Social norms shape behavior by defining what is acceptable within a community, influencing interactions and social cohesion. They often operate subconsciously, guiding Your decisions and expectations in various settings. Explore the rest of the article to understand how social norms impact daily life and influence societal change.
Table of Comparison
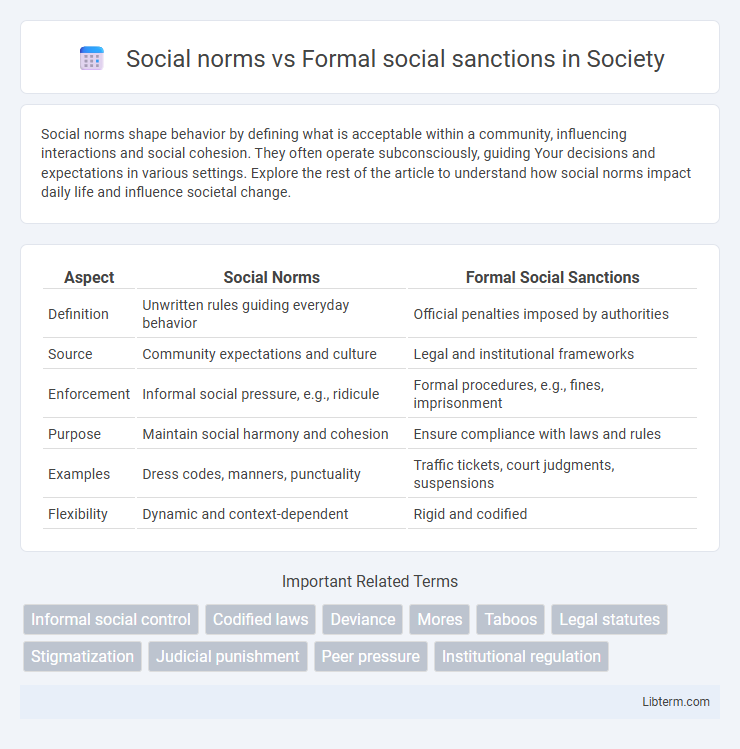
| Aspect | Social Norms | Formal Social Sanctions |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unwritten rules guiding everyday behavior | Official penalties imposed by authorities |
| Source | Community expectations and culture | Legal and institutional frameworks |
| Enforcement | Informal social pressure, e.g., ridicule | Formal procedures, e.g., fines, imprisonment |
| Purpose | Maintain social harmony and cohesion | Ensure compliance with laws and rules |
| Examples | Dress codes, manners, punctuality | Traffic tickets, court judgments, suspensions |
| Flexibility | Dynamic and context-dependent | Rigid and codified |
Defining Social Norms: Unwritten Rules of Society
Social norms represent the unwritten rules and expectations that guide behavior within a society, shaping everyday interactions without formal codification. These informal guidelines influence actions by promoting conformity and social cohesion through shared values and beliefs. Unlike formal social sanctions, which involve official penalties enforced by institutions, social norms rely on subtle social pressures such as approval, disapproval, and peer influence to regulate conduct.
Understanding Formal Social Sanctions
Formal social sanctions are official measures enforced by institutions or authorities to regulate behavior and maintain social order. These sanctions include laws, regulations, fines, and imprisonment, ensuring compliance through legally defined consequences. Understanding formal social sanctions highlights their role in deterring deviance and promoting conformity within structured societal systems.
Key Differences Between Social Norms and Formal Sanctions
Social norms are unwritten rules guiding everyday behavior within a community, while formal social sanctions are officially prescribed punishments or rewards enforced by institutions like governments or organizations. Social norms rely on collective social approval or disapproval, often resulting in informal consequences such as social exclusion or praise. Formal sanctions are legally or institutionally codified, involving penalties like fines, imprisonment, or official commendations that ensure compliance through explicit authority.
The Role of Social Norms in Shaping Behavior
Social norms serve as unwritten rules that guide individual behavior within a group by establishing expectations for acceptable conduct, whereas formal social sanctions involve explicit penalties enforced by institutions for violations. The role of social norms in shaping behavior lies in their power to promote conformity and social cohesion through informal social pressure, often resulting in voluntary compliance without the need for formal enforcement. These collective behavioral standards influence daily interactions, decision-making processes, and long-term social order by internalizing shared values and norms within individuals.
How Formal Sanctions Enforce Societal Order
Formal social sanctions enforce societal order by imposing legal penalties, fines, or imprisonment on individuals who violate established laws and regulations, ensuring compliance through authoritative means. These sanctions are codified and systematically applied by institutions such as courts, law enforcement agencies, and government bodies, which maintain social stability by deterring deviant behavior. The clarity and consistency of formal sanctions reinforce societal norms, promoting predictable interactions and safeguarding public welfare.
Examples of Social Norms in Everyday Life
Social norms shape everyday behavior, such as waiting in line, dressing appropriately for occasions, or greeting others politely, which help maintain social order without legal enforcement. Formal social sanctions, like fines for littering or punishments for violating laws, are codified and enforced by institutions. These differences highlight how unwritten customs guide daily interactions while formal sanctions uphold societal rules through official mechanisms.
Legal Systems and the Implementation of Formal Sanctions
Legal systems enforce formal social sanctions through codified laws and regulatory frameworks that prescribe specific penalties for violations, ensuring compliance and maintaining social order. Formal sanctions, such as fines, imprisonment, and community service, are applied by authorized institutions like courts and law enforcement agencies to uphold established legal norms. Effective implementation of these sanctions depends on the clarity of legislation, judicial efficiency, and consistent enforcement mechanisms within the legal system.
Social Norms vs. Formal Sanctions: Strengths and Limitations
Social norms, as unwritten rules governing behavior within a community, foster social cohesion through informal sanctions like peer approval or ostracism, promoting internalized conformity. Formal sanctions, enforced by institutions such as governments or organizations, provide clear, codified penalties or rewards that ensure compliance through legal or official authority. While social norms excel in adaptability and social bonding, formal sanctions offer consistency and enforceability, though both face limitations in universality and contextual application.
The Interaction Between Informal Norms and Formal Rules
Social norms influence individual behavior through shared expectations within a community, while formal social sanctions are enforced by institutions using explicit laws and regulations. The interaction between informal norms and formal rules shapes social order by reinforcing compliance; informal norms often fill gaps where formal regulations are ambiguous or unenforced. Understanding this dynamic reveals how social cohesion relies on both internalized cultural values and external legal mechanisms to regulate conduct effectively.
The Impact of Changing Social Norms on Formal Sanctions
Shifts in social norms significantly influence the evolution of formal social sanctions by reshaping legal frameworks and enforcement priorities, reflecting contemporary values. As societal attitudes toward issues like same-sex marriage and marijuana use have liberalized, formal sanctions have correspondingly relaxed or been repealed to align with prevailing social acceptance. This dynamic demonstrates the reciprocal relationship where changing public consensus drives legislative reform and modification of punitive measures in social institutions.
Social norms Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com