Social boundaries define the limits of acceptable behavior within relationships and communities, shaping interactions and promoting mutual respect. Understanding these boundaries helps maintain personal space and emotional well-being, preventing conflicts and fostering healthy connections. Explore the full article to learn how recognizing and setting social boundaries can improve your relationships and social experiences.
Table of Comparison
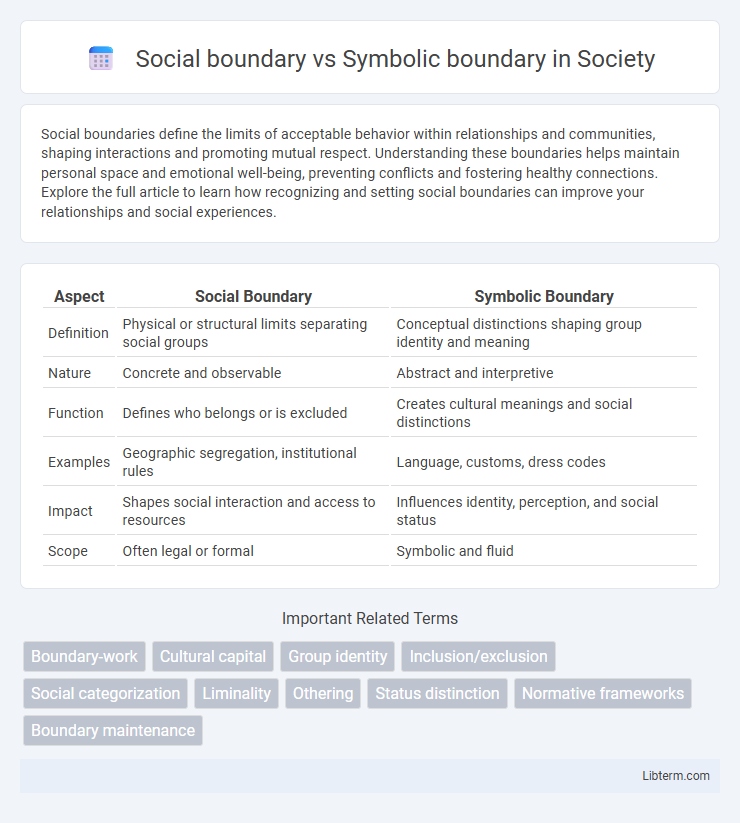
| Aspect | Social Boundary | Symbolic Boundary |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Physical or structural limits separating social groups | Conceptual distinctions shaping group identity and meaning |
| Nature | Concrete and observable | Abstract and interpretive |
| Function | Defines who belongs or is excluded | Creates cultural meanings and social distinctions |
| Examples | Geographic segregation, institutional rules | Language, customs, dress codes |
| Impact | Shapes social interaction and access to resources | Influences identity, perception, and social status |
| Scope | Often legal or formal | Symbolic and fluid |
Introduction to Social and Symbolic Boundaries
Social boundaries delineate group membership based on measurable factors like race, class, and occupation, shaping access to resources and social opportunities. Symbolic boundaries involve the cultural distinctions and value judgments that define insiders versus outsiders within social groups, influencing identity and social cohesion. Understanding both boundaries is essential for analyzing social inequality and group dynamics in sociological research.
Defining Social Boundaries
Social boundaries define tangible divisions between groups based on socioeconomic status, ethnicity, or geography, shaping access to resources and opportunities. Symbolic boundaries are abstract, created through cultural values, norms, and perceptions that distinguish "us" from "them" in social identity and group membership. These boundaries together influence social inequality and cohesion by regulating inclusion and exclusion within societies.
What Are Symbolic Boundaries?
Symbolic boundaries are the conceptual distinctions made by social actors to categorize objects, people, practices, and even time and space, which help define group identities and social order. They differ from social boundaries, which are the actual social differences and exclusionary practices that separate groups in society. These symbolic distinctions shape how people perceive and enact social divides, influencing social cohesion and conflict.
Key Differences Between Social and Symbolic Boundaries
Social boundaries refer to the explicit, tangible divisions between groups based on factors like class, race, or legal status, which regulate access to resources and social opportunities. Symbolic boundaries are the intangible distinctions made through cultural practices, values, and meanings that define group identity and social inclusion or exclusion. Key differences lie in social boundaries being structural and externally imposed, while symbolic boundaries are culturally constructed and shape perceptions and interactions within society.
Origins and Development of Social Boundaries
Social boundaries emerge from historical processes of social differentiation and exclusion, structuring group identities based on class, ethnicity, or race to influence access to resources and power. Symbolic boundaries, conceptualized by sociologist Michele Lamont, are the cultural distinctions and meanings that individuals and communities create to categorize people and practices, shaping perceptions of inclusion and exclusion. The development of social boundaries arises from material conditions and institutional practices, while symbolic boundaries evolve through cultural interpretations and social interactions, collectively reinforcing social hierarchies and group cohesion.
Formation and Function of Symbolic Boundaries
Symbolic boundaries form through cultural practices, language, and shared norms that distinguish groups by meanings and identities, transcending physical or social divisions. They function to create social cohesion within groups by defining insiders and outsiders, regulating behavior, and establishing moral distinctions that maintain group solidarity. These boundaries shape social structure by influencing access to resources and power through symbolic inclusion or exclusion.
Social Boundaries in Everyday Life
Social boundaries in everyday life define the tangible limits and divisions between groups based on observable characteristics such as class, race, gender, and occupation, shaping interactions and access to resources. These boundaries often manifest through social norms, physical segregation, or institutional policies that regulate inclusion and exclusion within communities. Understanding social boundaries is crucial for analyzing patterns of social inequality and how individuals navigate their social identities in daily contexts.
The Role of Symbolic Boundaries in Society
Symbolic boundaries define the conceptual distinctions that individuals and groups use to classify people, practices, and objects, shaping social identity and cultural meaning. These boundaries influence inclusion and exclusion by creating shared values and norms, thereby reinforcing group cohesion and social hierarchies. Unlike social boundaries, which are more tangible and institutionalized, symbolic boundaries operate at a cognitive and symbolic level, guiding social interactions and perception within society.
Interrelationships Between Social and Symbolic Boundaries
Social boundaries define tangible divisions between groups based on socioeconomic status, ethnicity, or geography, shaping access to resources and social opportunities. Symbolic boundaries involve the cultural distinctions people use to categorize others, such as values, beliefs, or lifestyles, influencing identity and social inclusion. The interrelationship between social and symbolic boundaries reinforces social stratification, as symbolic distinctions justify and perpetuate material inequalities embedded within social boundaries.
Implications for Social Integration and Exclusion
Social boundaries denote tangible divisions based on socioeconomic status, ethnicity, or geography that shape access to resources and opportunities, directly influencing social integration and exclusion. Symbolic boundaries involve cultural distinctions such as language, values, or norms that reinforce social identity and group membership, affecting inclusion through shared meanings and exclusion through perceived differences. Both types of boundaries interplay to construct social cohesion or fragmentation, with social boundaries limiting structural access and symbolic boundaries shaping collective perceptions and social solidarity.
Social boundary Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com