A physical boundary refers to any tangible, visible barrier that separates spaces, such as walls, fences, or natural features like rivers and mountains. These boundaries play a crucial role in defining personal space, property limits, and organizational zones, enhancing security and privacy. Explore the rest of the article to understand how physical boundaries impact your environment and interactions.
Table of Comparison
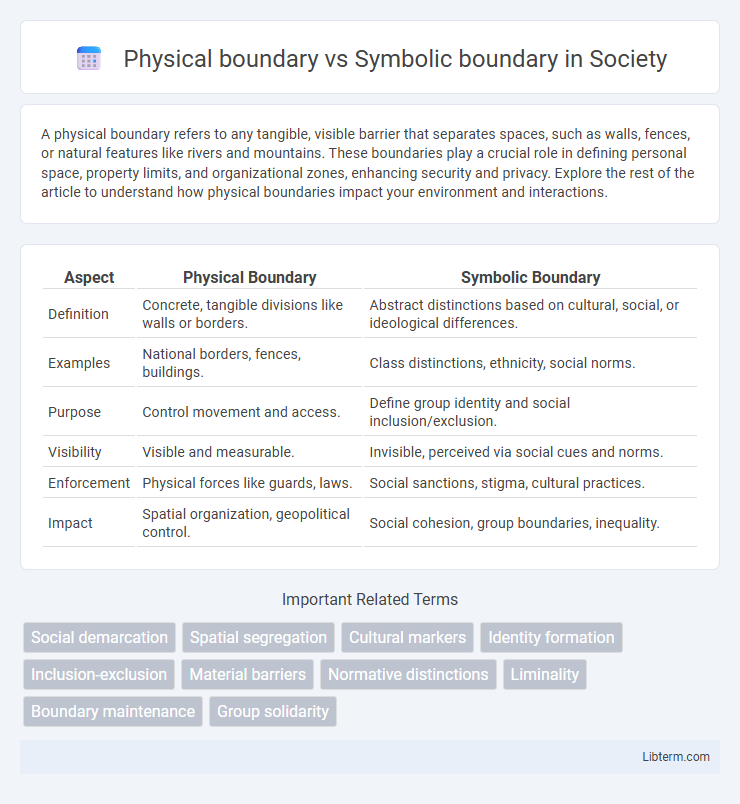
| Aspect | Physical Boundary | Symbolic Boundary |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Concrete, tangible divisions like walls or borders. | Abstract distinctions based on cultural, social, or ideological differences. |
| Examples | National borders, fences, buildings. | Class distinctions, ethnicity, social norms. |
| Purpose | Control movement and access. | Define group identity and social inclusion/exclusion. |
| Visibility | Visible and measurable. | Invisible, perceived via social cues and norms. |
| Enforcement | Physical forces like guards, laws. | Social sanctions, stigma, cultural practices. |
| Impact | Spatial organization, geopolitical control. | Social cohesion, group boundaries, inequality. |
Understanding Physical and Symbolic Boundaries
Physical boundaries are tangible and visible markers such as walls, fences, or geographical features that delineate distinct spaces or territories. Symbolic boundaries, on the other hand, represent intangible divisions created by cultural values, social norms, or collective identity, shaping group membership and social distinctions. Understanding physical and symbolic boundaries involves recognizing how concrete separations coexist with abstract social constructs to organize societies and influence interactions.
Defining Physical Boundaries
Defining physical boundaries involves identifying tangible, geographical, or structural limits that separate spaces, such as walls, fences, or natural features like rivers and mountains. These boundaries serve to control access, ensure security, and delineate ownership or jurisdiction. Unlike symbolic boundaries, which are abstract social or cultural distinctions, physical boundaries are concrete and visible markers that can be measured and mapped precisely.
Defining Symbolic Boundaries
Symbolic boundaries are conceptual distinctions that people create to categorize objects, behaviors, or individuals, shaping social identities and group memberships. These boundaries influence social inclusion and exclusion by defining what is considered acceptable or deviant within cultural or social contexts. Unlike physical boundaries, which are tangible and geographical, symbolic boundaries operate through shared meanings, rituals, and language that reinforce social hierarchies and cultural divides.
Key Differences Between Physical and Symbolic Boundaries
Physical boundaries refer to tangible, visible separations such as walls, fences, or geographical features that clearly demarcate spaces or territories. Symbolic boundaries are intangible and represent social, cultural, or psychological distinctions, like class divisions or cultural norms, that influence group identity and social interactions. The key difference lies in physical boundaries enforcing spatial separation, while symbolic boundaries shape perceptions and social behaviors without physical markers.
Historical Evolution of Boundaries
Physical boundaries, such as walls, rivers, or mountain ranges, have historically served as tangible markers delineating territories and defining political or cultural regions. Symbolic boundaries, emerging from social constructs like language, religion, or customs, evolve through historical processes that shape group identities and societal norms beyond mere geography. Over time, the interplay between physical and symbolic boundaries has influenced the formation of nation-states, colonial borders, and cultural divisions, reflecting both material constraints and ideational distinctions.
The Role of Physical Boundaries in Society
Physical boundaries, such as walls, fences, and geographical features, serve crucial roles in defining territorial limits and ensuring security within societies. These tangible demarcations help regulate social interactions, resource distribution, and political jurisdiction, reinforcing group identity and social order. By controlling access and movement, physical boundaries shape social organization and influence cultural and economic exchanges between communities.
Symbolic Boundaries and Social Identity
Symbolic boundaries are invisible distinctions that separate groups based on values, beliefs, and cultural practices, playing a crucial role in shaping social identity by defining who belongs and who does not. These boundaries influence social cohesion and exclusion by reinforcing group identities and differentiating social categories such as class, ethnicity, and religion. Understanding symbolic boundaries helps explain how individuals construct their social identity through shared meanings and cultural markers beyond physical or geographical separation.
Interplay Between Physical and Symbolic Boundaries
Physical boundaries such as fences, walls, and geographical features create tangible separations between spaces, while symbolic boundaries represent intangible divisions based on social, cultural, or ideological differences. The interplay between physical and symbolic boundaries often reinforces social distinctions, as physical markers can embody and legitimize symbolic meanings attached to identity, power, or exclusion. Understanding this dynamic reveals how spatial organization influences social interaction and group membership within communities.
Examples in Contemporary Culture
Physical boundaries manifest as tangible divisions such as walls, borders, and fences like the US-Mexico border wall or the Berlin Wall's remnants. Symbolic boundaries represent intangible cultural distinctions exemplified by language differences, social class markers, or fashion trends that delineate group identity, like hip-hop culture's unique slang and style versus corporate business attire. Contemporary examples include the digital divide which functions as a symbolic boundary in access to technology, contrasting with physical territorial disputes over land and resources.
Implications for Conflict and Cooperation
Physical boundaries such as rivers, mountains, and walls create tangible separations that can limit interaction and escalate territorial conflicts due to clear demarcations of control. Symbolic boundaries, including cultural, religious, or social distinctions, often lead to identity-based conflicts by fostering in-group and out-group divisions but also enable cooperation through shared norms and values within groups. Understanding the interplay between physical and symbolic boundaries is crucial for conflict resolution and promoting cooperation in diverse societies.
Physical boundary Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com