Digital literacy encompasses the essential skills needed to navigate, evaluate, and create information using digital technologies effectively. Mastering these competencies ensures your ability to participate fully in the modern digital world, enhancing communication, problem-solving, and critical thinking. Explore the rest of the article to discover practical strategies for boosting your digital literacy today.
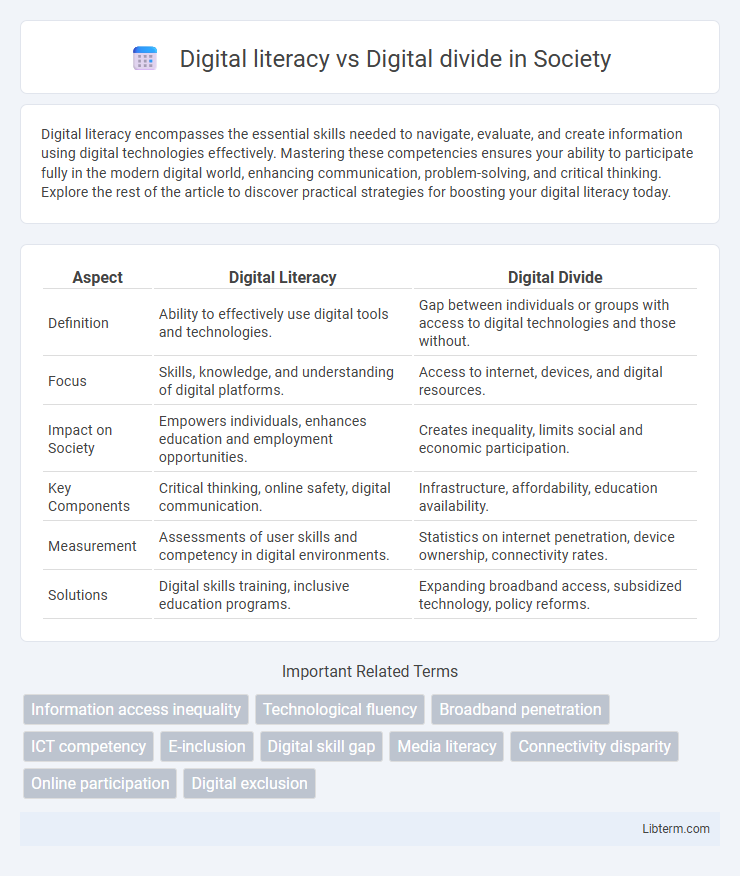
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Digital Literacy | Digital Divide |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ability to effectively use digital tools and technologies. | Gap between individuals or groups with access to digital technologies and those without. |
| Focus | Skills, knowledge, and understanding of digital platforms. | Access to internet, devices, and digital resources. |
| Impact on Society | Empowers individuals, enhances education and employment opportunities. | Creates inequality, limits social and economic participation. |
| Key Components | Critical thinking, online safety, digital communication. | Infrastructure, affordability, education availability. |
| Measurement | Assessments of user skills and competency in digital environments. | Statistics on internet penetration, device ownership, connectivity rates. |
| Solutions | Digital skills training, inclusive education programs. | Expanding broadband access, subsidized technology, policy reforms. |
Understanding Digital Literacy: Key Concepts
Digital literacy encompasses the essential skills and knowledge required to effectively navigate, evaluate, and create information using digital technologies, including critical thinking and online communication abilities. Understanding digital literacy involves recognizing competencies such as information retrieval, digital safety, ethical behavior, and technical proficiency across various devices and platforms. The digital divide highlights disparities in access to these skills and technological resources, often influenced by socioeconomic status, geographic location, and educational opportunities.
Defining the Digital Divide
The digital divide refers to the gap between individuals and communities that have access to modern information and communication technologies and those that do not. This divide often correlates with socioeconomic factors, geographic location, age, and education level, influencing disparities in digital literacy and online opportunities. Addressing the digital divide is essential for fostering inclusive digital literacy, ensuring equitable access to technology, and bridging knowledge gaps in the digital era.
The Relationship Between Digital Literacy and Digital Divide
Digital literacy significantly influences the digital divide by determining individuals' ability to effectively use technology and access digital resources. Increased digital literacy reduces the digital divide by empowering marginalized communities with essential skills for navigating online platforms, thereby promoting social inclusion. Limited digital literacy exacerbates the digital divide, creating barriers to education, employment, and civic participation in an increasingly digital world.
Factors Influencing Digital Literacy
Access to technology, quality of education, and socioeconomic status are key factors influencing digital literacy levels across different populations. Digital literacy depends heavily on both availability of digital devices and the ability to effectively use online resources for communication, learning, and problem-solving. The digital divide persists where disparities in infrastructure, affordability, and digital skills limit equitable access to digital tools and knowledge.
Causes and Consequences of the Digital Divide
The digital divide stems from unequal access to technology and the internet, driven by socioeconomic disparities, geographic location, and inadequate infrastructure. Limited digital literacy exacerbates this gap, restricting individuals' ability to utilize digital tools effectively, which in turn hampers educational and economic opportunities. Consequences of the digital divide include widened social inequality, reduced access to essential services, and diminished participation in the digital economy.
Digital Literacy in Education and Workforce
Digital literacy in education equips students with essential skills to navigate, evaluate, and create information using digital technologies, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving abilities vital for academic success and lifelong learning. In the workforce, digital literacy enhances employee productivity by enabling efficient use of digital tools, supporting remote work, and driving innovation in various industries such as technology, healthcare, and finance. Narrowing the digital divide requires targeted policies to ensure equitable access to digital literacy programs, bridging gaps caused by socioeconomic disparities and preparing all individuals for competitive participation in the digital economy.
Impact of the Digital Divide on Communities
The digital divide significantly impacts communities by limiting access to essential online resources such as education, healthcare, and employment opportunities, which exacerbates social inequalities. Inadequate digital literacy deepens this divide, as individuals lacking basic technological skills struggle to engage effectively in the digital economy. Bridging this gap requires targeted investments in infrastructure and training programs to enhance digital inclusion and foster equitable community development.
Bridging the Gap: Strategies to Foster Digital Literacy
Bridging the digital divide requires comprehensive strategies that enhance digital literacy through targeted education programs, accessible technology infrastructure, and community-based training initiatives. Implementing inclusive digital skills workshops and providing affordable internet access empower underserved populations to navigate digital platforms effectively. Collaboration between governments, nonprofits, and private sectors boosts equitable technology adoption and reduces disparities in digital competency.
Policy Solutions for Reducing the Digital Divide
Policy solutions for reducing the digital divide prioritize expanding affordable broadband access and investing in digital literacy programs across underserved communities. Governments implement initiatives that provide subsidized devices, enhance digital skills training in schools, and support public Wi-Fi hotspots to increase connectivity. Emphasizing equitable technology infrastructure and inclusive education policies addresses disparities in digital literacy and access, fostering broader social and economic participation.
Future Trends in Digital Inclusion and Literacy
Emerging trends in digital inclusion emphasize bridging the digital divide through expanded access to affordable high-speed internet and tailored digital literacy programs targeting underserved communities. Advances in adaptive learning technologies and AI-driven platforms are enhancing personalized digital skills training, ensuring equitable competency development across diverse populations. Policy initiatives increasingly focus on integrating digital literacy into formal education and lifelong learning frameworks to prepare individuals for an evolving digital economy.
Digital literacy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com