Holistic education nurtures the intellectual, emotional, social, physical, creative, and spiritual potentials of learners, fostering well-rounded development beyond traditional academics. It integrates experiential learning, mindfulness, and community engagement to prepare students for real-world challenges. Explore the full article to discover how holistic education can transform Your learning experience.
Table of Comparison
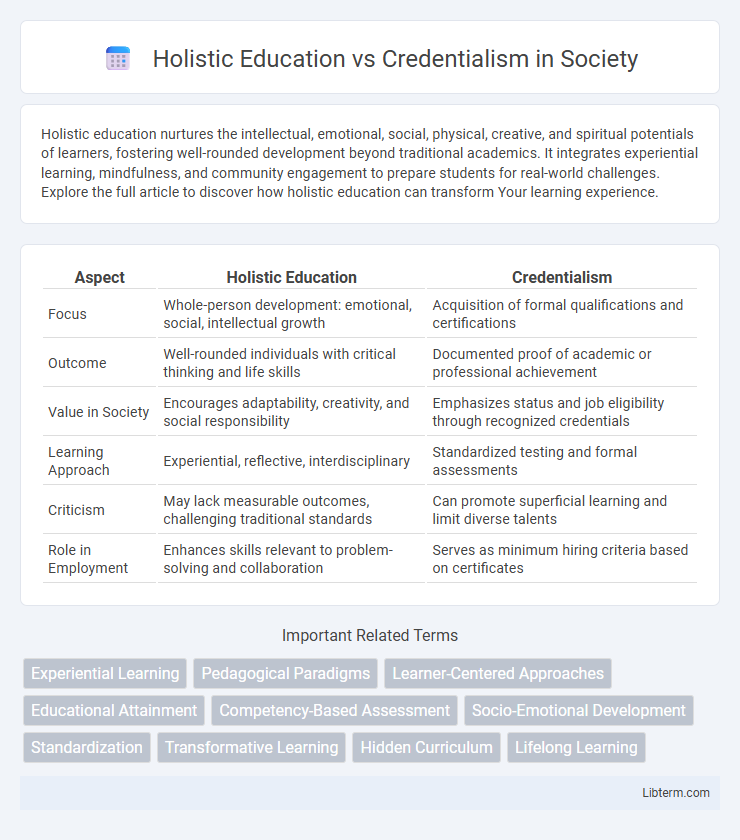
| Aspect | Holistic Education | Credentialism |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Whole-person development: emotional, social, intellectual growth | Acquisition of formal qualifications and certifications |
| Outcome | Well-rounded individuals with critical thinking and life skills | Documented proof of academic or professional achievement |
| Value in Society | Encourages adaptability, creativity, and social responsibility | Emphasizes status and job eligibility through recognized credentials |
| Learning Approach | Experiential, reflective, interdisciplinary | Standardized testing and formal assessments |
| Criticism | May lack measurable outcomes, challenging traditional standards | Can promote superficial learning and limit diverse talents |
| Role in Employment | Enhances skills relevant to problem-solving and collaboration | Serves as minimum hiring criteria based on certificates |
Understanding Holistic Education
Holistic education emphasizes the development of the whole person, integrating intellectual, emotional, social, physical, artistic, creative, and spiritual potentials. It fosters critical thinking, emotional intelligence, and lifelong learning skills rather than solely prioritizing standardized qualifications or diplomas. This approach contrasts with credentialism, which values formal certifications as the primary measure of competency and success in education and employment.
What Is Credentialism?
Credentialism refers to an overemphasis on formal qualifications and certifications as the primary measure of an individual's ability or competence. This approach prioritizes degrees and diplomas over skills, creativity, and critical thinking, often restricting access to opportunities based solely on educational credentials. In contrast to holistic education, which values comprehensive personal development, credentialism can limit the recognition of diverse talents and experiential learning essential for innovation and adaptability.
Core Principles of Holistic Education
Holistic education emphasizes the development of the whole person, integrating intellectual, emotional, social, physical, creative, and spiritual growth to foster lifelong learning and self-awareness. Core principles include experiential learning, emotional intelligence, interconnectedness, and nurturing critical thinking beyond rote memorization, contrasting with credentialism's narrow focus on acquiring diplomas and standardized qualifications. This approach promotes adaptability and moral responsibility, equipping students with skills essential for complex real-world challenges rather than mere credential attainment.
Key Drivers Behind Credentialism
The key drivers behind credentialism include the increasing demand for standardized verification of skills and qualifications in competitive job markets, influencing employers to prioritize formal degrees over practical experience. Economic shifts towards knowledge-based industries amplify reliance on credentials as proxies for competence and ability to adapt. Social and cultural factors also reinforce credentialism by equating formal education with social status and upward mobility, creating systemic pressure to obtain certifications regardless of actual skill application.
Comparing Learning Outcomes
Holistic education emphasizes critical thinking, creativity, emotional intelligence, and lifelong learning, fostering well-rounded individuals capable of adapting to complex real-world challenges. Credentialism prioritizes acquiring diplomas and certifications, often leading to narrow knowledge focused on passing exams rather than practical application or personal growth. Studies reveal holistic approaches result in higher levels of motivation, problem-solving skills, and interpersonal competence compared to credential-centered systems that primarily measure academic achievement through standardized metrics.
Impact on Student Development
Holistic education fosters comprehensive student development by promoting critical thinking, emotional intelligence, and interpersonal skills, surpassing mere academic achievement. Credentialism concentrates primarily on acquiring degrees or certificates, often neglecting practical competencies and personal growth. Emphasizing holistic learning cultivates adaptable, well-rounded individuals better prepared for complex real-world challenges.
Real-World Relevance and Employability
Holistic education emphasizes the development of critical thinking, creativity, and interpersonal skills, aligning closely with real-world problem-solving and adaptability in dynamic job markets. Credentialism prioritizes formal qualifications and certifications, often overlooking the practical skills and emotional intelligence required for long-term employability. Integrating holistic learning approaches enhances workforce readiness by fostering versatile competencies beyond academic credentials.
Challenges and Criticisms of Both Approaches
Holistic education faces challenges such as inconsistent assessment methods and resource-intensive implementation, leading to difficulties in measuring student outcomes effectively. Credentialism is criticized for emphasizing formal qualifications over actual skills and critical thinking, often resulting in credential inflation and social inequality. Both approaches struggle with balancing comprehensive skill development and standardized recognition, complicating educational and employment pathways.
Integrating Holistic Education with Credential Requirements
Integrating holistic education with credential requirements enhances student development by balancing comprehensive skill sets with formal qualifications, fostering critical thinking, creativity, and practical expertise. Educational institutions adopting competency-based frameworks successfully align holistic learning outcomes with accreditation standards, ensuring graduates meet industry demands and societal expectations. This synthesis supports lifelong learning and adaptability in dynamic job markets by validating both academic achievements and essential soft skills.
The Future of Education: Finding Balance
The future of education demands a balanced integration of holistic education and credentialism, emphasizing critical thinking, creativity, and emotional intelligence alongside recognized qualifications. Employers increasingly value interdisciplinary skills and adaptability, prompting educational systems to embed real-world experiences and soft skills within credential frameworks. This balanced approach supports lifelong learning and prepares students for dynamic career landscapes marked by rapid technological and societal change.
Holistic Education Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com