Open space offers immense benefits for mental health, creativity, and social interaction by providing a natural environment that encourages relaxation and activity. These areas play a crucial role in urban planning, contributing to improved air quality, biodiversity, and overall community well-being. Explore the rest of this article to discover how open spaces can enhance your life and surroundings.
Table of Comparison
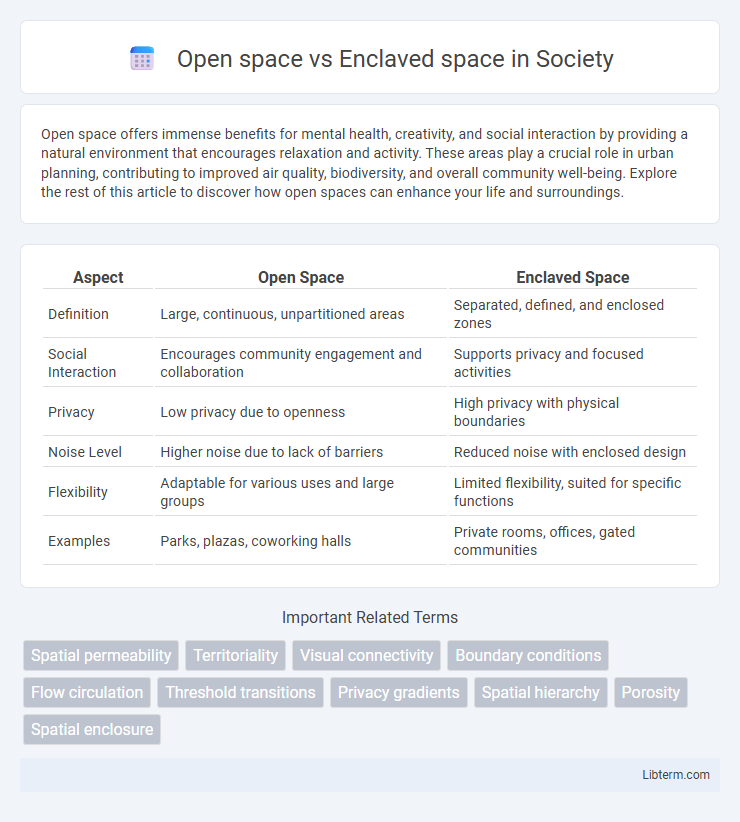
| Aspect | Open Space | Enclaved Space |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Large, continuous, unpartitioned areas | Separated, defined, and enclosed zones |
| Social Interaction | Encourages community engagement and collaboration | Supports privacy and focused activities |
| Privacy | Low privacy due to openness | High privacy with physical boundaries |
| Noise Level | Higher noise due to lack of barriers | Reduced noise with enclosed design |
| Flexibility | Adaptable for various uses and large groups | Limited flexibility, suited for specific functions |
| Examples | Parks, plazas, coworking halls | Private rooms, offices, gated communities |
Understanding Open Space: Definition and Characteristics
Open space refers to areas that are unobstructed and freely accessible, promoting visibility, flexibility, and social interaction. Characterized by minimal physical barriers, open spaces often feature expansive layouts with natural light and seamless flow between zones. These spaces enhance collaboration and spatial awareness, making them ideal for dynamic environments such as offices, parks, and urban plazas.
What Is Enclaved Space? Key Features Explained
Enclaved space refers to a distinct, enclosed area within a larger environment, designed to provide privacy, security, and focused functionality. Key features of enclaved spaces include physical boundaries such as walls or partitions, controlled access points, and often specialized interior design tailored to specific activities or occupants. These spaces contrast with open spaces by offering isolation from external stimuli, enhancing concentration and comfort in residential, office, or public settings.
Benefits of Open Space in Urban Design
Open space in urban design enhances community well-being by promoting social interaction, physical activity, and mental health through accessible parks and green areas. It improves environmental quality by mitigating urban heat, reducing pollution, and supporting biodiversity within cities. Open spaces also increase property values and encourage sustainable development by providing multifunctional areas that adapt to various public uses.
Advantages and Drawbacks of Enclaved Spaces
Enclaved spaces offer privacy and controlled environments, making them ideal for focused tasks and confidential meetings, but they often reduce natural lighting and limit social interaction compared to open spaces. These spaces can enhance acoustic control and minimize distractions, yet they may contribute to feelings of isolation and decrease team collaboration. Despite providing clear boundaries and personalization options, enclaved spaces tend to require more physical infrastructure and reduce overall spatial flexibility.
Psychological Impact: How Space Design Affects Wellbeing
Open space design promotes psychological well-being by enhancing natural light exposure and encouraging social interaction, which reduces stress and boosts mood. Enclaved spaces offer privacy and security, supporting focused work and reducing sensory overload for individuals sensitive to environmental stimuli. Balancing open and enclaved spaces within architectural planning optimizes mental health by catering to diverse psychological needs in both community and solitary settings.
Open Space vs Enclaved Space: A Comparative Analysis
Open space and enclaved space represent contrasting spatial concepts where open space emphasizes freedom, accessibility, and visual connectivity, promoting social interaction and environmental benefits such as natural light and ventilation. Enclaved space prioritizes privacy, security, and controlled access, often creating intimate, protected environments suited for focused activities or exclusive use. Understanding the trade-offs between openness and enclosure is crucial for urban planners and architects aiming to balance community engagement with personal comfort in spatial design.
Cultural Influences on Space Preferences
Cultural influences significantly shape preferences for open versus enclaved spaces, with collectivist societies often favoring open spaces that promote social interaction and community cohesion, while individualistic cultures tend to prefer enclaved spaces that emphasize privacy and personal boundaries. Studies reveal that East Asian cultures, valuing harmony and group identity, frequently design environments with flexible, shared areas, whereas Western cultures prioritize compartmentalized spaces that reflect autonomy and control. These cultural dimensions impact architectural design, interior layouts, and urban planning, highlighting the need to consider sociocultural context in space utilization and user satisfaction.
Case Studies: Successful Open and Enclaved Space Implementations
Successful open space implementations, such as the Googleplex in Mountain View, foster collaboration and innovation through flexible layouts and communal areas. In contrast, enclaved spaces like traditional law firm offices in New York emphasize privacy and concentration with private rooms and soundproof zones. Case studies reveal that combining open and enclaved spaces tailored to specific organizational needs enhances productivity and employee satisfaction.
Balancing Openness and Privacy in Modern Architecture
Balancing openness and privacy in modern architecture involves integrating open spaces that foster social interaction with enclaved areas that ensure personal retreat and confidentiality. Open spaces typically feature large windows, flexible layouts, and minimal partitions to enhance natural light and visual connectivity, while enclaved spaces rely on strategic walls, soundproofing, and spatial zoning to create privacy without isolation. Effective design harmonizes these contrasting needs, promoting adaptive environments that support both communal engagement and individual privacy.
Future Trends: Evolving Concepts of Space in Urban Planning
Future trends in urban planning emphasize a shift from enclosed, segmented spaces toward expansive, flexible open spaces that promote community interaction and ecological sustainability. The increasing demand for smart cities integrates technology into open spaces to enhance usability, safety, and environmental monitoring. Adaptive design strategies prioritize multifunctional open environments over traditional enclaved spaces to support urban resilience and social connectivity in rapidly growing metropolitan areas.
Open space Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com