Social continuity ensures the seamless transfer of cultural values, traditions, and social norms across generations, fostering a strong sense of identity and community cohesion. It plays a vital role in maintaining societal stability, enabling individuals to thrive within a familiar social framework. Dive into the rest of the article to explore how social continuity impacts your daily life and community dynamics.
Table of Comparison
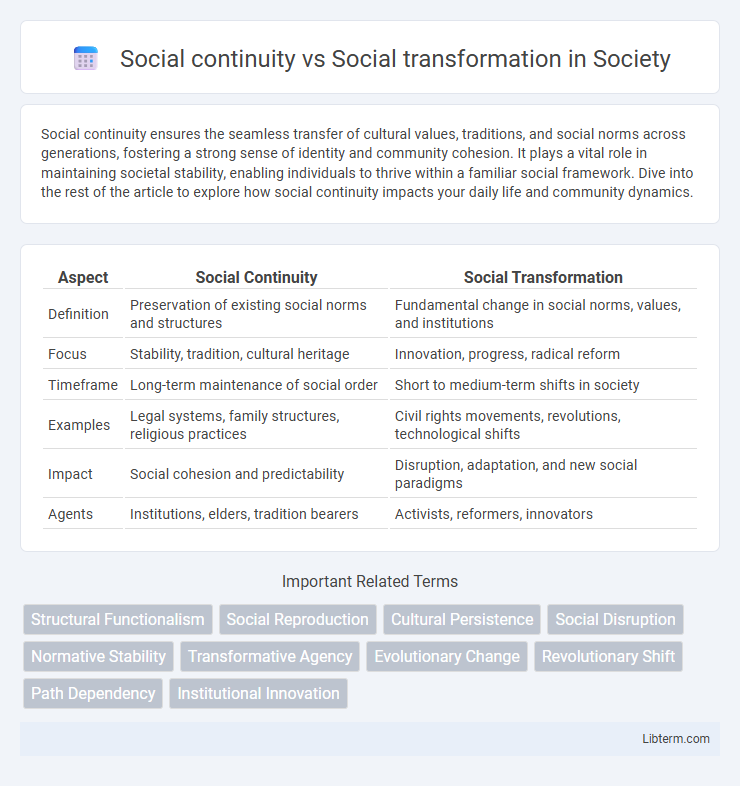
| Aspect | Social Continuity | Social Transformation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Preservation of existing social norms and structures | Fundamental change in social norms, values, and institutions |
| Focus | Stability, tradition, cultural heritage | Innovation, progress, radical reform |
| Timeframe | Long-term maintenance of social order | Short to medium-term shifts in society |
| Examples | Legal systems, family structures, religious practices | Civil rights movements, revolutions, technological shifts |
| Impact | Social cohesion and predictability | Disruption, adaptation, and new social paradigms |
| Agents | Institutions, elders, tradition bearers | Activists, reformers, innovators |
Introduction to Social Continuity and Social Transformation
Social continuity refers to the sustained preservation of cultural practices, social norms, and institutional structures that maintain stability within a society over time. Social transformation involves profound changes in social organization, values, and power dynamics, often driven by technological advances, economic shifts, or political movements. Understanding both concepts is essential for analyzing how societies balance heritage preservation with adaptive innovation.
Defining Social Continuity: Meaning and Importance
Social continuity refers to the preservation and transmission of cultural values, traditions, and social structures across generations, ensuring societal stability and identity. It plays a crucial role in maintaining a community's collective memory and social cohesion, fostering a sense of belonging and shared purpose. Understanding social continuity highlights the importance of balancing change with the retention of core social elements to sustain long-term societal well-being.
Understanding Social Transformation: Key Concepts
Social transformation involves profound and systemic changes in societal structures, norms, and power dynamics that redefine collective identities and social relations. Key concepts include the disruption of established institutions, shifts in cultural paradigms, and the reconfiguration of social hierarchies to promote equity or address systemic injustices. Understanding these processes requires analyzing the catalysts of change, such as social movements, technological advances, and policy reforms that drive profound social evolution beyond mere continuity.
Historical Perspectives: Continuity vs Transformation
Historical perspectives on social continuity emphasize the preservation of cultural norms, traditions, and institutional structures that maintain stability across generations. Social transformation highlights significant shifts in societal organization, values, and power dynamics driven by factors such as revolutions, technological advancements, and ideological movements. Analyzing historical events reveals the dynamic interplay between enduring legacies and transformative changes shaping the evolution of societies over time.
Drivers of Social Continuity in Societies
Drivers of social continuity in societies include established cultural norms, shared values, and institutionalized practices that maintain social order and collective identity. Family structures, religious traditions, and legal systems reinforce these patterns, ensuring stability and predictability across generations. Economic stability and educational systems also play crucial roles in preserving societal functions and facilitating the transmission of knowledge and customs.
Agents of Social Transformation: Who Initiates Change?
Agents of social transformation are typically individuals, groups, or institutions that challenge existing norms and structures to create meaningful change in society. These agents include social movements, political leaders, grassroots organizations, and cultural influencers who mobilize resources and public support to alter social practices and policies. Their actions contrast with forces of social continuity that aim to preserve traditional values and stable social orders, highlighting the dynamic interplay between change and stability in social evolution.
The Impact of Tradition on Social Continuity
Tradition serves as a foundational element in social continuity by preserving cultural norms, values, and practices across generations, reinforcing community identity and stability. Social institutions such as family, religion, and education act as conduits for transmitting these traditions, ensuring the persistence of societal structures over time. The entrenched nature of tradition can both stabilize societies and resist rapid change, influencing the dynamics between social continuity and transformation.
The Role of Innovation in Social Transformation
Innovation acts as a catalyst in social transformation by introducing new technologies, ideas, and practices that disrupt traditional social structures and norms. It accelerates changes in economic systems, communication, and cultural values, enabling societies to adapt to evolving challenges and opportunities. The integration of innovative solutions fosters social progress by reshaping education, governance, and community engagement, thereby shifting collective behaviors and expectations.
Balancing Continuity and Change: Societal Challenges
Balancing social continuity and social transformation requires addressing the tension between preserving cultural heritage and embracing progressive change to meet evolving societal needs. Effective strategies involve adaptive governance, inclusive policymaking, and community engagement to manage challenges such as technological disruption, demographic shifts, and social inequalities. Achieving harmony between tradition and innovation fosters social cohesion while enabling sustainable development and resilience in complex social systems.
Future Trends: Navigating Social Continuity and Transformation
Future trends in social dynamics reveal a complex interplay between social continuity and transformation, driven by technological advancements, demographic shifts, and cultural evolution. Emerging digital platforms foster persistent social norms while simultaneously enabling rapid changes in communication and identity expression. Navigating these trends requires adaptive policies that balance preserving core societal values with embracing innovation and inclusivity.
Social continuity Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com