Postmodernization challenges traditional narratives by emphasizing fragmentation, diversity, and the deconstruction of grand ideologies. It reshapes cultural, social, and architectural expressions, highlighting the subjective nature of reality and encouraging multiple perspectives. Explore the rest of the article to understand how postmodernization influences contemporary thought and your world.
Table of Comparison
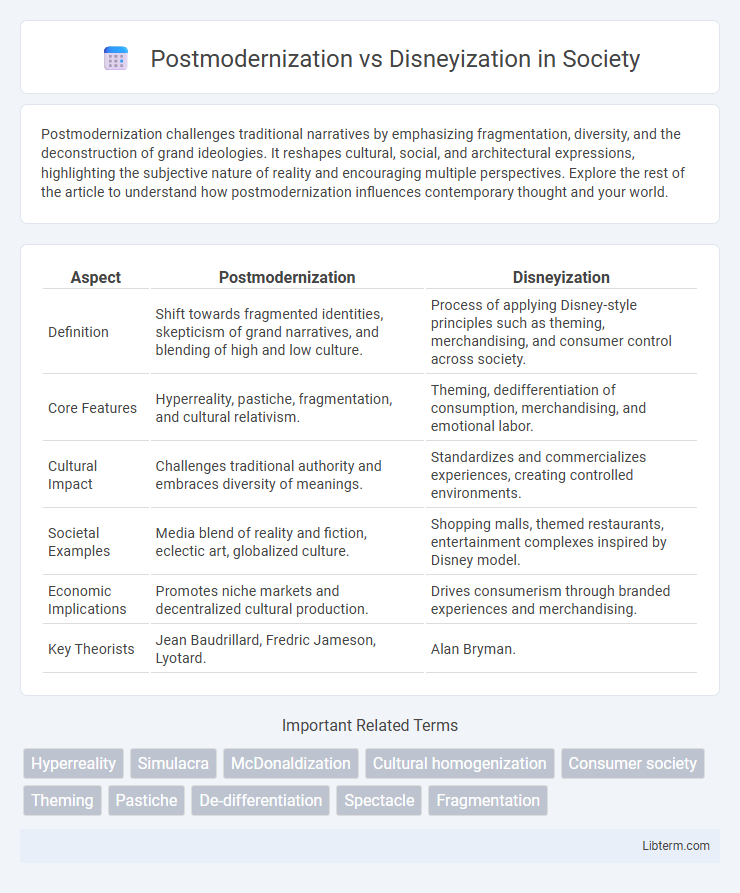
| Aspect | Postmodernization | Disneyization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Shift towards fragmented identities, skepticism of grand narratives, and blending of high and low culture. | Process of applying Disney-style principles such as theming, merchandising, and consumer control across society. |
| Core Features | Hyperreality, pastiche, fragmentation, and cultural relativism. | Theming, dedifferentiation of consumption, merchandising, and emotional labor. |
| Cultural Impact | Challenges traditional authority and embraces diversity of meanings. | Standardizes and commercializes experiences, creating controlled environments. |
| Societal Examples | Media blend of reality and fiction, eclectic art, globalized culture. | Shopping malls, themed restaurants, entertainment complexes inspired by Disney model. |
| Economic Implications | Promotes niche markets and decentralized cultural production. | Drives consumerism through branded experiences and merchandising. |
| Key Theorists | Jean Baudrillard, Fredric Jameson, Lyotard. | Alan Bryman. |
Understanding Postmodernization: Key Concepts
Postmodernization involves the shift from modernist ideals to a fragmented, pluralistic society where reality is often seen as subjective and constructed through media and cultural narratives. Key concepts include hyperreality, where simulations or representations become more real than reality itself, and pastiche, the mixing of different styles and genres without a central unifying theme. This transformation emphasizes diversity, irony, and self-referentiality, contrasting with the standardized, themed consumer experiences central to Disneyization.
Defining Disneyization: Origins and Characteristics
Disneyization, a concept developed by sociologist Alan Bryman, refers to the transformation of society through principles derived from Disney theme parks, emphasizing theming, dedifferentiation of consumption, merchandising, and emotional labor. Originating in the 1990s, Disneyization captures how cultural and commercial spaces adopt immersive, branded environments that prioritize customer experience and spectacle over traditional authenticity. This process contrasts with postmodernization by foregrounding commercialization and standardized entertainment formats as key drivers of social and economic change.
Historical Context: From Modernity to Postmodernity
Postmodernization emerges as a critical response to the principles of modernity, challenging grand narratives and embracing fragmented, diverse perspectives in cultural and social contexts. Disneyization, a concept coined by sociologist Alan Bryman, reflects the commodification and homogenization of culture, emphasizing theming, hybrid consumption, merchandising, and emotional labor rooted in consumer capitalist society. Both phenomena signify shifts from modernist ideals of progress and rationality to a postmodern context where simulation, spectacle, and consumer experiences redefine social and cultural landscapes.
Core Principles of Postmodernization
Postmodernization centers on the fragmentation of grand narratives, celebrating diversity, pastiche, and paradox, which contrasts with Disneyization's emphasis on theming, merchandising, and emotional labor. Core principles of postmodernization include skepticism toward universal truths, the blending of high and low culture, and the embrace of multiple, often conflicting, identities and realities. This cultural shift highlights decentralization and deconstruction, promoting pluralism and the fluidity of meaning in contemporary society.
The Four Dimensions of Disneyization
Disneyization encompasses four key dimensions: theming, which involves applying a narrative or story to environments and products; hybrid consumption, where different types of consumption experiences blend, such as combining retail and entertainment; merchandising, focusing on the extensive use of branded products; and performative labor, emphasizing employee performances to enhance consumer engagement. Unlike postmodernization, which centers on fragmented cultural narratives and skepticism toward grand narratives, Disneyization strategically creates immersive, controlled environments that encourage consumer participation and emotional attachment. These dimensions transform spaces into experiential attractions, reflecting a shift toward consumer-centric commercialization distinct from postmodern cultural critiques.
Cultural Impact: Postmodernization vs Disneyization
Postmodernization challenges traditional cultural narratives by embracing pluralism, fragmentation, and skepticism toward grand stories, reshaping societal identity through diverse and often conflicting perspectives. Disneyization, characterized by theming, dedifferentiation of consumption, merchandising, and emotional labor, transforms cultural spaces into sanitized, commodified experiences that prioritize entertainment and commercial appeal over authenticity. This shift influences cultural consumption by promoting homogenized, spectacularized environments that can dilute local traditions and reduce complex cultural expressions to simplified, market-driven spectacles.
Consumer Society and Hyperreality
Postmodernization and Disneyization critically shape consumer society through immersive experiences and hyperreal environments that blur authenticity and simulation. Disneyization intensifies hyperreality by commodifying culture into themed, controlled spaces that encourage consumption beyond traditional marketplaces. These processes reinforce consumer identity as performative and fragmented, driven by symbolic exchange within hyperreal settings that reflect postmodern skepticism toward grand narratives.
Globalization: Spreading Postmodern and Disneyized Models
Globalization accelerates the spread of postmodernization by promoting diverse cultural expressions, fragmenting traditional narratives, and encouraging pastiche and hybridity across societies. Disneyization, as a specific facet of globalization, standardizes consumer experiences by disseminating themed environments, merchandising, and emotional labor, often resulting in homogenized cultural consumption worldwide. Both processes reshape global cultural landscapes, blending local traditions with globalized models that reflect postmodern eclecticism and Disney's commercial spectacle.
Criticisms and Controversies Surrounding Each Paradigm
Postmodernization faces criticism for promoting superficial interpretations of culture, leading to the dilution of historical and ideological depth in favor of fragmented, consumer-driven narratives. Disneyization is often condemned for its commodification of culture, transforming authentic cultural experiences into sanitized, commercialized attractions that prioritize profitability over originality and local significance. Both paradigms provoke debates about authenticity, cultural homogenization, and the impact of commercialization on societal values and identity.
Future Prospects: Postmodernization vs Disneyization
Future prospects of postmodernization emphasize increased cultural hybridity, fragmented narratives, and fluid identities, which foster creative innovation and digital integration. In contrast, Disneyization projects continued expansion of themed experiences, standardized commodification, and immersive consumer environments that prioritize spectacle and brand loyalty. Both trends shape evolving social landscapes, influencing how culture and commerce intersect in the digital age.
Postmodernization Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com