Inclusivity fosters a culture where diverse perspectives and backgrounds are valued, leading to richer collaboration and innovation within organizations. Embracing inclusivity not only enhances employee engagement but also drives better decision-making by incorporating varied viewpoints. Discover how fostering inclusivity can transform your workplace culture and boost overall performance in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
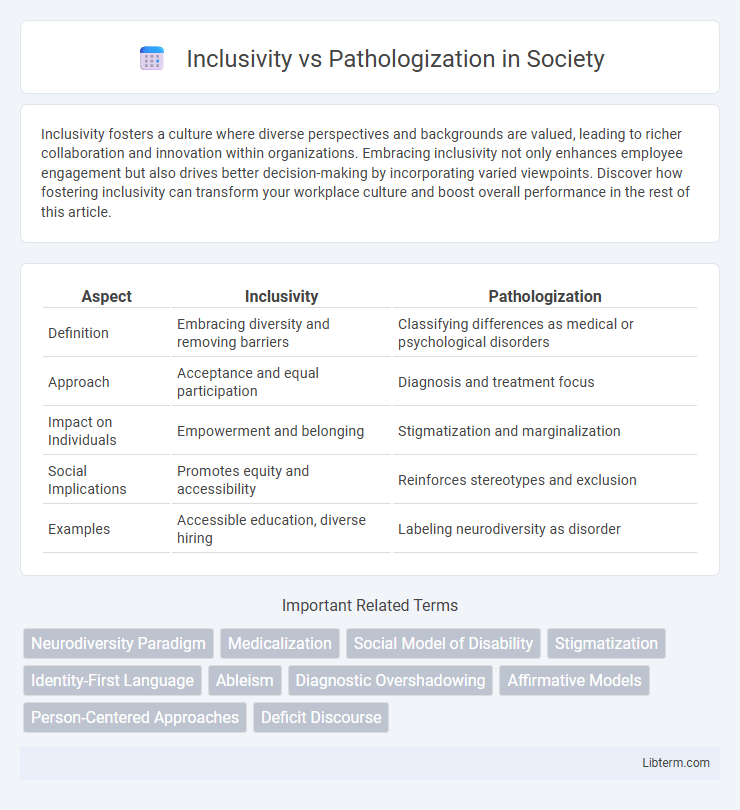
| Aspect | Inclusivity | Pathologization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Embracing diversity and removing barriers | Classifying differences as medical or psychological disorders |
| Approach | Acceptance and equal participation | Diagnosis and treatment focus |
| Impact on Individuals | Empowerment and belonging | Stigmatization and marginalization |
| Social Implications | Promotes equity and accessibility | Reinforces stereotypes and exclusion |
| Examples | Accessible education, diverse hiring | Labeling neurodiversity as disorder |
Defining Inclusivity in Modern Society
Inclusivity in modern society emphasizes recognizing and valuing diverse identities, experiences, and abilities without labeling them as disorders or deficiencies. It promotes creating environments where all individuals have equitable access to opportunities, respect, and representation, fostering social cohesion and mutual understanding. Defining inclusivity involves moving beyond pathologization by appreciating neurodiversity, cultural differences, and varied perspectives as strengths rather than problems.
Understanding Pathologization: Origins and Impacts
Pathologization originates from medical and psychological frameworks that label diverse behaviors or identities as disorders, often marginalizing individuals. This process reinforces stigma by framing natural variations in human experience as abnormalities requiring treatment. Understanding pathologization's origins reveals its role in perpetuating discrimination and highlights the importance of promoting inclusivity to affirm diverse identities without judgment.
Historical Context: From Exclusion to Pathologization
Historically, marginalized groups were often excluded from mainstream society before being subjected to pathologization, where their identities or behaviors were labeled as medical or psychological disorders. This shift from social exclusion to medicalization served to control and stigmatize those who deviated from normative standards, reinforcing systemic oppression. Understanding this historical trajectory is essential for addressing contemporary debates on inclusivity and the medical framing of diversity.
The Intersection of Culture, Identity, and Diagnosis
The intersection of culture, identity, and diagnosis reveals critical challenges in balancing inclusivity and pathologization within mental health frameworks. Cultural norms and identity factors shape symptom expression and influence diagnostic criteria, risking misdiagnoses or exclusion when cultural context is overlooked. Prioritizing culturally sensitive approaches reduces pathologization of diverse identities and promotes inclusive, accurate mental health care.
Inclusivity in Healthcare: Moving Beyond Labels
Inclusivity in healthcare prioritizes recognizing and respecting diverse identities and experiences without reducing patients to diagnostic labels, fostering a more empathetic and personalized approach. This paradigm shift encourages clinicians to focus on holistic well-being, addressing social determinants of health and cultural competence. Emphasizing inclusivity reduces stigma and barriers, improving access and outcomes for marginalized populations.
Pathologization and Its Effects on Mental Health
Pathologization refers to the tendency to classify diverse behaviors or experiences as medical or psychological disorders, often leading to stigma and marginalization of individuals. This approach can exacerbate mental health challenges by fostering feelings of alienation, reducing access to appropriate support, and discouraging people from seeking help due to fear of being labeled. Research indicates that pathologization negatively impacts self-esteem and increases anxiety and depression among affected populations, highlighting the need for more inclusive, non-stigmatizing mental health frameworks.
Social Policy: Encouraging Acceptance Over Stigmatization
Social policy plays a crucial role in promoting inclusivity by creating frameworks that encourage acceptance rather than stigmatization of diverse identities and behaviors. Emphasizing support systems and anti-discrimination laws reduces the pathologization of marginalized groups, enabling equitable access to services and opportunities. Prioritizing education and community engagement fosters a societal shift toward understanding, dismantling harmful stereotypes entrenched in traditional medical or psychological models.
Media Representation: Narratives of Difference
Media representation plays a pivotal role in shaping societal perceptions of difference by either promoting inclusivity or reinforcing pathologization. Inclusive narratives highlight diverse identities and experiences without framing them as deficits or disorders, fostering empathy and social acceptance. Conversely, pathologizing media depictions often frame difference as abnormal or problematic, perpetuating stigma and marginalization of marginalized groups.
Empowerment Through Inclusive Practices
Empowerment through inclusive practices fosters a sense of belonging and self-worth by recognizing diverse identities without labeling them as pathological. Emphasizing acceptance and support, these practices challenge stigmatization and promote mental health equity across marginalized communities. Inclusive environments enhance resilience and personal growth by validating individual experiences and dismantling systemic barriers.
Building a Future Beyond Pathologization
Building a future beyond pathologization demands embracing inclusivity by recognizing diverse identities and experiences without labeling them as disorders. This approach promotes mental health frameworks centered on acceptance, social support, and empowerment rather than stigmatization. Inclusive practices enhance well-being by validating individual differences and dismantling harmful diagnostic biases.
Inclusivity Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com