Individual-centric approaches prioritize the unique needs, preferences, and experiences of each person to foster personalized solutions and meaningful connections. Emphasizing empathy and customization enhances engagement and satisfaction across various contexts, from healthcare to education. Explore the rest of the article to discover how individual-centric strategies can transform your interactions and outcomes.
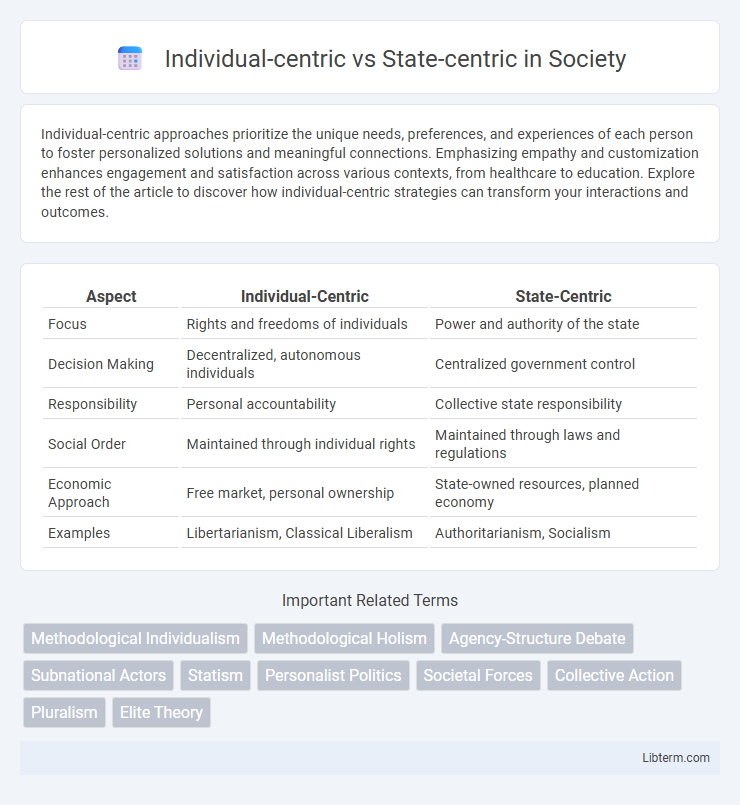
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Individual-Centric | State-Centric |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Rights and freedoms of individuals | Power and authority of the state |
| Decision Making | Decentralized, autonomous individuals | Centralized government control |
| Responsibility | Personal accountability | Collective state responsibility |
| Social Order | Maintained through individual rights | Maintained through laws and regulations |
| Economic Approach | Free market, personal ownership | State-owned resources, planned economy |
| Examples | Libertarianism, Classical Liberalism | Authoritarianism, Socialism |
Introduction to Individual-centric and State-centric Approaches
The individual-centric approach prioritizes personal freedoms, rights, and responsibilities, emphasizing the autonomy and agency of individuals within society. In contrast, the state-centric approach focuses on the authority and sovereignty of the state, underscoring the role of government institutions in maintaining order and security. These frameworks shape political theories, governance models, and policy-making by defining the balance between individual rights and state power.
Defining Individual-centric Perspectives
Individual-centric perspectives emphasize personal autonomy, rights, and freedoms as the foundation for social and political analysis. This approach prioritizes the individual's experiences, choices, and responsibilities over collective or state-centered interests. It shapes frameworks where policies and governance focus on protecting individual liberties and encouraging self-determination.
Understanding State-centric Frameworks
State-centric frameworks prioritize the authority and sovereignty of the state in international relations, emphasizing its role as the principal actor in global governance and security. These frameworks analyze how states pursue national interests, maintain power, and interact through diplomacy, war, and alliances within an anarchic international system. Understanding state-centric approaches is crucial for interpreting realist theories, state sovereignty debates, and the dynamics of international conflict and cooperation.
Historical Roots: Individualism vs. Statism
Individual-centric approaches trace their historical roots to Enlightenment thinkers like John Locke, emphasizing personal liberty, natural rights, and self-determination as foundational principles. In contrast, state-centric ideologies derive from classical political theories associated with figures like Thomas Hobbes and Jean Bodin, who prioritized sovereign authority and centralized power to maintain order and security. The tension between individualism and statism highlights the evolving debate over the locus of political power and social organization throughout history.
Core Principles of Individual-centric Societies
Individual-centric societies emphasize personal freedom, autonomy, and rights, ensuring that individuals have the power to make decisions about their own lives. Core principles include respect for individual dignity, protection of civil liberties, and promotion of self-expression and personal responsibility. These societies prioritize legal frameworks and social norms that safeguard individual interests over collective or state authority.
Foundational Values in State-centric Systems
State-centric systems prioritize foundational values such as sovereignty, national security, and collective welfare over individual rights, emphasizing the authority and legitimacy of the state as the primary actor. These systems often promote social order, stability, and unity, aligning policies to maintain governmental control and national interests. Emphasizing state authority ensures that laws and governance structures reflect the collective goals rather than personal autonomy.
Impact on Governance and Policy-making
Individual-centric approaches prioritize citizen empowerment, enhancing participatory governance by enabling direct input in policy decisions, which fosters transparency and accountability. State-centric models centralize authority, facilitating cohesive policy implementation and national security but may limit public engagement and responsiveness to local needs. The balance between these frameworks significantly shapes governance effectiveness, influencing policy adaptability, citizen trust, and democratic legitimacy.
Social and Economic Outcomes of Both Approaches
Individual-centric approaches prioritize personal freedoms and market-driven solutions, leading to innovation and economic growth through entrepreneurship and competition. State-centric models emphasize collective welfare and regulatory frameworks, often resulting in more equitable social outcomes and reduced income disparities. Balancing these approaches can optimize social safety nets while sustaining economic productivity and inclusivity.
Contemporary Debates: Balancing Individual and State Interests
Contemporary debates on individual-centric versus state-centric approaches emphasize the importance of balancing personal freedoms with collective security and governance. Scholars analyze how policies that prioritize individual rights coexist or conflict with state sovereignty and public welfare mandates. The discourse often centers on legal frameworks, human rights protections, and the role of state intervention in ensuring social justice without undermining individual autonomy.
Future Trends and Evolving Paradigms
Future trends in international relations indicate a shift from state-centric models toward individual-centric frameworks, emphasizing human security, digital identity, and personal data sovereignty. Evolving paradigms prioritize cross-border networks, transnational activism, and decentralized governance enabled by blockchain and AI technologies. This transformation challenges traditional sovereignty concepts, urging integration of individual rights with state responsibilities for global stability.
Individual-centric Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com