Taboos are powerful social prohibitions that shape behavior and cultural norms by defining what is considered unacceptable or forbidden within a community. Understanding the origins and impacts of taboos can reveal deep insights into human psychology and societal values. Explore the rest of the article to learn how taboos influence your daily interactions and social dynamics.
Table of Comparison
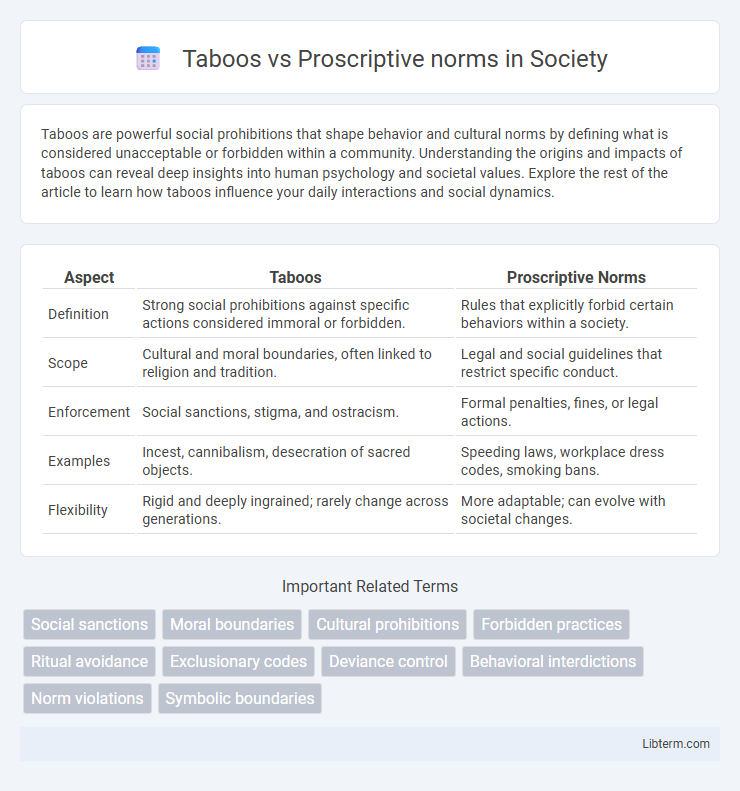
| Aspect | Taboos | Proscriptive Norms |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Strong social prohibitions against specific actions considered immoral or forbidden. | Rules that explicitly forbid certain behaviors within a society. |
| Scope | Cultural and moral boundaries, often linked to religion and tradition. | Legal and social guidelines that restrict specific conduct. |
| Enforcement | Social sanctions, stigma, and ostracism. | Formal penalties, fines, or legal actions. |
| Examples | Incest, cannibalism, desecration of sacred objects. | Speeding laws, workplace dress codes, smoking bans. |
| Flexibility | Rigid and deeply ingrained; rarely change across generations. | More adaptable; can evolve with societal changes. |
Understanding Taboos: Definition and Origins
Taboos are deeply ingrained prohibitions rooted in cultural, religious, or social beliefs that evoke strong emotional reactions and fear of severe sanctions if violated. These prohibitions often originate from ancient customs, myths, or moral codes designed to protect community cohesion and individual well-being. Understanding taboos involves examining their symbolic significance and the role they play in maintaining social order and identity.
What Are Proscriptive Norms?
Proscriptive norms are social rules that explicitly forbid certain behaviors, guiding individuals on what not to do within a community or society. These norms often carry moral or legal weight, discouraging actions considered harmful, unethical, or disruptive. Unlike taboos, which evoke strong emotional aversion and are deeply ingrained in cultural or religious contexts, proscriptive norms are enforceable standards that maintain social order by outlining prohibited conduct.
Key Differences Between Taboos and Proscriptive Norms
Taboos are strong prohibitions against actions considered deeply offensive or forbidden by a culture, often linked to moral or religious beliefs, whereas proscriptive norms are general social rules that discourage undesirable behaviors without the extreme severity of taboos. Violating a taboo typically results in significant social ostracism or legal penalties, while breaching proscriptive norms may lead to mild sanctions like social disapproval. The key differences lie in the intensity of prohibition, the cultural or moral weight assigned, and the consequences imposed for non-compliance.
The Psychological Impact of Breaking Taboos
Breaking taboos often leads to intense psychological distress, including feelings of shame, guilt, and social isolation, due to their deep-rooted cultural and emotional significance. Unlike proscriptive norms, which primarily guide behavior through social consequences, taboos trigger a stronger internalized emotional response linked to identity and moral values. This psychological impact can result in long-term trauma, reinforcing adherence to taboos through fear and anxiety.
Social Consequences of Violating Proscriptive Norms
Violating proscriptive norms, which are explicit prohibitions against certain behaviors, often leads to significant social sanctions such as ostracism, legal penalties, or loss of reputation. These norms regulate actions deemed harmful or morally unacceptable by society, reinforcing social cohesion through deterrence. The severity of consequences depends on cultural context and the specific norm breached, highlighting the role of proscriptive norms in maintaining societal order.
Cultural Variations in Taboos and Proscriptive Norms
Taboos and proscriptive norms vary significantly across cultures, reflecting distinct societal values and moral codes. In some cultures, taboos concerning food, such as the prohibition against pork in Islamic and Jewish traditions, contrast with proscriptive norms like dress codes that regulate attire but with less moral weight. Understanding these cultural variations is essential for cross-cultural communication and social integration, as what is taboo in one society may be merely a guideline in another.
How Taboos Shape Collective Identity
Taboos function as powerful cultural boundaries that shape collective identity by delineating behaviors considered morally or socially unacceptable, thereby reinforcing group cohesion and shared values. They operate beyond formal laws, embedding deeply in societal consciousness to regulate interactions and maintain social order. The internalization of taboos fosters a unified sense of belonging and cultural continuity within communities.
Proscriptive Norms in Modern Society
Proscriptive norms in modern society define behaviors that are explicitly forbidden, serving as critical guidelines for maintaining social order and preventing harm. These norms frequently evolve, reflecting changes in cultural values and legal standards, such as prohibitions against discrimination, drug abuse, and cyberbullying. Enforcement mechanisms ranging from social sanctions to legal penalties underscore the significance of proscriptive norms in shaping ethical conduct and reinforcing collective responsibility.
Evolving Taboos: Change and Persistence Over Time
Evolving taboos reflect society's dynamic structure where certain behaviors transition from being strictly prohibited to socially acceptable or vice versa, highlighting cultural shifts over time. Proscriptive norms, which prescribe actions to avoid, often contrast with taboos in their flexibility and degree of social enforcement. Changes in taboos can result from historical events, technological advancements, or increased cross-cultural interactions, yet some taboos persist due to deep-rooted cultural, religious, or moral foundations.
Navigating Taboos and Proscriptive Norms in a Globalized World
Navigating taboos and proscriptive norms in a globalized world requires a deep understanding of cultural sensitivities and context-specific behavioral expectations. Taboos, as deeply entrenched prohibitions, often evoke strong emotional reactions and can vary widely across societies, while proscriptive norms provide explicit rules delineating unacceptable conduct. Successfully managing these differences involves cultural competence, respectful communication, and adapting to local customs to foster collaboration and avoid social missteps.
Taboos Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com