A reference group influences your attitudes, behaviors, and perceptions by serving as a social benchmark for comparison. These groups shape consumer choices and preferences through shared values and norms. Explore how identifying your reference groups can impact your decisions throughout this article.
Table of Comparison
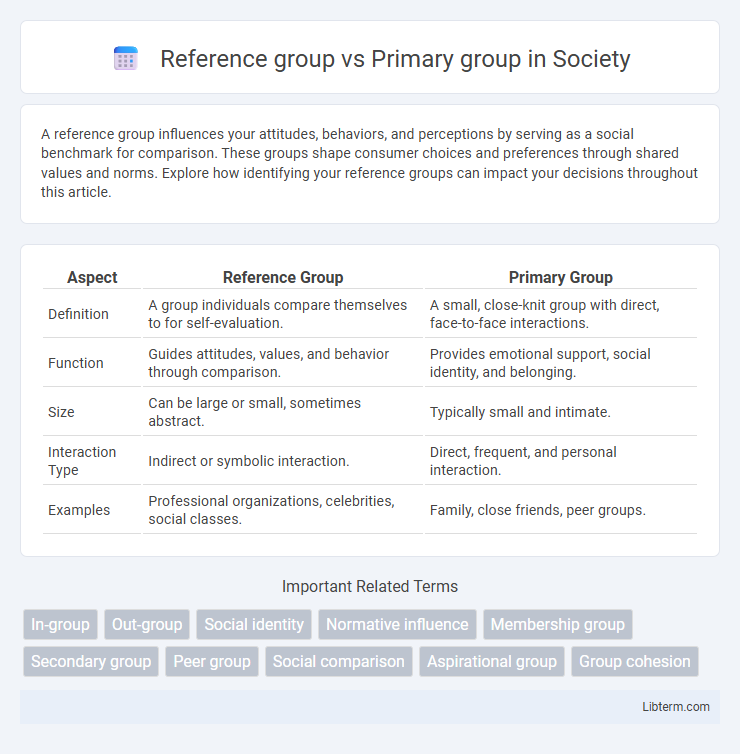
| Aspect | Reference Group | Primary Group |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A group individuals compare themselves to for self-evaluation. | A small, close-knit group with direct, face-to-face interactions. |
| Function | Guides attitudes, values, and behavior through comparison. | Provides emotional support, social identity, and belonging. |
| Size | Can be large or small, sometimes abstract. | Typically small and intimate. |
| Interaction Type | Indirect or symbolic interaction. | Direct, frequent, and personal interaction. |
| Examples | Professional organizations, celebrities, social classes. | Family, close friends, peer groups. |
Introduction to Reference Groups and Primary Groups
Reference groups serve as standards for individuals to evaluate their attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors, influencing social norms without requiring direct interaction. Primary groups consist of close, personal relationships characterized by frequent, face-to-face contact, emotional depth, and strong influence on socialization. Understanding the distinction helps in analyzing social dynamics and the impact of group affiliations on individual identity formation.
Definition of Reference Group
A reference group is a social group that individuals use as a benchmark for evaluating their own behaviors, attitudes, and values, influencing their decision-making and self-identity. Unlike a primary group, which involves direct, face-to-face interactions and emotional bonds, a reference group may include people or groups with whom individuals do not have close personal relationships. Marketers and sociologists study reference groups to understand consumer behavior and social conformity patterns.
Definition of Primary Group
A primary group is a small social group whose members share close, personal, and enduring relationships, typically characterized by frequent face-to-face interactions and emotional bonds. Unlike reference groups, which serve as standards for self-evaluation and behavior, primary groups provide a fundamental source of social support and identity formation. Examples include family and close friends, where intimacy and loyalty are central elements.
Key Differences Between Reference and Primary Groups
Reference groups influence an individual's attitudes and behaviors by serving as a standard for self-evaluation, while primary groups consist of close-knit, personal relationships providing direct social interaction and emotional support. Reference groups are often larger, more impersonal, and may not involve regular face-to-face interaction, whereas primary groups include family, close friends, and intimate social circles with frequent and meaningful contact. The key difference lies in the function: reference groups guide self-identity and aspirations, whereas primary groups fulfill fundamental social and emotional needs.
Characteristics of Reference Groups
Reference groups influence individual attitudes and behaviors by serving as a standard for self-evaluation and decision-making. They are characterized by indirect social interaction, a lack of close personal ties, and often include aspirational or comparative groups that individuals look up to or benchmark against. These groups provide norms, values, and expectations that shape consumer choices and social identity without requiring direct, ongoing personal relationships.
Characteristics of Primary Groups
Primary groups are characterized by close, personal, and enduring relationships, often found within family or close-knit social circles, where members engage in frequent, face-to-face interactions. These groups provide emotional support, socialization, and a strong sense of identity and belonging. In contrast, reference groups serve as standards for self-evaluation and social comparison without necessarily involving intimate or direct relationships.
Influence on Individual Behavior
Reference groups shape individual behavior by providing benchmarks for self-evaluation and influencing attitudes, values, and aspirations, often extending beyond personal connections. Primary groups, such as family and close friends, exert direct and intimate influence through frequent interactions, emotional support, and strong social bonds, deeply affecting personal identity and day-to-day behavior. The intensity and nature of influence differ, with primary groups fostering conformity through close-knit relationships, while reference groups guide behavior through perceived social norms and desired social status.
Examples of Reference and Primary Groups
Reference groups include professional associations, celebrity fan clubs, and cultural communities that individuals use as standards for evaluating their own behavior and attitudes. Primary groups consist of close-knit social circles such as family units, childhood friends, and intimate peer groups that provide emotional support and direct interaction. For instance, a teenager might look to a sports team as a reference group for style choices while relying on close friends as their primary group for daily emotional connection.
Role in Socialization Processes
Primary groups, such as family and close friends, play a crucial role in socialization processes by providing intimate relationships that shape an individual's values, norms, and identity from early childhood. Reference groups, which may include peers, coworkers, or social media influencers, influence socialization by serving as standards or benchmarks for behavior, attitudes, and self-evaluation. The interaction within primary groups fosters emotional support and direct social learning, while reference groups guide decision-making and social comparison in broader social contexts.
Conclusion: Significance in Social Dynamics
Primary groups, such as family and close friends, provide emotional support and foster strong, enduring social bonds crucial for individual identity formation. Reference groups, which individuals compare themselves to for self-evaluation and social standards, influence behavior, attitudes, and social norms within a broader community context. Understanding the interplay between primary and reference groups highlights their combined significance in shaping social dynamics, guiding social interactions, and influencing personal and collective identities.
Reference group Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com