Non-governmental organizations (NGOs) play a crucial role in addressing social, environmental, and humanitarian issues worldwide. These independent entities leverage resources and expertise to support sustainable development, advocate for human rights, and provide disaster relief. Discover how NGOs can impact your community and contribute to global progress by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
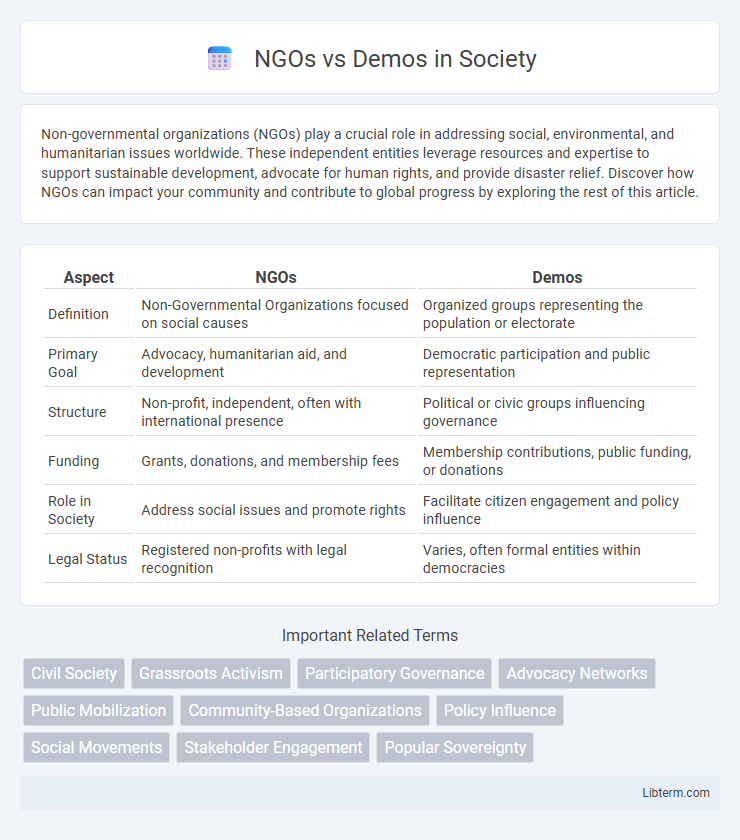
| Aspect | NGOs | Demos |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Non-Governmental Organizations focused on social causes | Organized groups representing the population or electorate |
| Primary Goal | Advocacy, humanitarian aid, and development | Democratic participation and public representation |
| Structure | Non-profit, independent, often with international presence | Political or civic groups influencing governance |
| Funding | Grants, donations, and membership fees | Membership contributions, public funding, or donations |
| Role in Society | Address social issues and promote rights | Facilitate citizen engagement and policy influence |
| Legal Status | Registered non-profits with legal recognition | Varies, often formal entities within democracies |
Understanding NGOs: Definition and Roles
Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs) are independent entities that operate without government control, focusing on social, environmental, humanitarian, and development issues worldwide. Their roles include advocating for policy change, providing essential services, conducting research, and raising public awareness to address global challenges. Understanding NGOs involves recognizing their capacity to mobilize resources, influence legislation, and foster community participation to drive sustainable development.
What Are Demos? A Comprehensive Overview
Demos refers to grassroots organizations focused on democratic participation and social justice, often engaging in policy advocacy, public education, and electoral reform efforts. Unlike traditional NGOs, which may address a wide range of issues including humanitarian aid and development, Demos specifically prioritizes strengthening democratic processes and empowering marginalized communities through data-driven research and civic engagement. Their work involves influencing legislation, mobilizing communities, and promoting equity to enhance democratic governance at local, national, and global levels.
Core Differences Between NGOs and Demos
NGOs primarily operate as nonprofit organizations focused on advocacy, humanitarian aid, and development projects, functioning independently of government control. Demos refer to the collective population or citizenry engaged in democratic governance, embodying the principle of political participation and decision-making. The core difference lies in NGOs being structured entities with specific missions, while demos represent the broader community whose voice shapes democratic processes.
Historical Evolution of NGOs and Demos
NGOs originated in the 19th century as voluntary associations addressing social reforms, evolving through international collaborations post-World War II to influence global humanitarian and development policies. Demos emerged from the concept of participatory democracy rooted in ancient Athens, gaining prominence in the 20th century as movements advocating for broader citizen engagement and institutional reforms. The historical evolution of NGOs and demos reflects a shift from localized activism to structured organizations and collective civic participation shaping modern governance and civil society.
Governance Structures: NGOs vs Demos
NGOs typically operate with hierarchical governance structures featuring boards of directors, executive leadership, and formal oversight mechanisms, ensuring accountability and strategic direction. In contrast, demos rely on participatory governance models emphasizing direct citizen involvement, consensus-building, and decentralized decision-making processes. The structural differences between NGOs and demos influence transparency, responsiveness, and stakeholder engagement in shaping public policy.
Funding and Resource Mobilization: A Comparative Analysis
NGOs primarily rely on grants, donations, and international funding agencies to sustain their operations, whereas demos often mobilize resources through community fundraising, membership fees, and local sponsorships. NGOs typically have structured funding mechanisms with formal accountability, enabling access to large-scale, multi-year funding. In contrast, demos depend on grassroots support and local engagement, which can limit their financial scope but enhance agility and direct resource utilization within communities.
Impact on Society: Measuring Effectiveness
NGOs often apply targeted programs with measurable outcomes, such as reduced poverty rates or improved literacy, using rigorous data collection and impact assessments. Demos influence society primarily through public discourse and policy advocacy, with effectiveness gauged by shifts in public opinion and legislative changes. Combining quantitative metrics from NGOs and qualitative influence from demos provides a comprehensive understanding of societal impact.
Accountability and Transparency Issues
NGOs often face criticism for inconsistent accountability mechanisms, as their funding sources and decision-making processes can lack transparency compared to democratic institutions. Demos, rooted in participatory governance, typically emphasize public accountability through electoral processes and open deliberation, enhancing transparency. However, NGOs sometimes achieve greater flexibility and innovation in addressing social issues despite these challenges in formal accountability structures.
Challenges Faced by NGOs and Demos
NGOs often encounter funding instability, regulatory hurdles, and limited access to decision-making platforms, which constrain their operational effectiveness and advocacy efforts. Demos face challenges such as sustaining public engagement, addressing diverse stakeholder interests, and overcoming misinformation that undermines democratic processes. Both entities struggle with transparency demands and accountability pressures, requiring innovative strategies to maintain trust and impact.
Future Trends: Collaboration or Competition?
NGOs and democratic movements are increasingly exploring collaborative models to leverage shared goals in social justice, human rights, and environmental sustainability. Emerging trends indicate a shift towards partnership frameworks that enhance resource sharing, advocacy impact, and policy influence, driven by digital platforms and global networks. Competitive dynamics persist but are gradually overshadowed by strategic alliances that foster innovation and amplify grassroots voices for systemic change.
NGOs Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com