Government welfare programs provide essential support for individuals and families facing financial hardships, ensuring access to basic needs such as food, housing, and healthcare. These programs aim to reduce poverty, promote economic stability, and improve overall quality of life. Explore the rest of this article to understand how these initiatives impact your community and the options available to you.
Table of Comparison
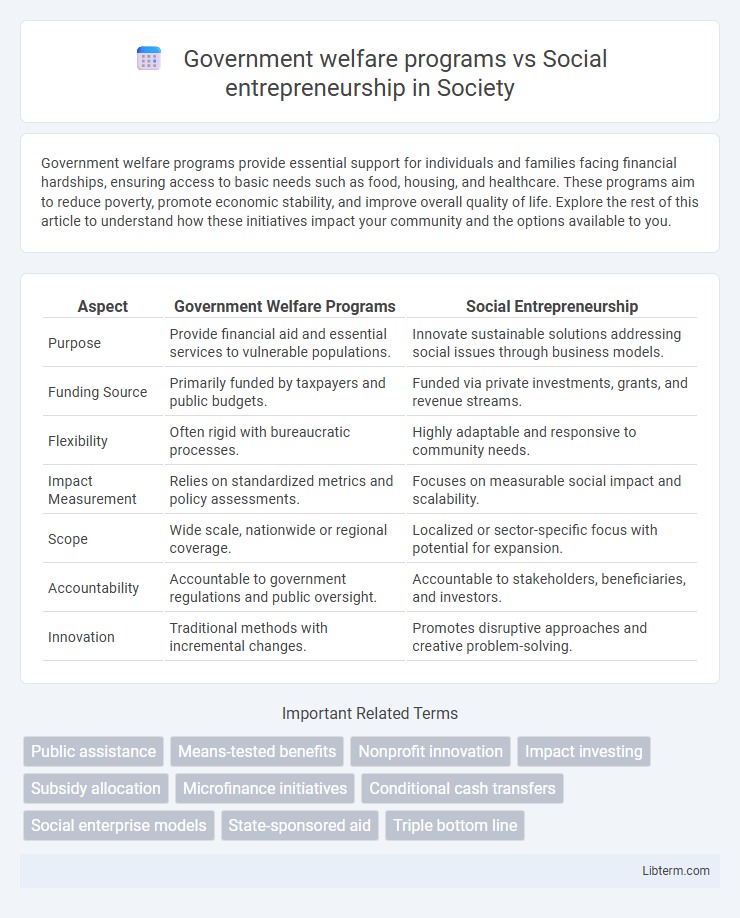
| Aspect | Government Welfare Programs | Social Entrepreneurship |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Provide financial aid and essential services to vulnerable populations. | Innovate sustainable solutions addressing social issues through business models. |
| Funding Source | Primarily funded by taxpayers and public budgets. | Funded via private investments, grants, and revenue streams. |
| Flexibility | Often rigid with bureaucratic processes. | Highly adaptable and responsive to community needs. |
| Impact Measurement | Relies on standardized metrics and policy assessments. | Focuses on measurable social impact and scalability. |
| Scope | Wide scale, nationwide or regional coverage. | Localized or sector-specific focus with potential for expansion. |
| Accountability | Accountable to government regulations and public oversight. | Accountable to stakeholders, beneficiaries, and investors. |
| Innovation | Traditional methods with incremental changes. | Promotes disruptive approaches and creative problem-solving. |
Understanding Government Welfare Programs
Government welfare programs deliver structured financial assistance and social services to vulnerable populations, aiming to reduce poverty and promote social equity through initiatives like unemployment benefits, food stamps, and healthcare subsidies. These programs are funded and regulated by public agencies, ensuring a standardized approach to welfare distribution across regions. Understanding their mechanisms helps evaluate the effectiveness and reach of public support compared to the innovative and community-driven models seen in social entrepreneurship.
Defining Social Entrepreneurship
Social entrepreneurship involves creating innovative solutions to address social issues by blending business principles with social missions, contrasting with government welfare programs that rely on public funding to provide direct aid and services. Unlike government initiatives, social entrepreneurs focus on sustainable impact through market-driven approaches, generating revenue while solving community problems. This approach emphasizes scalability, efficiency, and self-sufficiency to complement or replace traditional welfare systems.
Objectives of Welfare Programs vs Social Enterprises
Government welfare programs primarily aim to provide immediate relief and social safety nets for vulnerable populations by addressing basic needs such as healthcare, housing, and income support. Social enterprises focus on creating sustainable social impact by combining business methods with social objectives, promoting innovation and self-sufficiency through market-driven solutions. While welfare programs emphasize redistribution and support, social enterprises prioritize empowerment and long-term community development.
Funding Sources and Financial Models
Government welfare programs primarily rely on tax revenues and government budgets to provide direct financial support, ensuring stable and large-scale funding for social services. Social entrepreneurship leverages diverse financial models including impact investments, grants, crowdfunding, and revenue-generating activities to achieve sustainability and scalability. While government funding emphasizes accountability and policy alignment, social entrepreneurship prioritizes innovation and market-driven solutions to address social issues.
Measuring Social Impact and Outcomes
Measuring social impact and outcomes in government welfare programs often relies on standardized metrics such as benefit uptake, poverty rate reduction, and service delivery efficiency to evaluate effectiveness. Social entrepreneurship emphasizes innovative, scalable solutions with impact measurement through social return on investment (SROI), beneficiary feedback, and long-term community empowerment indicators. Combining quantitative data with qualitative insights enhances the comprehensive assessment of both models' contributions to social well-being.
Scalability and Sustainability of Approaches
Government welfare programs often rely on large-scale funding and regulatory frameworks to provide widespread social support but can face challenges in long-term sustainability due to budget constraints and bureaucratic inefficiencies. Social entrepreneurship employs innovative business models focused on sustainable impact and scalability by reinvesting profits and adapting quickly to community needs. The synergy of government resources with the agility of social enterprises can enhance both scalability and sustainability in addressing social issues effectively.
Accountability and Transparency Issues
Government welfare programs often face challenges with accountability and transparency due to bureaucratic inefficiencies and limited oversight mechanisms, leading to misallocation of resources and corruption risks. Social entrepreneurship emphasizes transparent operational models and direct impact measurement, fostering greater accountability through stakeholder engagement and innovative reporting tools. Enhanced transparency in social enterprises typically drives higher trust and more efficient resource utilization compared to traditional government welfare systems.
Integration with Local Communities
Government welfare programs often rely on top-down approaches that may lack deep integration with local communities, limiting their effectiveness in addressing specific local needs. Social entrepreneurship emphasizes grassroots engagement and collaborative problem-solving, fostering stronger community involvement and sustainable impact. This localized integration enhances responsiveness and empowerment, creating tailored solutions that government programs sometimes struggle to achieve.
Addressing Root Causes vs Short-Term Relief
Government welfare programs primarily provide short-term relief through direct financial assistance and essential services to vulnerable populations, addressing immediate needs such as food, housing, and healthcare. In contrast, social entrepreneurship targets the root causes of social issues by developing innovative, sustainable business models that empower communities and foster long-term economic self-sufficiency. This approach emphasizes systemic change and scalability, often complementing government efforts by creating social value beyond temporary aid.
Future Trends: Collaboration and Innovation
Government welfare programs are increasingly integrating with social entrepreneurship to leverage innovative solutions for complex social issues, enhancing resource efficiency and impact measurement. Future trends emphasize public-private partnerships that foster co-creation of services, utilizing data analytics and digital platforms to tailor interventions and scale successful models. Collaborative ecosystems combining policy support, community engagement, and entrepreneurial agility are set to redefine sustainable social impact frameworks globally.
Government welfare programs Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com