like the Women's March and Black Lives Matter mobilize millions globally, leveraging social media platforms to raise awareness and drive policy changes. Grassroots organizations emphasize education, legal reform, and community support to dismantle systemic discrimination and promote equity.
Moving Forward: Building Inclusive Communities
Building inclusive communities requires addressing both sexism and racism through comprehensive education and policy reforms that promote equality and respect for diversity. Implementing programs that encourage empathy, cultural awareness, and active dismantling of systemic biases fosters environments where all individuals can thrive. Collaborative efforts between governments, organizations, and grassroots movements are essential to create sustainable change and advance social justice.
Sexism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com