Libertarianism emphasizes individual liberty, limited government intervention, and free-market principles as the foundation for a just society. Advocates argue that personal freedom and voluntary cooperation lead to greater prosperity and social harmony. Discover how libertarian ideas could transform your views on governance and economics by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
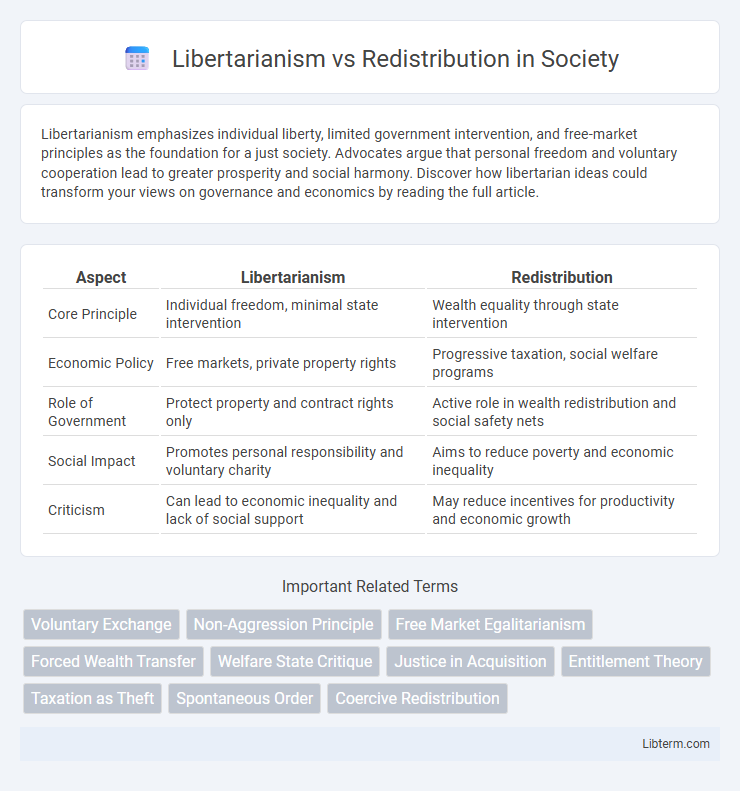
| Aspect | Libertarianism | Redistribution |
|---|---|---|
| Core Principle | Individual freedom, minimal state intervention | Wealth equality through state intervention |
| Economic Policy | Free markets, private property rights | Progressive taxation, social welfare programs |
| Role of Government | Protect property and contract rights only | Active role in wealth redistribution and social safety nets |
| Social Impact | Promotes personal responsibility and voluntary charity | Aims to reduce poverty and economic inequality |
| Criticism | Can lead to economic inequality and lack of social support | May reduce incentives for productivity and economic growth |
Defining Libertarianism: Core Principles
Libertarianism centers on individual liberty, emphasizing minimal government intervention and the protection of private property rights. It advocates for a free-market economy where voluntary exchange and personal responsibility drive wealth distribution rather than state-imposed redistribution policies. Core principles include limited taxation, strong property rights, and the belief that economic outcomes should result from personal choices and market dynamics rather than government mandates.
Understanding Economic Redistribution
Economic redistribution involves reallocating wealth through taxation and social programs to reduce income inequality and provide public goods. Libertarianism opposes extensive redistribution, emphasizing individual property rights, minimal government intervention, and voluntary charity as means to address social welfare. The debate centers on balancing economic freedom with social equity, considering the effects on incentives, economic growth, and poverty alleviation.
Historical Contexts: Libertarianism and Redistribution
Libertarianism traces its roots to Enlightenment thinkers like John Locke, emphasizing individual property rights and minimal state intervention, contrasting sharply with redistribution policies that emerged prominently during the 20th century to address economic inequality and social welfare. Historical contexts reveal that libertarianism advocates for free markets and voluntary exchanges, opposing wealth redistribution as a form of coercive government interference. Redistribution gained momentum with the New Deal era and Keynesian economics, prioritizing state-led efforts to redistribute income through taxation and social programs to reduce poverty and stimulate economic stability.
Individual Freedom vs. Collective Welfare
Libertarianism emphasizes individual freedom, advocating minimal government intervention and prioritizing personal property rights and voluntary exchanges. Redistribution, rooted in collective welfare, seeks to reduce economic inequalities through taxation and social programs aimed at ensuring basic needs and social justice. The tension between these approaches centers on balancing maximum personal autonomy with the societal responsibility of equitable resource allocation.
Property Rights in Libertarian Thought
Libertarianism emphasizes strong property rights as a fundamental principle, asserting that individuals have the moral ownership of the fruits of their labor and voluntary exchanges. Redistribution is viewed as a violation of these rights since it involves coercive transfers of property from one individual to another without consent. This respect for property rights underpins libertarian opposition to state-enforced wealth redistribution policies.
Redistribution Mechanisms: Taxes and Transfers
Redistribution mechanisms primarily involve progressive taxation and targeted transfer payments designed to reduce income inequality and support vulnerable populations. Libertarianism critiques such mechanisms for undermining individual property rights and economic freedom, advocating minimal government intervention. Empirical studies indicate that while taxation and transfers can decrease poverty rates, excessive redistribution may dampen incentives for productivity and innovation.
Moral Arguments: Justice, Fairness, and Equality
Libertarianism emphasizes individual rights and justice as respecting personal freedom and property without forced redistribution, viewing it as morally unjust. Redistribution advocates argue fairness and equality require correcting economic disparities to ensure equal opportunities and social justice. Debates center on whether justice prioritizes individual ownership or collective well-being to achieve a fair society.
Economic Outcomes: Efficiency and Incentives
Libertarianism emphasizes minimal government intervention, arguing that market-driven economic outcomes maximize efficiency by preserving incentives for innovation, investment, and productivity. Redistribution policies can reduce economic efficiency by imposing higher taxes and altering incentives, potentially discouraging work and entrepreneurship. Empirical evidence shows that excessive redistribution may lead to slower economic growth, while targeted social programs can address inequality without significantly harming incentives.
Real-World Examples: Policy and Practice
Libertarianism emphasizes minimal government intervention and strong property rights, as seen in countries like Switzerland, where low taxation and deregulated markets promote individual freedom and economic growth. In contrast, redistribution policies in Nordic countries such as Sweden and Denmark utilize progressive taxation and extensive welfare programs to reduce inequality and support social safety nets. These real-world models highlight the trade-offs between fostering personal liberty through limited state control and achieving social equity via redistribution efforts.
Future Debates: Navigating Libertarianism and Redistribution
Future debates on libertarianism and redistribution will critically examine the balance between individual freedom and social equity, emphasizing the impact of policy on economic mobility and wealth concentration. Discussions will increasingly incorporate data on universal basic income pilots, tax reforms, and market-driven solutions to social safety nets, highlighting the nuanced trade-offs between minimal government intervention and targeted redistribution. Advancements in technology and shifting demographics will further shape arguments, with libertarian perspectives challenging redistribution policies on grounds of efficiency and autonomy while proponents advocate for equitable access to resources in evolving economies.
Libertarianism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com