Egalitarianism promotes the principle that all individuals deserve equal rights and opportunities regardless of race, gender, or socioeconomic status. This philosophy underpins social justice movements and influences policies aimed at reducing disparities in education, healthcare, and income. Explore the article to understand how egalitarianism shapes modern society and what it means for your role in fostering equality.
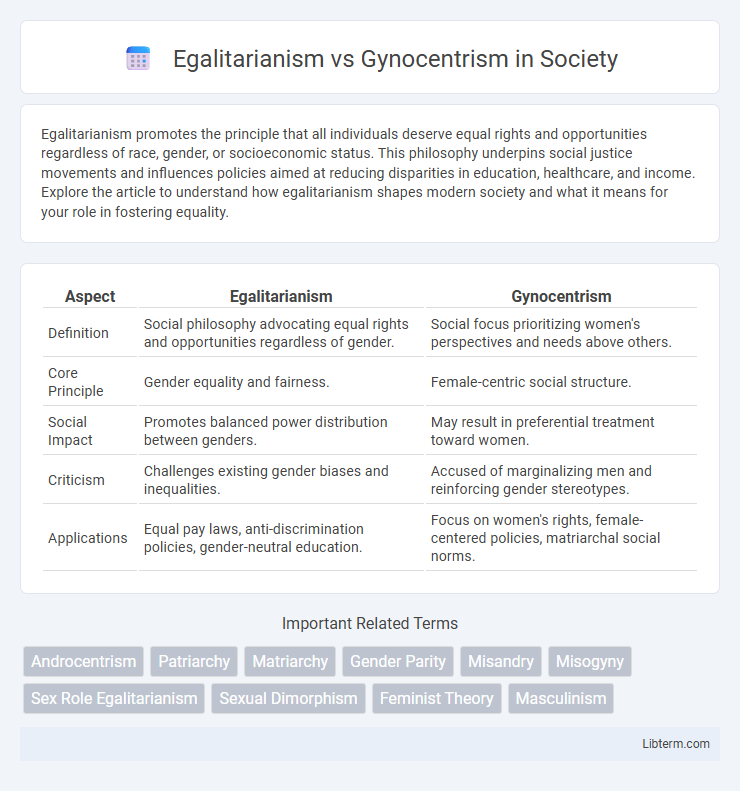
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Egalitarianism | Gynocentrism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Social philosophy advocating equal rights and opportunities regardless of gender. | Social focus prioritizing women's perspectives and needs above others. |
| Core Principle | Gender equality and fairness. | Female-centric social structure. |
| Social Impact | Promotes balanced power distribution between genders. | May result in preferential treatment toward women. |
| Criticism | Challenges existing gender biases and inequalities. | Accused of marginalizing men and reinforcing gender stereotypes. |
| Applications | Equal pay laws, anti-discrimination policies, gender-neutral education. | Focus on women's rights, female-centered policies, matriarchal social norms. |
Defining Egalitarianism: Principles and Perspectives
Egalitarianism advocates for equal rights, responsibilities, and opportunities regardless of gender, emphasizing fairness and nondiscrimination in all social, political, and economic spheres. It challenges systemic biases by promoting balanced power dynamics and the dismantling of privilege linked to gender hierarchies. Egalitarian principles prioritize inclusion, equal treatment, and meritocracy to foster a just society where all individuals can thrive without gender-based disparities.
Understanding Gynocentrism: Key Concepts
Gynocentrism centers on prioritizing women's perspectives and experiences, often influencing social structures and cultural norms to favor female interests. This concept contrasts with egalitarianism, which advocates for equal rights and opportunities regardless of gender. Understanding gynocentrism involves examining its impact on policy-making, social expectations, and gender dynamics within various societies.
Historical Roots of Egalitarian Beliefs
Egalitarianism traces its roots to Enlightenment thinkers such as John Locke and Jean-Jacques Rousseau, who advocated for equal rights and social contracts that emphasize individual liberty and fairness. This philosophical foundation challenged traditional hierarchies by promoting the idea that all humans deserve equal treatment regardless of gender, race, or class. In contrast, gynocentrism historically centers social and cultural norms around women's experiences and interests, often resulting in gender-specific roles rather than universal equality.
The Rise and Influence of Gynocentric Societies
Gynocentric societies prioritize women's perspectives, values, and interests, often leading to social structures that emphasize female well-being and empowerment. This rise stems from historical shifts towards recognizing gender-based injustices and advocating for women's rights, influencing policies and cultural norms. The impact of gynocentrism contrasts with egalitarianism by centering gender-specific experiences, which can reshape family dynamics, legal frameworks, and social expectations.
Egalitarianism vs Gynocentrism: Core Differences
Egalitarianism promotes equal rights and opportunities for all genders, emphasizing fairness and non-discrimination across social, economic, and political spheres. Gynocentrism centers on prioritizing women's needs and perspectives, often advocating for female-focused policies and cultural norms. The core difference lies in egalitarianism's universal approach to gender equality versus gynocentrism's emphasis on elevating women's interests, sometimes leading to perceived imbalances in gender dynamics.
Gender Roles and Social Expectations
Egalitarianism advocates for equal rights and responsibilities between genders, challenging traditional gender roles and promoting balanced social expectations in workplaces and households. Gynocentrism emphasizes prioritizing women's needs and perspectives, often reinforcing conventional female-centric social roles. Understanding the impact of these frameworks on gender dynamics is crucial for addressing disparities in power, opportunity, and cultural norms.
Impacts on Policy and Legislation
Egalitarianism promotes equal rights and opportunities regardless of gender, influencing policies that advocate gender-neutral laws and anti-discrimination measures. Gynocentrism prioritizes women's experiences and needs, often leading to legislation favoring female welfare, such as maternity benefits and protections against gender-based violence. These contrasting frameworks shape the balance between equality-driven reforms and gender-specific policies in legal systems worldwide.
Cultural Narratives and Media Representations
Cultural narratives often frame egalitarianism as a pursuit of equal rights and opportunities for all genders, promoting balanced power dynamics and mutual respect. In contrast, gynocentrism places female experiences and perspectives at the center, which media representations amplify through stories highlighting women's struggles and triumphs. These contrasting portrayals influence societal attitudes, shaping public discourse around gender roles, equity policies, and the prioritization of gender-related issues in cultural contexts.
Critiques and Controversies
Egalitarianism faces critiques for overlooking historical gender disparities by advocating equal treatment without addressing systemic inequities, while gynocentrism is contested for prioritizing women's interests, sometimes at the expense of men's rights and gender balance. Critics argue gynocentrism can perpetuate gender bias by emphasizing female perspectives in social policies, leading to controversial debates over fairness in legal and social frameworks. Both perspectives spark controversy in discussions on gender equality, as they challenge societal norms and highlight the complexity of achieving true gender justice.
Toward a Balanced Approach: Future Directions
Egalitarianism promotes equal rights and opportunities regardless of gender, challenging gynocentrism's focus on prioritizing women's perspectives and needs. Future directions call for integrating nuanced policies that recognize gender-specific experiences without privileging one gender over another, fostering fairness and mutual respect. Research on balanced frameworks emphasizes collaborative dialogue and institutional reforms targeting systemic biases within all genders.
Egalitarianism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com