Folkways are the informal norms and everyday customs that guide social behavior within communities, shaping cultural identity and maintaining social order. They influence Your interactions by defining what is considered polite or acceptable without strict enforcement. Explore the rest of the article to understand how folkways impact societal cohesion and cultural continuity.
Table of Comparison
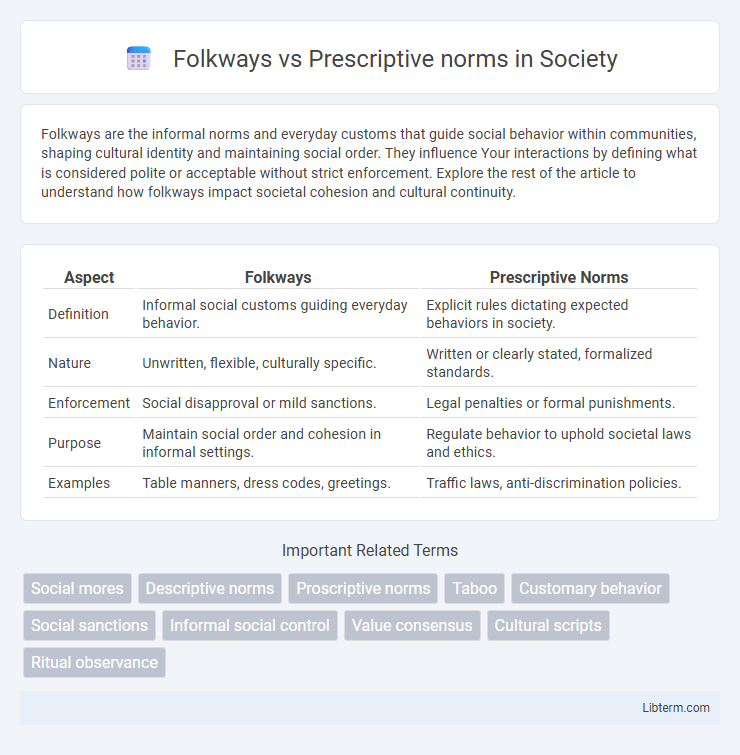
| Aspect | Folkways | Prescriptive Norms |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Informal social customs guiding everyday behavior. | Explicit rules dictating expected behaviors in society. |
| Nature | Unwritten, flexible, culturally specific. | Written or clearly stated, formalized standards. |
| Enforcement | Social disapproval or mild sanctions. | Legal penalties or formal punishments. |
| Purpose | Maintain social order and cohesion in informal settings. | Regulate behavior to uphold societal laws and ethics. |
| Examples | Table manners, dress codes, greetings. | Traffic laws, anti-discrimination policies. |
Introduction to Folkways and Prescriptive Norms
Folkways are informal social rules and customs that guide everyday behavior, such as dress codes and table manners, reflecting the cultural values of a community without strict enforcement. Prescriptive norms specify expected behaviors and set clear standards for conduct, often backed by social sanctions or formal rules to ensure compliance. Understanding the distinction between folkways and prescriptive norms highlights how societies regulate behavior through both subtle customs and explicit directives.
Defining Folkways: Everyday Social Customs
Folkways encompass everyday social customs that guide routine behavior within a community, such as dress codes, greetings, and dining etiquette. Unlike prescriptive norms, which dictate strict rules and punish unacceptable actions, folkways are informal expectations that facilitate smooth social interactions without severe sanctions. These customs evolve naturally and reflect cultural values, promoting social cohesion through shared, habitual practices.
Understanding Prescriptive Norms: Enforced Social Rules
Prescriptive norms dictate explicit behaviors that society enforces through rewards and punishments to maintain order and cohesion. These social rules guide actions deemed necessary or forbidden, ensuring conformity within communities and institutions. Enforcement mechanisms often include laws, regulations, or formal sanctions that uphold collective expectations and discourage deviance.
Origins and Development of Folkways
Folkways originated from informal social interactions and shared cultural practices within communities, evolving through everyday customs rather than formal regulations. These norms develop gradually over time, shaped by tradition, habit, and collective consensus, guiding routine behavior without explicit enforcement. Unlike prescriptive norms, folkways lack strict moral significance and tend to regulate manners and conventions within specific cultural contexts.
Formation and Evolution of Prescriptive Norms
Prescriptive norms form through social consensus about appropriate behaviors that are often codified in laws, rules, or ethical standards, evolving in response to cultural values, societal needs, and shifts in collective morality. Unlike folkways, which are informal customs guiding everyday behavior without strict enforcement, prescriptive norms carry explicit sanctions or rewards to ensure compliance and social order. Over time, changes in political, economic, and technological contexts drive the adaptation or creation of new prescriptive norms to address emerging challenges and maintain societal cohesion.
Key Differences Between Folkways and Prescriptive Norms
Folkways are informal social customs that guide everyday behavior, often rooted in tradition and cultural practices, whereas prescriptive norms are explicit rules that dictate what individuals should do to conform to societal expectations. Folkways typically incur mild social sanctions if violated, such as disapproval or awkwardness, while breaching prescriptive norms can result in stronger consequences like punishment or legal action. The key difference lies in the level of formal enforcement and the clarity of expectations, with prescriptive norms being more rigid and codified compared to the flexible and culturally varied nature of folkways.
Social Functions of Folkways vs. Prescriptive Norms
Folkways serve the social function of maintaining everyday social order through informal behaviors and customary practices that foster group cohesion without strict enforcement. Prescriptive norms guide behaviors by providing explicit rules and standards, often backed by formal sanctions, to regulate actions and ensure conformity within societies. Together, folkways and prescriptive norms balance flexibility and control, enabling societies to function smoothly by guiding both informal interactions and formal conduct.
Real-World Examples of Folkways
Folkways are informal social norms that guide everyday behavior, such as greeting customs and dress codes, exemplified by the American practice of shaking hands when meeting someone. Unlike prescriptive norms, which dictate strict rules or laws like traffic regulations, folkways allow for flexibility and vary across cultures. For instance, in Japan, bowing is a common folkway showing respect, demonstrating how these norms shape social interactions without legal enforcement.
Common Examples of Prescriptive Norms
Prescriptive norms dictate specific behaviors deemed appropriate or required in social contexts, such as laws mandating seatbelt use, workplace dress codes, and etiquette rules like saying "please" and "thank you." These norms carry explicit expectations and often formal consequences for non-compliance, distinguishing them from folkways, which are informal customs without strict enforcement. Common examples include traffic regulations, school conduct codes, and professional standards that guide acceptable conduct in daily life and organizational settings.
Impact on Society: Folkways and Prescriptive Norms
Folkways shape everyday social interactions by guiding informal behaviors and fostering community cohesion through unwritten cultural rules. Prescriptive norms impose explicit rules and often carry moral or legal consequences, significantly influencing societal order and compliance. The interplay between folkways and prescriptive norms helps balance social flexibility with structured governance, impacting social harmony and behavioral expectations.
Folkways Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com