Feminism advocates for gender equality by challenging societal norms that perpetuate discrimination against women and marginalized groups. It encompasses a diverse range of movements aimed at achieving political, economic, and social rights for all genders. Explore the rest of the article to understand how feminism continues to shape modern society and affect your life.
Table of Comparison
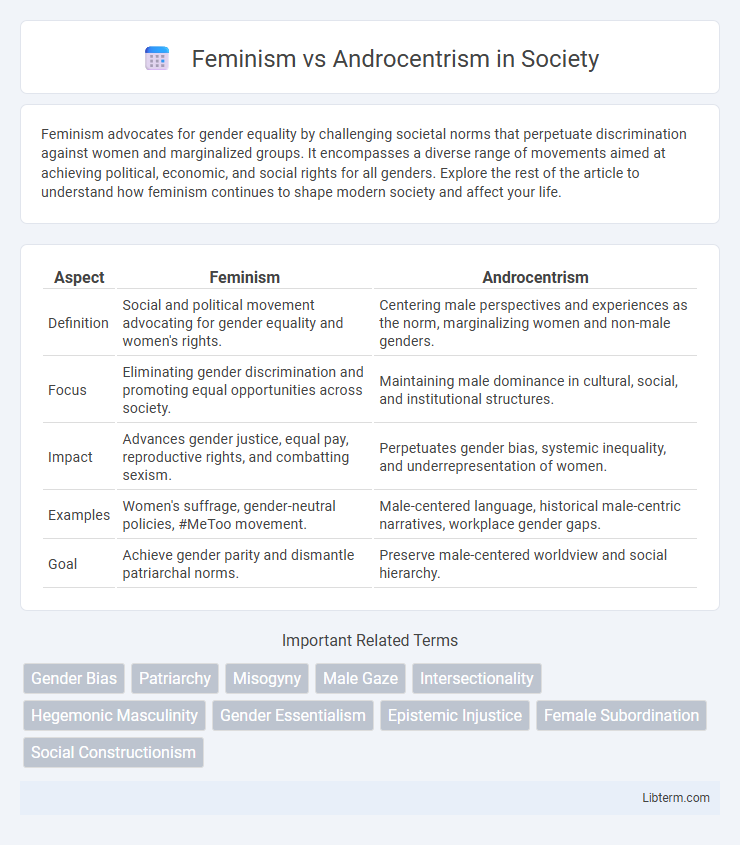
| Aspect | Feminism | Androcentrism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Social and political movement advocating for gender equality and women's rights. | Centering male perspectives and experiences as the norm, marginalizing women and non-male genders. |
| Focus | Eliminating gender discrimination and promoting equal opportunities across society. | Maintaining male dominance in cultural, social, and institutional structures. |
| Impact | Advances gender justice, equal pay, reproductive rights, and combatting sexism. | Perpetuates gender bias, systemic inequality, and underrepresentation of women. |
| Examples | Women's suffrage, gender-neutral policies, #MeToo movement. | Male-centered language, historical male-centric narratives, workplace gender gaps. |
| Goal | Achieve gender parity and dismantle patriarchal norms. | Preserve male-centered worldview and social hierarchy. |
Understanding Feminism: Core Principles and Goals
Feminism advocates for gender equality by challenging androcentrism, the practice of centering male experiences and perspectives in society. It emphasizes dismantling systemic patriarchy to ensure equal rights, opportunities, and representation for women and marginalized genders. Core goals include ending gender discrimination, promoting social justice, and achieving equitable power distribution across all societal sectors.
Defining Androcentrism: Origins and Impact
Androcentrism, rooted in patriarchal societal structures, positions male experiences and perspectives as the universal standard, often marginalizing or ignoring female viewpoints. This bias originates from historical power dynamics that prioritize male dominance in cultural, social, and political institutions. The impact of androcentrism manifests in gender inequalities, reinforcing stereotypes and limiting women's representation and agency across various domains.
Historical Context: The Rise of Feminist Movements
Feminist movements emerged prominently in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, challenging androcentrism--the historical practice of centering male experiences and perspectives in social, cultural, and political spheres. Landmark events such as the Seneca Falls Convention of 1848 and the suffragette campaigns in the early 1900s catalyzed demands for women's voting rights and legal equality, confronting entrenched androcentric norms. The rise of feminism redefined gender discourse by advocating for female agency and critiquing male-centric power structures entrenched since antiquity.
Androcentrism in Society: Manifestations and Consequences
Androcentrism in society manifests through the dominance of male perspectives in cultural norms, media representation, and institutional policies, often marginalizing women's experiences and contributions. This male-centered bias results in unequal power dynamics, limited opportunities for women, and systemic discrimination across sectors such as education, employment, and politics. Long-term consequences include perpetuated gender inequality, social stereotyping, and hindered progress toward inclusive and equitable societal structures.
Comparing Feminist and Androcentric Perspectives
Feminist perspectives emphasize gender equality by challenging androcentrism, which centers male experiences as the norm. Androcentric views often marginalize or overlook women's contributions and perspectives in social, cultural, and academic contexts. Feminism seeks to deconstruct male-centered biases and promote inclusive narratives that recognize the diversity of gender experiences.
Gender Representation in Media and Literature
Feminism challenges androcentrism by advocating for equitable gender representation in media and literature, aiming to dismantle male-centric narratives that dominate storytelling and character development. Studies reveal that women are underrepresented and often portrayed through stereotypical roles, while feminist critiques push for diverse, complex female characters that reflect real-life experiences. Increasing inclusion of feminist perspectives promotes balanced gender representation, thereby enriching cultural discourse and challenging systemic biases in media industries.
Feminism’s Challenge to Androcentric Norms
Feminism systematically challenges androcentric norms by advocating for gender equality and dismantling male-centered perspectives entrenched in social, cultural, and institutional structures. It highlights the biases inherent in androcentrism that marginalize women's experiences and promotes inclusive narratives that recognize diverse gender identities. Feminist theory reshapes discourse by questioning patriarchal power dynamics and striving for equitable representation across political, economic, and academic spheres.
The Role of Education in Shaping Gender Narratives
Education plays a pivotal role in shaping gender narratives by challenging androcentrism and promoting feminist perspectives that emphasize equality and inclusivity. Curricula that integrate diverse gender experiences and critically analyze male-centered biases help dismantle entrenched stereotypes and empower students to question traditional power structures. Implementing gender-sensitive pedagogy fosters awareness, encouraging equitable social attitudes and supporting the development of more inclusive societies.
Addressing Gender Bias in Policies and Institutions
Feminism actively challenges androcentrism by addressing gender bias embedded in policies and institutions that prioritize male perspectives and experiences. Reform efforts emphasize inclusive policy-making, equitable resource allocation, and gender-sensitive frameworks to dismantle systemic inequalities. Research indicates that integrating feminist principles in institutional reforms leads to more balanced representation and improved social outcomes for all genders.
Toward Gender Equity: Bridging the Feminism-Androcentrism Divide
Feminism challenges androcentrism by advocating for equal representation and dismantling male-centered norms that marginalize women's experiences. Addressing the divide requires integrating feminist perspectives into social, political, and academic frameworks to promote gender equity. Bridging this gap fosters inclusive policies that recognize diverse gender identities and dismantle systemic biases entrenched in androcentric institutions.
Feminism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com