Policy impact assessment evaluates the potential effects and outcomes of proposed policies on various sectors and stakeholders, ensuring informed decision-making and effective resource allocation. This process identifies both positive and negative consequences, helping policymakers optimize benefits while minimizing risks. Discover how a thorough policy impact assessment can strengthen Your strategic planning by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
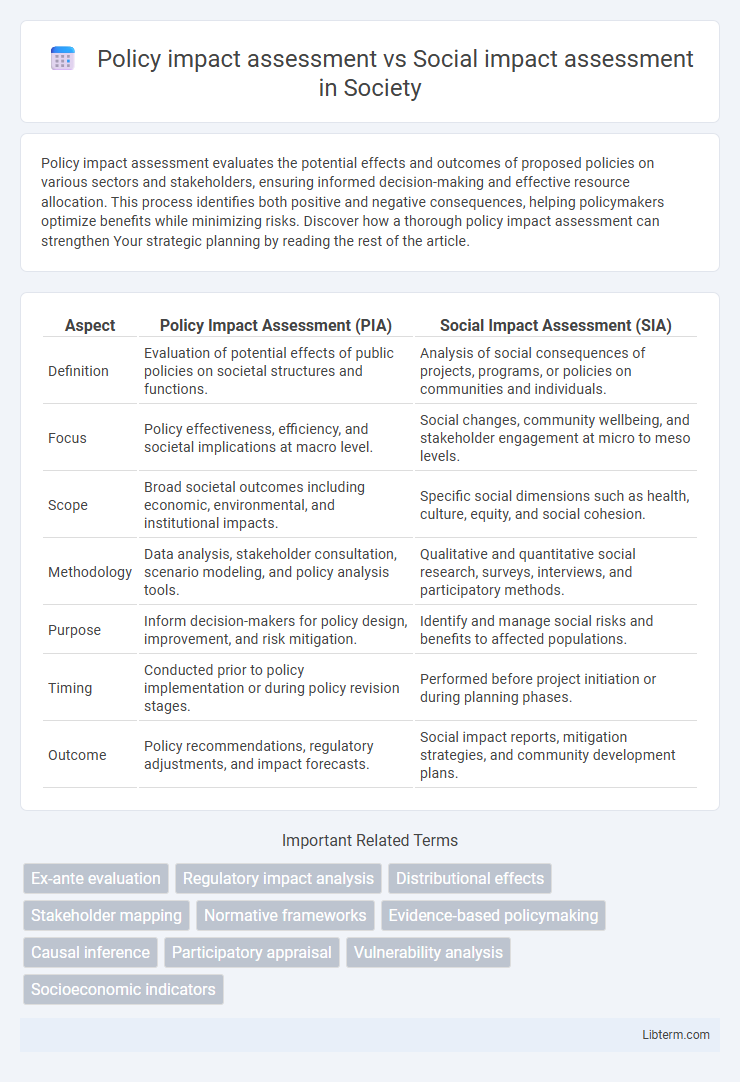
| Aspect | Policy Impact Assessment (PIA) | Social Impact Assessment (SIA) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Evaluation of potential effects of public policies on societal structures and functions. | Analysis of social consequences of projects, programs, or policies on communities and individuals. |
| Focus | Policy effectiveness, efficiency, and societal implications at macro level. | Social changes, community wellbeing, and stakeholder engagement at micro to meso levels. |
| Scope | Broad societal outcomes including economic, environmental, and institutional impacts. | Specific social dimensions such as health, culture, equity, and social cohesion. |
| Methodology | Data analysis, stakeholder consultation, scenario modeling, and policy analysis tools. | Qualitative and quantitative social research, surveys, interviews, and participatory methods. |
| Purpose | Inform decision-makers for policy design, improvement, and risk mitigation. | Identify and manage social risks and benefits to affected populations. |
| Timing | Conducted prior to policy implementation or during policy revision stages. | Performed before project initiation or during planning phases. |
| Outcome | Policy recommendations, regulatory adjustments, and impact forecasts. | Social impact reports, mitigation strategies, and community development plans. |
Introduction to Impact Assessments
Policy impact assessment evaluates the potential effects of proposed policies on economic, environmental, and social factors, aiming to inform decision-making and optimize outcomes. Social impact assessment specifically examines the consequences of projects or policies on communities, culture, and social well-being, emphasizing stakeholder engagement and social equity. Both assessments utilize data collection, analysis, and public consultation to predict and mitigate adverse impacts while enhancing positive effects.
Defining Policy Impact Assessment
Policy Impact Assessment evaluates the potential effects of proposed or existing policies on economic, environmental, and social factors to inform decision-making. It systematically analyzes policy outcomes to ensure alignment with strategic goals and regulatory standards, often incorporating quantitative and qualitative data. Distinct from Social Impact Assessment, which centers specifically on social consequences, Policy Impact Assessment provides a broader evaluation of policy implications across multiple domains.
Defining Social Impact Assessment
Social Impact Assessment (SIA) systematically evaluates the consequences of projects, policies, or programs on communities' social structures, cultural norms, and overall well-being. Unlike Policy Impact Assessment, which broadly examines economic, environmental, or regulatory effects of policies, SIA zeroes in on changes in social dynamics, livelihoods, health, and access to resources. Key components of Social Impact Assessment include stakeholder engagement, baseline social data collection, and mitigation strategies to address adverse social effects.
Key Objectives of Policy Impact Assessment
Policy Impact Assessment (PIA) aims to evaluate the potential effects of proposed policies on economic, environmental, and social factors to support informed decision-making and optimize policy outcomes. Its key objectives include identifying potential risks and benefits, ensuring regulatory compliance, and enhancing transparency and stakeholder engagement throughout the policy development process. Unlike Social Impact Assessment, which primarily focuses on social consequences, PIA provides a comprehensive analysis to guide policymakers in achieving balanced, sustainable impacts across multiple domains.
Core Principles of Social Impact Assessment
Policy impact assessment evaluates the effects of policies on economic, environmental, and social dimensions, while social impact assessment (SIA) specifically examines the consequences for communities' well-being, culture, and social structures. Core principles of SIA include stakeholder engagement, anticipatory and participatory processes, and the promotion of sustainable development by identifying and mitigating negative social impacts. Emphasizing transparency, inclusivity, and adaptability ensures SIA effectively informs decision-making and supports social justice outcomes.
Methodological Differences
Policy impact assessment primarily uses quantitative data analysis and forecasting models to evaluate the outcomes of proposed policies, focusing on economic, environmental, and regulatory metrics. Social impact assessment emphasizes qualitative methods such as stakeholder interviews, participatory appraisal, and ethnographic research to understand effects on communities, social structures, and cultural dynamics. While policy impact assessment relies on cost-benefit and risk analysis, social impact assessment integrates subjective social values and lived experiences for a comprehensive evaluation.
Stakeholder Engagement in Assessments
Policy impact assessment emphasizes engaging a broad range of stakeholders, including policymakers, industry representatives, and affected communities, to identify potential policy outcomes and unintended consequences. Social impact assessment prioritizes direct involvement of local communities, vulnerable groups, and social organizations to understand how proposed projects or policies affect social dynamics, equity, and well-being. Both assessments use participatory methods but differ in stakeholder focus and the scope of engagement tailored to policy-making versus community-level impacts.
Role in Decision-Making Processes
Policy Impact Assessment evaluates potential effects of proposed policies on economic, environmental, and social dimensions, providing decision-makers with evidence-based forecasts to optimize policy design and mitigate risks. Social Impact Assessment specifically examines the consequences of projects or policies on communities, focusing on social well-being, equity, and inclusion to ensure stakeholder interests and rights are addressed. Their roles in decision-making processes complement each other, with Policy Impact Assessment offering a broad strategic evaluation and Social Impact Assessment delivering granular insights into community-level outcomes.
Case Studies: Policy vs Social Impacts
Case studies comparing policy impact assessment and social impact assessment reveal distinct evaluation scopes and methodologies. Policy impact assessments prioritize regulatory effectiveness, economic outcomes, and legislative compliance, often quantifying changes in public behavior and governance metrics. In contrast, social impact assessments emphasize community well-being, cultural shifts, and social equity, employing qualitative analyses derived from stakeholder interviews and ethnographic research to measure societal change.
Comparative Analysis and Future Trends
Policy impact assessment evaluates the effectiveness, efficiency, and equity of policies through quantitative and qualitative metrics, while social impact assessment focuses on understanding the consequences of projects or policies on community well-being, social structures, and cultural dynamics. Comparative analysis reveals that policy impact assessments prioritize regulatory compliance and economic outcomes, whereas social impact assessments emphasize stakeholder engagement and social sustainability. Future trends indicate integration of big data analytics and AI-driven modeling to enhance predictive accuracy and the incorporation of participatory approaches to democratize impact evaluations across both assessment types.
Policy impact assessment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com