Multiculturalism fosters an inclusive society by embracing diverse cultures, traditions, and perspectives, enriching social interactions and promoting mutual respect. It enhances creativity and innovation by blending different viewpoints, contributing to economic growth and community development. Explore the full article to understand how multiculturalism can positively impact your environment and daily life.
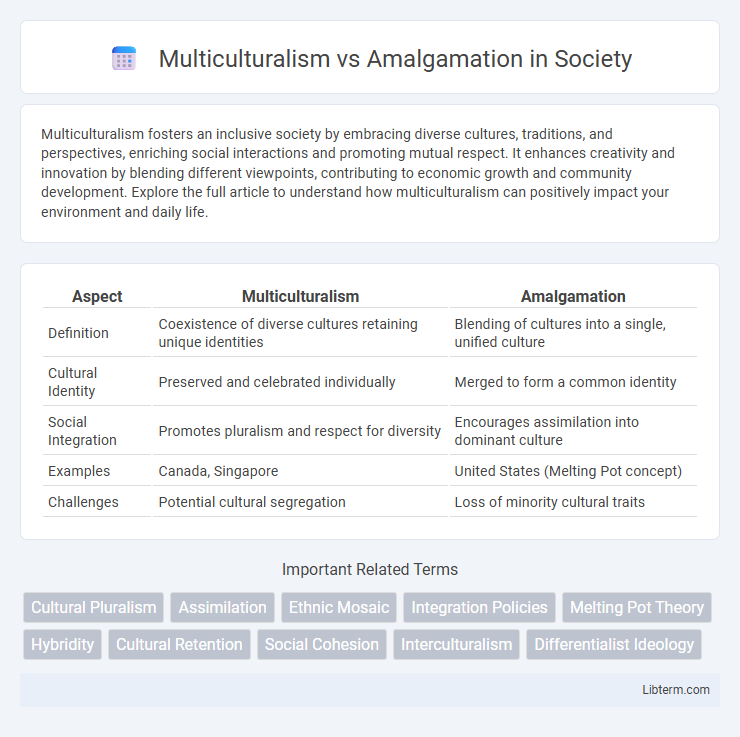
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Multiculturalism | Amalgamation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Coexistence of diverse cultures retaining unique identities | Blending of cultures into a single, unified culture |
| Cultural Identity | Preserved and celebrated individually | Merged to form a common identity |
| Social Integration | Promotes pluralism and respect for diversity | Encourages assimilation into dominant culture |
| Examples | Canada, Singapore | United States (Melting Pot concept) |
| Challenges | Potential cultural segregation | Loss of minority cultural traits |
Understanding Multiculturalism: Definition and Principles
Multiculturalism emphasizes the coexistence of diverse cultural identities within a society, where each group maintains its distinct traditions, languages, and values while participating equally in social and political life. It promotes principles of cultural pluralism, mutual respect, and intercultural dialogue, recognizing the intrinsic value of cultural diversity as a social asset. This approach contrasts with amalgamation, which seeks to blend cultural differences into a single, homogeneous identity, often at the expense of cultural distinctiveness.
What is Amalgamation? A Comprehensive Overview
Amalgamation refers to the process through which diverse cultural groups blend into a single, unified society by merging customs, traditions, and identities, resulting in a new, hybrid culture. Unlike multiculturalism, which encourages preserving distinct cultural identities within a society, amalgamation emphasizes integration and the creation of a cohesive collective identity. This concept plays a crucial role in shaping social dynamics, policies on immigration, and cultural assimilation in pluralistic societies.
Historical Roots of Multicultural Societies
Multicultural societies have historical roots in immigration patterns, colonial encounters, and trade networks that fostered cultural exchanges and coexistence. Unlike amalgamation, which emphasizes blending distinct cultural identities into a single homogeneous culture, multiculturalism preserves diverse cultural heritages within a shared societal framework. Key examples include the Ottoman Empire's millet system and Canada's cultural mosaic policy, both recognizing multiple cultural groups while maintaining their unique identities.
The Evolution of Amalgamation in Modern Nations
The evolution of amalgamation in modern nations reflects a shift toward blending diverse cultural identities into a single national identity, often driven by globalization and urbanization. This process emphasizes social cohesion and unified citizenship while occasionally risking the erosion of distinct cultural heritages. Recent trends show governments implementing policies that balance integration with respect for cultural diversity to foster inclusive societies.
Social Integration: Multiculturalism vs Amalgamation
Social integration under multiculturalism emphasizes the coexistence of diverse cultural identities within a shared society, allowing individuals to maintain their unique traditions while participating fully in social, economic, and political life. In contrast, amalgamation promotes the blending of distinct cultural groups into a single, unified culture, often leading to the erosion of original cultural identities in favor of a common national identity. These differing approaches impact social cohesion, with multiculturalism fostering pluralism and respect for diversity, while amalgamation seeks homogenization and collective solidarity.
Preserving Cultural Identity in a Diverse Society
Multiculturalism emphasizes preserving distinct cultural identities within a diverse society, allowing communities to maintain their unique traditions, languages, and customs. In contrast, amalgamation promotes blending different cultures into a single, unified identity, which can lead to the erosion of individual cultural characteristics. Preserving cultural identity under multiculturalism fosters social inclusion and respect for diversity, supporting the coexistence of multiple cultural groups without forcing assimilation.
Economic Impacts: Comparing Multiculturalism and Amalgamation
Multiculturalism fosters economic growth by promoting diverse skill sets, innovation, and global market access through cultural inclusivity. Amalgamation emphasizes economic efficiency and social cohesion by integrating immigrant groups into a unified culture, potentially reducing cultural conflicts and streamlining workforce collaboration. Studies show that multicultural economies benefit from increased creativity and niche markets, while amalgamated economies often experience stronger national identity and streamlined policy implementation.
Challenges and Criticisms of Each Approach
Multiculturalism faces challenges such as social fragmentation and the potential for cultural isolation, where distinct groups may prioritize preserving their unique identities over societal integration. Amalgamation is criticized for promoting cultural homogenization, often resulting in the loss of minority traditions and identities under dominant cultural norms. Both approaches struggle with balancing individual cultural expression and collective social cohesion, leading to ongoing debates in policy and social frameworks.
Successful Global Examples: Multiculturalism vs Amalgamation
Successful global examples of multiculturalism include Canada and Switzerland, where diverse cultural groups coexist with respect for individual identities and legal protections. Amalgamation is exemplified by the United States' "melting pot" approach, blending various cultures into a unified national identity. These models highlight the balance between preserving cultural diversity and fostering social cohesion in global societies.
The Future of Inclusivity: Which Model Leads the Way?
Multiculturalism promotes the coexistence of diverse cultural identities, fostering inclusivity through recognition and respect for differences, while amalgamation encourages blending distinct cultures into a unified identity, potentially enhancing social cohesion but risking cultural homogenization. Emerging trends in inclusivity emphasize adaptive models that balance cultural preservation with integration, leveraging policies that support both individual cultural expression and societal unity. Research suggests that hybrid approaches combining multicultural acceptance with elements of amalgamation may lead the most effective path toward a harmonious, inclusive future.
Multiculturalism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com