Integration streamlines complex systems by connecting diverse applications and data sources into a unified platform. This process enhances operational efficiency and improves real-time decision-making. Discover how effective integration can transform Your business by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
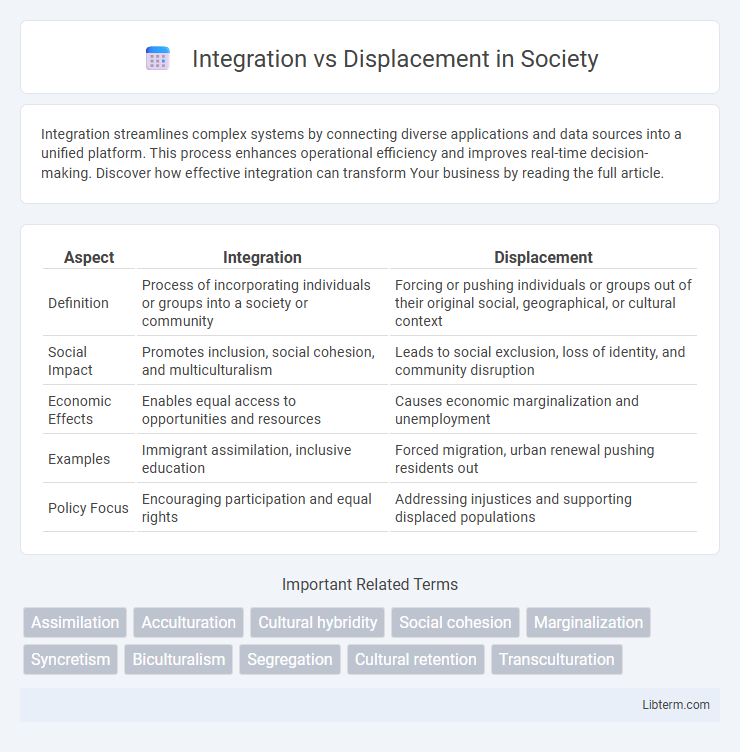
| Aspect | Integration | Displacement |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of incorporating individuals or groups into a society or community | Forcing or pushing individuals or groups out of their original social, geographical, or cultural context |
| Social Impact | Promotes inclusion, social cohesion, and multiculturalism | Leads to social exclusion, loss of identity, and community disruption |
| Economic Effects | Enables equal access to opportunities and resources | Causes economic marginalization and unemployment |
| Examples | Immigrant assimilation, inclusive education | Forced migration, urban renewal pushing residents out |
| Policy Focus | Encouraging participation and equal rights | Addressing injustices and supporting displaced populations |
Understanding Integration and Displacement
Integration involves incorporating diverse cultural identities into a unified social framework, fostering coexistence and mutual respect, while displacement refers to the forced removal of individuals from their original homes, often due to conflict or environmental factors. Understanding integration requires analyzing social policies, community support systems, and cultural adaptation processes that enable harmonious living. Displacement understanding centers on the causes, consequences, and humanitarian responses aimed at protecting and resettling affected populations.
Historical Overview of Integration and Displacement
The historical overview of integration and displacement reflects the evolving dynamics of social, cultural, and economic relationships among diverse groups. Integration historically involved efforts to incorporate marginalized communities into mainstream society through policies such as desegregation, civil rights legislation, and multicultural education. In contrast, displacement often resulted from colonization, urban renewal projects, and forced migrations, leading to the physical and cultural removal of populations, which reshaped demographic patterns and social structures worldwide.
Key Drivers of Integration in Society
Key drivers of integration in society include shared cultural values, inclusive economic policies, and equitable access to education and social services. Social cohesion is strengthened through community engagement and intercultural dialogue, fostering mutual respect and reducing prejudices. Effective political frameworks that promote diversity and protect minority rights also play a crucial role in facilitating integration.
Causes and Consequences of Displacement
Displacement occurs when development projects, natural disasters, or conflicts force communities to relocate, disrupting social networks and livelihoods. Causes include infrastructure expansion, environmental degradation, and armed conflicts, which often lead to loss of homes, economic instability, and cultural disintegration. Displacement results in increased vulnerability, reduced access to essential services, and long-term socio-economic challenges for affected populations.
Integration vs Displacement: Comparative Analysis
Integration involves combining new elements into existing social, economic, or cultural systems, promoting cohesion and mutual adaptation. Displacement refers to the forced removal or relocation of individuals or communities, often resulting in disruption, loss of identity, and socio-economic challenges. Comparative analysis of integration versus displacement highlights that integration fosters sustainable development and social stability, whereas displacement frequently leads to marginalization and long-term instability.
Social and Economic Impacts
Integration fosters social cohesion and economic inclusivity by allowing displaced populations to access employment, education, and public services, which enhances community resilience and economic productivity. Displacement often leads to social fragmentation, increased poverty rates, and strain on local resources, resulting in higher unemployment and social tensions. Economically, integration supports market expansion and labor diversity, whereas displacement disrupts local economies and increases dependency on aid.
Cultural Perspectives on Integration and Displacement
Cultural perspectives on integration emphasize the blending of diverse traditions, fostering mutual respect and shared identity within multicultural societies. Displacement often leads to cultural loss and identity challenges as individuals are forced to detach from their native cultural contexts. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for policymakers to facilitate social cohesion while respecting cultural heritage.
Policy Approaches and Solutions
Policy approaches to integration emphasize inclusive frameworks that promote social cohesion by ensuring equitable access to education, employment, and housing for immigrants. Displacement strategies often involve restrictive measures aimed at controlling migration flows through border enforcement and repatriation programs. Effective solutions balance integration policies with targeted support services, such as language training and legal assistance, to facilitate immigrant inclusion while addressing displacement challenges through regional cooperation and development initiatives.
Challenges in Achieving Effective Integration
Challenges in achieving effective integration include overcoming cultural differences and communication barriers that hinder collaboration among diverse teams. Complex organizational structures and legacy systems often resist seamless data and process integration, leading to inefficiencies. Additionally, securing stakeholder buy-in and managing change are critical hurdles that impact the smooth adoption of integrated solutions.
Future Trends and Recommendations
Integration techniques are evolving with advances in AI-driven automation, enabling seamless interoperability between diverse systems for enhanced data synthesis and operational efficiency. Displacement models face challenges from increasing automation and augmented reality applications that prioritize human-machine collaboration rather than replacement. Fostering adaptive hybrid frameworks that combine integration capabilities with selective displacement strategies is recommended to maximize innovation and workforce resilience in future technology landscapes.
Integration Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com