Sectarianism fuels divisions by emphasizing differences between religious or social groups, often leading to conflict and social fragmentation. Understanding its roots and impacts is crucial for promoting tolerance and peaceful coexistence in diverse communities. Discover more about how sectarianism shapes societies and what can be done to address it in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
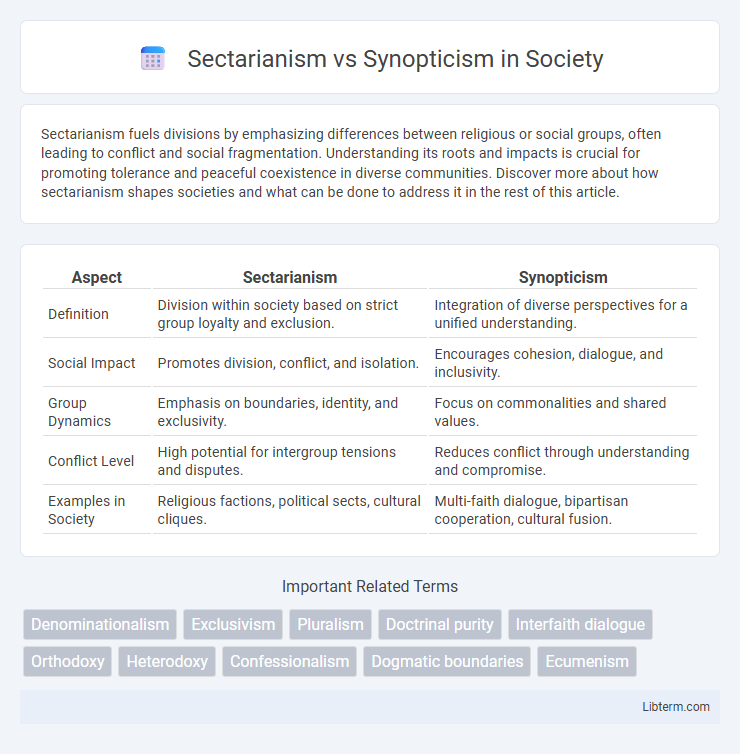
| Aspect | Sectarianism | Synopticism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Division within society based on strict group loyalty and exclusion. | Integration of diverse perspectives for a unified understanding. |
| Social Impact | Promotes division, conflict, and isolation. | Encourages cohesion, dialogue, and inclusivity. |
| Group Dynamics | Emphasis on boundaries, identity, and exclusivity. | Focus on commonalities and shared values. |
| Conflict Level | High potential for intergroup tensions and disputes. | Reduces conflict through understanding and compromise. |
| Examples in Society | Religious factions, political sects, cultural cliques. | Multi-faith dialogue, bipartisan cooperation, cultural fusion. |
Understanding Sectarianism: Definition and Origins
Sectarianism refers to rigid allegiance to a particular sect or group, often leading to social, religious, or political divisions. Originating from historical conflicts and ideological differences, sectarianism manifests in exclusionary practices and identity-based loyalty. Understanding its roots involves examining how sects form distinct boundaries to maintain group coherence and cultural distinctiveness.
Synopticism Explained: A Comprehensive Overview
Synopticism refers to the study and comparative analysis of the Synoptic Gospels--Matthew, Mark, and Luke--to identify their similarities and differences in content, structure, and wording. This approach reveals insights into the shared sources, editorial practices, and theological emphases used by the evangelists, highlighting the interconnected nature of these texts within the New Testament. Unlike sectarianism, which emphasizes distinct religious group identities and doctrines, synopticism focuses on textual harmony and divergence to understand early Christian narrative development.
Core Differences Between Sectarianism and Synopticism
Sectarianism emphasizes strict adherence to specific religious or ideological doctrines, often leading to division and exclusivity within a community. Synopticism promotes the comparative study and synthesis of diverse perspectives, aiming to identify common themes and foster inclusivity. The core difference lies in sectarianism's focus on separation and purity versus synopticism's pursuit of integration and broad understanding.
Historical Development of Sectarian and Synoptic Perspectives
Sectarianism emerged in the early religious landscape as distinct groups formed around exclusive doctrines and rigid boundaries, often leading to conflict and separation. Synopticism developed later as a scholarly approach to harmonize and compare multiple sources, particularly in religious texts, emphasizing similarities and shared teachings. The historical development of these perspectives reflects a shift from fragmentation toward synthesis, influencing theological discourse and interpretive methodologies.
Social and Cultural Impacts of Sectarianism
Sectarianism fosters division by promoting exclusive group identities that undermine social cohesion and exacerbate conflicts within communities. This fragmentation often leads to cultural isolation, inhibiting intercultural dialogue and diminishing shared social values. The persistence of sectarian tensions can hinder economic development and perpetuate cycles of mistrust and violence in affected regions.
Benefits and Challenges of Synoptic Approaches
Synoptic approaches offer the benefit of integrating diverse perspectives into a unified framework, enhancing comprehensive understanding across multiple disciplines. They facilitate holistic analysis, enabling the identification of interconnected patterns that sectarian methods might overlook. Challenges include the complexity of synthesizing heterogeneous data and potential dilution of specialized insights, which can complicate consensus-building and precise application in specialized fields.
Case Studies: Sectarianism and Synopticism in Practice
Case studies of sectarianism reveal rigid ideological divisions within religious or political movements that often lead to exclusion and conflict, as seen in the fragmentation of early Christianity and Shia-Sunni splits in Islam. Synopticism in practice emphasizes comparative analyses and integrated perspectives, demonstrated by scholars who examine the Synoptic Gospels to highlight shared narratives and theological themes, fostering a holistic understanding of texts. These approaches showcase how sectarianism enforces boundaries, whereas synopticism promotes synthesis and coherence across diverse sources.
Sectarianism vs. Synopticism in Modern Society
Sectarianism in modern society often fosters division and exclusion by emphasizing rigid group identities and ideological purity, whereas synopticism promotes comprehensive understanding through the integration of diverse perspectives. This contrast impacts social cohesion, with sectarianism leading to polarization and synopticism encouraging dialogue and collective problem-solving. The rise of digital media amplifies sectarian narratives, but also provides platforms for synoptic discourse by connecting disparate communities and ideas globally.
Strategies for Promoting Synopticism Over Sectarianism
Promoting synopticism over sectarianism requires fostering inclusive dialogue that emphasizes shared values and common goals among diverse groups, mitigating divisive narratives. Educational programs and community initiatives designed to highlight interconnected histories and mutual benefits encourage empathy and collective identity formation. Implementing policies that facilitate cross-cultural collaboration and representation strengthens social cohesion, reducing sectarian tensions through sustained interaction and understanding.
Towards a More Inclusive Future: Lessons from Both Sides
Sectarianism fosters division by emphasizing exclusive identities and rigid boundaries, while synopticism promotes inclusivity through integrating diverse perspectives and shared values. Embracing synoptic approaches encourages dialogue, mutual respect, and cooperation across different groups, creating a foundation for social cohesion. Lessons from both reveal the importance of balancing distinctiveness with unity to build a more inclusive future in pluralistic societies.
Sectarianism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com