An autonomous society operates independently, with communities managing their own resources, governance, and social systems without relying heavily on external control. This self-sufficiency fosters innovation, resilience, and localized decision-making tailored to specific cultural and environmental contexts. Explore the rest of the article to discover how your community can transition toward greater autonomy and its potential benefits.
Table of Comparison
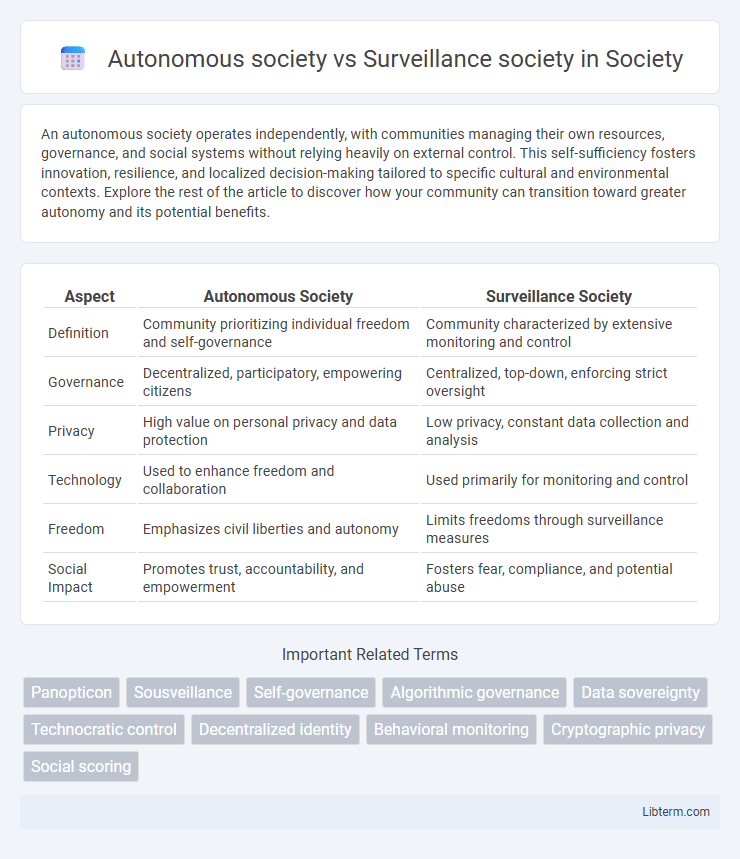
| Aspect | Autonomous Society | Surveillance Society |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Community prioritizing individual freedom and self-governance | Community characterized by extensive monitoring and control |
| Governance | Decentralized, participatory, empowering citizens | Centralized, top-down, enforcing strict oversight |
| Privacy | High value on personal privacy and data protection | Low privacy, constant data collection and analysis |
| Technology | Used to enhance freedom and collaboration | Used primarily for monitoring and control |
| Freedom | Emphasizes civil liberties and autonomy | Limits freedoms through surveillance measures |
| Social Impact | Promotes trust, accountability, and empowerment | Fosters fear, compliance, and potential abuse |
Defining Autonomous Society: Core Principles
An autonomous society emphasizes individual freedom, self-governance, and decentralized decision-making, fostering personal responsibility and privacy. Core principles include respect for human rights, transparent communication, and collective participation without central authority control. This model champions empowerment through technology that enhances autonomy rather than enabling pervasive surveillance.
What Constitutes a Surveillance Society?
A surveillance society is characterized by pervasive monitoring through advanced technologies such as CCTV cameras, biometric data collection, and digital tracking systems that gather personal information on a large scale. Governments and corporations employ data analytics and AI-driven algorithms to analyze behavioral patterns, enabling extensive control and influence over citizens' actions and privacy. This continuous observation undermines individual autonomy, creating power imbalances and ethical concerns about consent, security, and freedom.
Historical Evolution: Autonomy vs Surveillance
The historical evolution of autonomous societies traces back to Enlightenment ideals emphasizing individual freedom, self-governance, and decentralized power structures. In contrast, surveillance societies emerged with the development of modern state mechanisms, utilizing technological advancements like CCTV and digital monitoring to enforce social control and security. This tension between autonomy and surveillance reflects broader shifts from personal liberty toward pervasive observation in sociopolitical contexts.
Technology’s Role in Shaping Societal Structures
Technology plays a critical role in defining the boundaries between autonomous and surveillance societies by enabling both personal freedom and pervasive monitoring. Advanced algorithms, biometric systems, and IoT devices facilitate real-time data collection, empowering surveillance mechanisms that prioritize security and control. Conversely, decentralized networks, encryption technologies, and AI-driven personal assistants promote autonomy, supporting privacy, self-governance, and individualized decision-making.
Privacy in Autonomous Societies
Autonomous societies prioritize individual privacy by minimizing centralized data collection and empowering users with control over their personal information. Advanced encryption techniques and decentralized networks enable secure communication and protect against unauthorized surveillance. This privacy-centric approach contrasts sharply with surveillance societies, where pervasive monitoring undermines personal freedoms and data autonomy.
Control and Oversight in Surveillance Societies
Surveillance societies implement pervasive control through extensive monitoring technologies such as facial recognition, location tracking, and data analytics, enabling authorities to oversee individuals' behavior continuously. Oversight mechanisms in these societies often concentrate on centralized institutions with limited transparency, raising concerns about abuse of power and erosion of personal freedoms. In contrast to autonomous societies that emphasize decentralized decision-making and individual agency, surveillance societies prioritize security and order at the expense of privacy and autonomy.
Social Trust and Community Dynamics
Autonomous societies foster social trust through decentralized decision-making and individual empowerment, which enhances community cohesion and collaborative problem-solving. Surveillance societies often undermine social trust by prioritizing monitoring and control, leading to heightened suspicion and weakened interpersonal relationships. Community dynamics in autonomous contexts emphasize transparency and mutual respect, whereas surveillance-driven environments tend to generate social fragmentation and reduced civic engagement.
Impacts on Individual Rights and Freedoms
Autonomous societies prioritize individual rights and freedoms by empowering personal decision-making and limiting state intrusion through advanced technologies that ensure privacy and data protection. In contrast, surveillance societies often compromise civil liberties with pervasive monitoring systems that enable extensive data collection, threatening freedom of expression and association. The balance between security and autonomy shapes legal frameworks, impacting digital rights, autonomy in public spaces, and the right to anonymity.
Governance Models: Decentralization vs Centralization
Autonomous societies emphasize decentralized governance models that empower individuals and local communities with decision-making authority, fostering transparency and resilience through distributed networks and blockchain technologies. Surveillance societies rely on centralized governance structures where authority is concentrated in state or corporate entities, enabling extensive data collection and control mechanisms to monitor and influence population behavior. The tension between decentralization and centralization in governance profoundly impacts privacy, accountability, and citizen autonomy in emerging digital ecosystems.
Future Trajectories and Ethical Dilemmas
Autonomous societies prioritize individual freedom and decentralized decision-making, leveraging advanced AI and blockchain technologies to enhance privacy and self-governance, while surveillance societies depend heavily on pervasive data collection and centralized control to maintain security and social order. Future trajectories indicate a potential clash where autonomous models challenge the chilling effects of mass surveillance, raising ethical dilemmas about consent, data ownership, and the balance between personal liberty and collective safety. The debate intensifies around implementing transparent algorithms, protecting civil rights, and preventing authoritarian abuses in the digital age.
Autonomous society Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com