Educational organizations play a vital role in shaping learning environments that foster growth, innovation, and accessibility for diverse student populations. These institutions implement strategic programs and leverage resources to enhance curriculum quality and support professional development for educators. Explore the rest of the article to discover how your educational organization can maximize impact and drive student success.
Table of Comparison
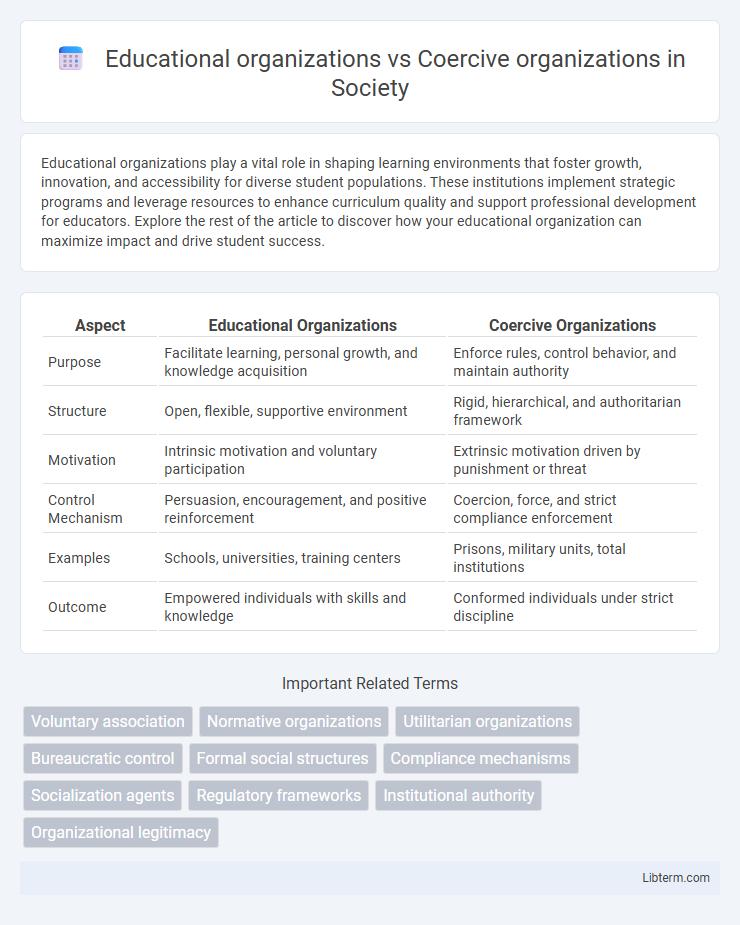
| Aspect | Educational Organizations | Coercive Organizations |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Facilitate learning, personal growth, and knowledge acquisition | Enforce rules, control behavior, and maintain authority |
| Structure | Open, flexible, supportive environment | Rigid, hierarchical, and authoritarian framework |
| Motivation | Intrinsic motivation and voluntary participation | Extrinsic motivation driven by punishment or threat |
| Control Mechanism | Persuasion, encouragement, and positive reinforcement | Coercion, force, and strict compliance enforcement |
| Examples | Schools, universities, training centers | Prisons, military units, total institutions |
| Outcome | Empowered individuals with skills and knowledge | Conformed individuals under strict discipline |
Defining Educational Organizations
Educational organizations are institutions designed to facilitate learning and knowledge acquisition through structured curricula, classrooms, and instructional methods aimed at intellectual and personal development. They prioritize voluntary participation, collaborative environments, and intrinsic motivation, contrasting with coercive organizations that rely on control, mandates, and enforced compliance. Examples include schools, universities, and training centers, which emphasize empowerment and skill-building rather than domination or punishment.
Understanding Coercive Organizations
Coercive organizations rely on formal authority and strict enforcement mechanisms to compel compliance, often using rules, punishments, and surveillance to maintain control. These organizations prioritize obedience and conformity, creating an environment where individual autonomy is limited and dissent is discouraged. Understanding coercive organizations involves analyzing their hierarchical structures, power dynamics, and legal frameworks that institutionalize control and restrict behavioral freedom.
Core Objectives: Education vs Compliance
Educational organizations prioritize fostering knowledge acquisition, critical thinking, and intellectual growth to empower individuals and promote lifelong learning. Coercive organizations emphasize enforcing compliance, adherence to rules, and maintaining order through authority and control mechanisms. The core objective of educational institutions centers on development and enlightenment, while coercive entities focus on discipline and conformity.
Structural Differences: Hierarchies and Authority
Educational organizations typically feature decentralized hierarchies that emphasize collaborative decision-making and autonomy among faculty and staff to foster innovation and academic freedom. Coercive organizations, in contrast, maintain rigid, top-down authority structures designed to enforce strict compliance, control, and uniformity in behavior. These structural differences reflect varying objectives: educational organizations prioritize intellectual development and flexibility, while coercive organizations focus on obedience and discipline through clear chains of command.
Methods of Influence and Control
Educational organizations employ methods of influence through knowledge dissemination, persuasion, and voluntary participation, fostering critical thinking and intrinsic motivation. Coercive organizations rely on force, threats, and compliance mechanisms to enforce rules and maintain control, often using surveillance and punishment to ensure adherence. The contrasting approaches reflect differing goals: educational bodies aim to cultivate understanding and growth, while coercive entities prioritize obedience and order.
Impact on Individual Autonomy
Educational organizations foster individual autonomy by promoting critical thinking, self-directed learning, and personal growth through supportive environments and participatory decision-making. Coercive organizations limit autonomy by enforcing strict rules, control mechanisms, and compliance through hierarchical authority and surveillance, often suppressing creativity and independent thought. The contrasting impacts on individual autonomy highlight the importance of organizational design in shaping personal freedom and empowerment within institutional settings.
Social Roles and Functions
Educational organizations primarily focus on the socialization and development of individuals by imparting knowledge, skills, and cultural values essential for societal participation. They shape social roles by preparing individuals for specific occupational and civic responsibilities, fostering social integration and collaboration. Coercive organizations maintain social order through control and regulation, often enforcing compliance with laws and rules, thus fulfilling functions related to discipline, security, and conformity within society.
Outcomes for Members
Educational organizations foster voluntary learning environments that enhance members' knowledge, skills, and personal development, leading to improved career opportunities and lifelong growth. Coercive organizations impose restrictive structures that limit individual autonomy, often resulting in compliance-driven behaviors and diminished personal motivation. Members of educational organizations generally experience higher satisfaction and empowerment, while those in coercive settings may face stress and reduced well-being.
Case Studies: Schools vs Prisons
Case studies comparing schools and prisons reveal marked differences in organizational goals and operational methods; schools prioritize educational development and knowledge acquisition through supportive environments, while prisons emphasize control, security, and compliance within rigid, punitive structures. Educational organizations implement individualized learning plans and foster cognitive and social skills, enhancing students' engagement and personal growth, whereas coercive organizations rely on strict rules and surveillance to manage inmate behavior and maintain order. Data from studies highlight how schools' collaborative culture contrasts with the hierarchical, disciplinary nature of prisons, impacting the psychological well-being and future outcomes of their populations.
Societal Implications and Ethical Considerations
Educational organizations promote autonomy and critical thinking, fostering societal progress through knowledge dissemination and ethical empowerment. Coercive organizations rely on enforced compliance, often limiting individual freedoms and raising ethical concerns about oppression and human rights violations. The societal implications include differing impacts on social cohesion, with educational entities enhancing democratic values while coercive entities may perpetuate control and social stratification.
Educational organizations Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com